Strength Assignment 1 – Maher
advertisement

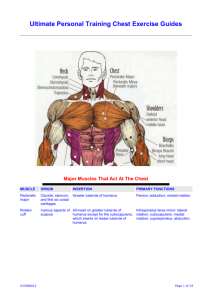
Grace Maher Assignment 1 We worked on a range of muscle groups this week but we really focused on body weight exercises. For example we did body weight squats and lunges on day 2 to work our legs and did pushups, mountain climbers and rage ball rugby relay on day 4 to work on our arm strength. In my opinion the most important weight room safety regulation is to have a spotter while lifting, as it could be really dangerous if you were to drop that amount of weight on yourself and then be unable to get it off yourself without any help. Even if the weight you are lifting you feel comfortable with something could go wrong and a muscle could give out and it could be really dangerous if you didn’t have a spotter there to help you. Not only does a spotter help you when you get stuck but it also gains your confidence because they are there to help you so you can try more weight. The advice I would give a beginner to do hand release pushups would be to focus on your breathing. You should be breathing in as you go down into your pushup and breathing out as you come up in your pushup. If you don’t do this it makes it extremely difficult to come up in your pushup and continue reps. Another thing to focus on while doing body release pushups is to not over extend your arms when releasing on the ground as you could over extend the muscles in your shoulders and chest. To properly execute a bench press you must: 1. Lie down on the flat bench with your eyes under the bar. Make sure your feet are flat on the floor as it provides stability. 2. Put your pinky on the ring marks of your bar. Hold the bar in the base of your palm with a full grip and straight wrists. 3. Take a breath and unrack the bar by straightening your arms. Move the bar over your shoulders with your elbows locked. 4. Lower the bar to your mid chest while tucking your elbows, keep your forearms vertical. 5. Press the bar from your mid chest to above your shoulders, keeping your back on the bench and lock your elbows at the top. Throughout the entire bench press it is important to remember to breathe. Bench presses work the pectoral muscles, which is the anatomical name for chest muscles. The pectoralis major is the part of the chest that gets activated when you are pushing the bar straight up. The pectoralis minor gets recruited when your shoulders shrug forward; the main emphasis is placed on the pectoralis major. The shoulder muscles get worked any time there is elevation of the upper arms, although you are in a lying position while doing bench presses, you upper arms are perpendicular to your body. The triceps are the major muscles on the backs of the upper arms. The triceps’ main responsibility is to extend the elbow, this takes place when you push the bar off your chest and upward, moving your arm from a bent to straight position. The biceps bracii is Grace Maher the muscle on the front of the upper arm, when you are doing a bench press this muscle gets used as a stabilizer. This muscle helps keep the arm moving back and forth during the lift. And although not commonly thought of with bench presses, the abs are a very important muscle group for proper execution of a bench press. You have to forcefully engage your abs to generate power and keep your body stable. When spotting a bench press the primary purpose of the spotter is to make sure the person on the bench doesn’t get stuck and pinned by the bar. The spotter is there to help you just in case you cannot complete a rep. The spotter would grab the bar on the inside of ones hands while the person hands stay on the bar and carefully help and guide the bar back onto the rack. Concentric muscle contraction – a type of muscle contraction in which the muscles shorten while generating force. This is typical of muscles that contract due to the sliding filament mechanism, and it occurs throughout the muscle. Isometric muscle contraction – when the muscle fires but there is no movement at a joint. In this type of muscle contraction there is no change in length of the muscle, and no movement at the joints but muscle fibers fire. Extension (joint movement) – when the joint is bent in order for the bones making up the joint to move closer together. Eccentric muscle contraction – the motion of an active muscle while its lengthening under load. Flexion (joint movement) – a bending movement that decreases the angle between a segment and its proximal segment Synovial joint - most common and most movable type of joint in the body of a mammal. Synovial joints achieve movement at the point of contact of the articulation bones.