Penny Lab Mrs. Johnston Science Class A, B, C & D Mrs. Johnston 9
advertisement

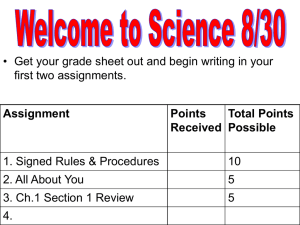
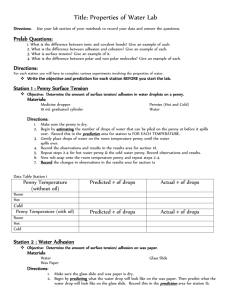
Penny Lab Mrs. Johnston Science Class A, B, C & D Mrs. Johnston 9/25/13 I) Introduction The purpose of this Penny Lab is to determine how soap on a penny affects the number of drops that it can hold, compared with a penny with no soap. Water molecules are attracted to each other, so they tend to try to stick together (cohesion). This cohesion causes surface tension, which allows for the penny to hold more water drops then one would anticipate. II) Experimental Design The experimental problem is: How does soap affect the number of water drops that the surface of a penny can hold, compared with the number of drops that a penny without soap can hold? The independent variable in the experiment is the soap and the dependent variable in the experiment is the number of water drops on the surface of the penny. The control is the penny without soap. III) Hypothesis If a penny is covered with soap, then it will not hold as many water drops because the soap does not allow for adequate surface tension to occur. IV) Test/Experiment Materials 1 penny 2 eye droppers (1 for water and 1 for soap) 3 beakers (1 for drops of water, 1 for soap and 1 for rinsing) Data sheet Paper towels for clean up Procedures 1. 2. 3. 4. Gather all materials. Make sure the two water beakers are filled with water. Begin your control experiment. Place the penny (tails side up) on a flat surface. Fill the eyedropper with water from the water beaker and carefully count the number of drops that fit on the penny until the water spills over the edge. Record this number on your data table under trial 1. 5. Rinse and dry the penny. Repeat step 4 two more times. 6. Calculate the average for the clean penny. 7. Place one drop of soap on the penny (tails side up) and rub on so that the soap covers the entire surface. 8. Fill the eyedropper with water from the water beaker and carefully count the number of drops that fit on the penny until the water spills over the edge. Record this number on your data table under trial 1. 9. Rinse and dry the penny. Repeat steps 7 & 8 two more times. 10. Calculate the average for the soapy penny. V) Observations See attached data table and graph. VI) Discussion The results of this experiment showed that the clean penny held more water drops than the penny with soap on it. Based on class data, the penny without soap held a range of 16 – 28 drops of water, compared with the soapy penny that had a range of on 7 – 16 drops. This observation was consistent with all groups and seems to show that the surface tension is compromised when the soap is placed on the penny. The soap does not allow for enough cohesion between the water molecules to allow for a large number of drops. More accurate measurement of the amount of soap is needed to make sure that each trial is consistent and this may have caused water to prematurely fall off due to too much soap. A determination of how far away the dropper needed to be held from the penny should also have been made, as a dropper too far could cause the water to prematurely fall off and a dropper held too close could cause a larger number of drops. VII Conclusion How does soap affect the number of water drops that the surface of a penny can hold, compared with the number of drops that a penny without soap can hold? In this experiment, the data collected did support the hypothesis that if a penny is covered with soap, then it will not hold as many water drops because the soap does not allow for adequate surface tension to occur. Class data showed that, on average, the clean penny held 10 more drops of water than the penny with soap on it. This indicates that there is a relationship between surface tension and an added substance on a surface. Multiple people in groups completed the drops, which could have affected the number of drops that stayed on the pennies. Time did not allow for more trials but more trials could further demonstrate the acceptance of the hypothesis. It would be interesting to complete additional experiments using substances other than soap, or dropping something other than water.