Biomedweek16 - dcsbiomedacademy
advertisement

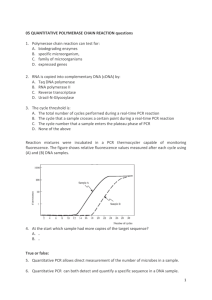
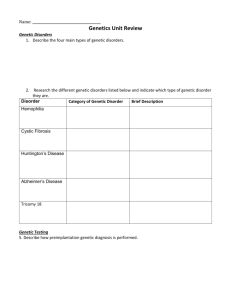
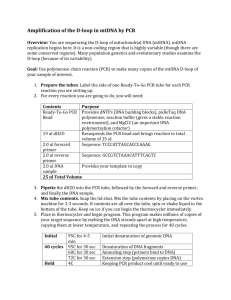
Biomed Academy Weekly Plans Week 16 Monday Objectives: Recognize that the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a laboratory procedure that produces multiple copies of a specific DNA sequence. Explain how single base pair changes called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be identified through genetic testing and often correlate to specific diseases or traits. Use laboratory techniques such as DNA extraction, PCR, and restriction analysis to identify single base pair differences in DNA. Analyze genetic testing results to predict phenotype. Process: MI-2.1.3. Parts 1, 2, 3 Isolation of DNA and PCR of DNA Closure: Postlab discussion of purpose of procedures carried out today. HW: Chapter 22 guided reading, Capstone Chapter 3. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Tuesday Objectives: Recognize that the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a laboratory procedure that produces multiple copies of a specific DNA sequence. Explain how single base pair changes called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be identified through genetic testing and often correlate to specific diseases or traits. Use laboratory techniques such as DNA extraction, PCR, and restriction analysis to identify single base pair differences in DNA. Analyze genetic testing results to predict phenotype. Process: Art MI-2.1.3. Part 4 Digestion of DNA Closure: Postlab discussion of purpose of procedures carried out today. HW: Chapter 22 guided reading, Capstone Chapter 3. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Wednesday Objectives: Recognize that the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a laboratory procedure that produces multiple copies of a specific DNA sequence. Explain how single base pair changes called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be identified through genetic testing and often correlate to specific diseases or traits. Use laboratory techniques such as DNA extraction, PCR, and restriction analysis to identify single base pair differences in DNA. Analyze genetic testing results to predict phenotype. Process: MI-2.1.3. Part 5 Electrophoresis Closure: Postlab discussion of purpose of procedures carried out today. HW: Chapter 22 guided reading, Capstone Chapter 3. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Thursday Objectives: Recognize that the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a laboratory procedure that produces multiple copies of a specific DNA sequence. Explain how single base pair changes called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be identified through genetic testing and often correlate to specific diseases or traits. Use laboratory techniques such as DNA extraction, PCR, and restriction analysis to identify single base pair differences in DNA. Analyze genetic testing results to predict phenotype. Process: Art Loose ends from 2.1.3-Student summary, PTC tasting day. Troubleshooting for Capstone Chapter 3. Closure: Today is a day of closure for the lab, and working out kinkds in capstone chapter 3. HW: Chapter 22 guided reading