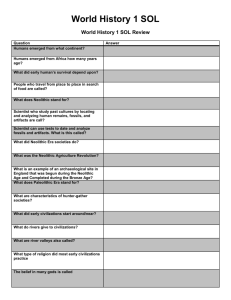
SOL Review Matching #1
advertisement

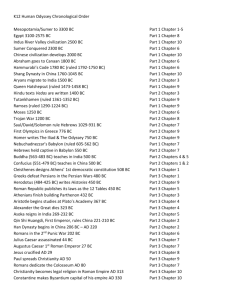
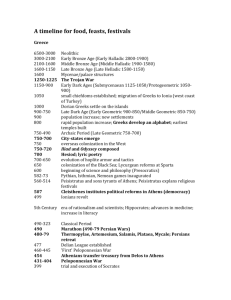
Name:___________________________ World history I block:_______ SOL Review Matching #1 Paleolithic and Neolithic 1. ___ Sumer A. A belief in more than one god 2. ___ Mesopotamia B. A government controlled by religious leaders 3. ___ Fertile Crescent C. The first civilization; near the Tigris River 4. ___ Homo Sapiens D. The first Egyptian king 5. ___ Silt E. Dirt/mud left behind by flooding rivers 6. ___ Polytheism F. Created a famous legal code 7. ___ City-state G. A curved region of quality farm land 8. ___ Menes H. Independent city controlling surrounding land 9. ___ Hammurabi I. Land between the rivers 10. ___ Theocracy J. Modern humans River Valleys 11. ___ Artifact A. A scientific test used to analyze the age of artifacts 12. ___ Archeology B. Good for farming 13. ___ Carbon dating C. The study of the human past by examining artifacts 14. ___ Paleolithic Era D. People who get food from collecting plants and hunting 15. ___ Agricultural Revolution E. Keeping and taming animals for work or food 16. ___ Migration F. Something made by people in the past 17. ___ Hunter-gatherers G. Groups with no permanent homes 18. ___ Nomads H. Invention of farming (a.k.a. Neolithic Revolution) 19. ___ Domestication I. Permanently moving from one place to another 20. ___ Fertile J. The Old Stone Age; there were humans (not civilization) 21. ___ River Valley A. A family of rulers that pass down power 22. ___ Ziggurat B. The first written language, invented in Sumer 23. ___ Cuneiform C. Egyptian god-kings 24. ___ Oracle bones D. Shells used to predict the future (in ancient China) 25. ___ Dynasty E. Region of Asia is separated by the Himalaya mountains 26. ___ Empire F. A time when good stuff happens 27. ___ Pharaoh G. The temple and city-center in ancient Mesopotamia 28. ___ Prosperity H. An agreement between God and people 29. ___ Covenant I. A kingdom made up of multiple ethnic groups 30. ___ Subcontinent J. An area with a river and a lot of good farm land China, India and Persia 31. ___ Zoroastrianism A. The sum of your good and bad deeds in life 32. ___ Caste system B. The Persian religion 33. ___ Moksha C. When the soul is reborn in a new body 34. ___ Karma D. Enlightenment for Buddhism 35. ___ Nirvana E. Buddha’s revelations about how the world works 36. ___ Reincarnation F. Perfect understanding in Hinduism 37. ___ Four Noble Truths G. Mauryan king who promoted Buddhism 38. ___ Autocracy H. Rigid social class structure in India 39. ___ Ashoka I. Chinese emperor who ruled through Legalism 40. ___ Shi Huangdi J. Government where the ruler has unlimited power Rome and Greece 41. ___ Civil service K. A government ruled by a single person 42. ___ Myth L. A government ruled by the rich landowners 43. ___ Themistocles M. People who pass tests to work for the government 44. ___ Leonidas N. Leader of Athens during the Golden Age 45. ___ Pericles O. A government ruled by the will of the people 46. ___ Monarchy P. A traditional story about how the world works 47. ___ Aristocracy Q. Leader of Athens during the Persian War 48. ___ Oligarchy R. Rich landowning class 49. ___ Democracy S. A government ruled by a small group 50. ___ Nobility T. Leader of the Spartan 300 51. ___ Scipio A. His teachings created the foundations of Christianity 52. ___ Hannibal B. He tried to destroy Rome by attacking from the north. 53. ___ Constantine C. Emperor; first ruler of the Pax Romana 54. ___ Paul D. Roman general who defeated Hannibal in Africa 55. ___ Julius Caesar E. Converted to Christianity and moved the capital of Rome 56. ___ Diocletian F. Christian follower who wrote letters and traveled 57. ___ Pompey G. Emperor who divided the Roman Empire 58. ___ Jesus H. Defeated general from the first Triumvirate 59. ___ Augustus I. Leader of the Huns 60. ___ Attila J. General who conquered Gaul, became dictator 61. ___ Herodotus A. A Greek dramatist 62. ___ Sophocles B. Philosopher, teacher of Alexander 63. ___ Aristotle C. The O.G. Greek philosopher 64. ___ Pythagoras D. The world’s first historian, wrote about the Persian War 65. ___ Aristophanes E. Historian/participant in the Peloponnesian War 66. ___ Euclid F. Reformer of the government of Athens 67. ___ Phidias G. A Greek comedy writer 68. ___ Socrates H. Greek sculptor and architect 69. ___ Solon I. Greek mathematician, invented geometry 70. ___ Thucydides J. Greek mathematician, liked triangles and music 71. ___ Patrician A. Two king-like government and military leaders 72. ___ Plebeian B. Elected representatives of the plebeians 73. ___ Consuls C. The head priest; the leader of Christianity on earth 74. ___ Senate D. Wealthy land-owning class (the upper class) 75. ___ Tribunes E. Poor working class peasants (the lower class) 76. ___ Veto F. When one official denies the actions of another official 77. ___ Twelve Tables G. Latin: Roman Peace. The golden age of ancient Rome 78. ___ Triumvirate H. Law-making (legislative) body 79. ___ Pax Romana I. Written and public law code of ancient Rome 80. ___ Pope J. A government where three equal leaders share power 81. ___ Schism A. Denial of communion; banning from the church 82. ___ Icon B. Arabic word for god 83. ___ Excommunication C. Successors to Muhammad 84. ___ Cyrillic D. A religious image used by Eastern Christians 85. ___ Qu’ran E. Sect of Islam, followers of Ali 86. ___ Allah F. The holy book of Islam, revealed to Muhammad 87. ___ Mosques G. Houses of worship for Muslims 88. ___ Caliphs H. Egalitarian religious community of all Muslims 89. ___ Umma I. Written alphabet invented for Slavic languages 90. ___ Shi’a J. A split, especially between beliefs 91. ___ Secular A. Worldly or non-religious 92. ___ Feudalism B. Social/governmental structure based on loyalty and land 93. ___ Lord C. Landowner in a feudal arrangement 94. ___ Serf D. Feudal peasant who is bound to the land 95. ___ Vassal E. Person who receives a fief from a lord 96. ___ Fief F. Piece of land shared in feudal arrangement 97. ___ Renaissance G. A rebirth of culture 98. ___ Manor H. Self-sufficient estate where the lord and his serfs live 99. ___ Patron I. Someone who supports a cause or person with money 100. ___ Humanism J. Study of classics, focus on human achievements 101. ___ Charles Martel A. Led Norman conquest of England 102. ___ Charlemagne B. English king forced to sign the Magna Carta 103. ___ William the Conqueror C. French king who defeated the Muslims 104. ___ Henry II D. Spanish king who expanded the empire in the Americas 105. ___ King John E. First Holy Roman Emperor 106. ___ Hugh Capet F. English king who created legal system of judge and jury 107. ___ Joan of Arc G. Russian leader who threw off the Mongols 108. ___ Charles V (Spain) H. Isabella’s partner, leader of Spain, Columbus’ patron 109. ___ Ivan the Great I. Young girl who led French forces to victory 110. ___ Ferdinand J. Founder of a French dynasty near Paris