Course Outline Essential Questions
advertisement

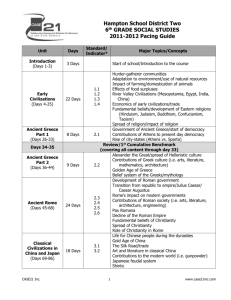
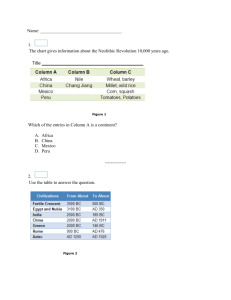
Ancient World History Ms. Noyes Course Outline I. Ancient River Valley Civilizations A. Human beginnings and the impact of agriculture Essential Question: What factors determine a Civilization? Essential Question: What economic, political, and social changes resulted from the rise of cities? 1. The Myth of Continents 2. 8 Requirements to be considered a Civilization. How realistic? 3. Ancient River Valley Civilizations 4. 7 Ancient Wonders of the World B. Tigris and Euphrates River Valley Essential Question: What were the important characteristics of the civilizations in Mesopotamia? Essential Question: How did Judaism impact the development of the Western World? 1. The Fertile Crescent/Mesopotamia a. Sumerians: City-states, Religion b. Phoenicians: Sea traders, Alphabet c. Babylonians: Hammurabi’s Code d. Hebrews: Monotheism, Kings, Old Testament, Abraham, Moses, Jerusalem C. Nile River Valley Essential Question: Why was Egypt called “the gift of the Nile” 1. Ancient Egypt b. Mythology and religion, Polytheism c. Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, New Kingdom (Narmer, Rameses II, KingTut d. Art and Architecture D. Indus River Valley Civilizations Essential Question: How did Aryan culture impact India, and the Western world? Essential Question: Why do civilizations rise and fall? 1. Harappan/Mohenjo-Daro Civilizations a. Urban Civilization, grid planning, advancements b. Culture, trade, religion c. Aryan invasions and the impact of the Caste System d. Ancient religions 1. Hinduism: Ancient gods, The Vedas, beliefs 2. Buddhism: Siddhartha Gautama, Enlightenment, 4 Nobel Truths 3. Tibet/Dalai lama E. Huang He River Valley Civilizations Essential Question: How have Chinese Dynasties impacted the development of Ancient China Essential Question: Why is Buddhism one of the fastest growing religions in the world today? 1. Shang Dynasty: Oracle bones 2. Zhou Dynasty: Dynastic cycle, Yin and Yang, Zhou technology, Chinese traditions 3. Qin Dynasty: Emperor Qin Shi Huangdi, Great Wall of China, Terracotta Warriors 4. Han Dynasty: Golden age of China, Confucianism, Chinese Contributions 5. The Last Emperor II. Ancient Greece Essential Question: How did geography influence Ancient Greece? Essential Question: Why is Ancient Greece considered to be the foundation of Western culture? Essential Question: How did Alexander’s conquests lead to cultural diffusion? A. Minoan society, Crete B. Mycenaeans 1. Impact of Geography 2. Greek City-states 3. Homer: The Trojan War C. Rise of Greek City-states 1. Athens: Democracy, Age of Pericles 2. Sparta: Warrior society D. The Persian Wars and Peloponnesian War 1. Causes, Battle of Marathon, Battle of Thermopylae, King Leonidas, Themistocles 2. Persian Empire: Darius, Xerxes 3. Athens vs. Sparta E. Greek Philosophy and Architecture 1. Socrates, Plate, Aristotle 2. Parthenon, Doric, Ionic, Corinthian F. Philip of Macedon and Alexander the Great 1. Philip unites Greek City-states 2. Alexander’s Empire, spread of Greek culture 3. Impact of the Hellenistic Period III. Roman Republic and Empire Essential Question: To what extent have the contributions of Ancient Rome influenced modern society? Essential Question: What caused the decline of the Roman Empire in the West? A. The Etruscans B. Roman Republic is established 1. Indirect Democracy, Consuls, Senate, Tribunes 2. Roman Expansion, Punic Wars, Hannibal and defeat of Carthage C. Origins of Western Culture 1. Hebrews and Judaism 2. Rise of Christianity a. Jesus’ teachings/contrast to Judaism b. Crucifixion D. From Republic to Empire 1. First Triumvirate, Crassus, Pompey, Julius Caesar 2. Dictator to Assassination 3. Fall of Cleopatra and Mark Antony 4. Rise of Octavian/Augustus/Pax Romana Period 5. Fall of Rome, corruption, the “bad” Emperors, Germanic tribes E. Roman Legacy 1. Roman Architecture 2. Roman Politics IV. The Byzantine Empire and the Slavs Essential Question: How did the Byzantine Empire carry on the traditions of the Roman Empire? Essential Question: What impact did the fall of Constantinople have on Western Europe, and to what extent was it a turning point in global history? A. Famous Byzantine Emperors 1. Constantine 2. Justinian a. The Hagia Sophia, Christianity, Justinian’s Code B. Division in the Roman Catholic Church 1. Eastern Orthodox Church C. Rise of the Russian State 1. The Vikings, Kievan Rus’ 2. Foundation of the Russian State a. Ivan the Great, Ivan the Terrible, St. Basil’s Cathedral, Romanov Dynasty 3. Mongol Empire a. invasion, Genghis Khan b. Khubilai Khan, Yuan Dynasty c. Mongol contributions V. Civilizations in the Americas Essential Question: What were the cultural similarities of the Aztecs, Mayans, and Incas? Essential Question: Was conquest by the Spaniards of the Americas exploration or exploitation? A. Early civilizations in Central America 1. Olmec Civilization 2. Teotihuacan a. America’s first Metropolis 3. Mayan Civilization a. Mayan Calendar 4. Aztec Civilization a. Tenochtitlan b. Quetzalcoatl c. Impact of Cortes 5. Human sacrifice B. Civilizations in South America 1. Incan Empire a. Machu Picchu b. Impact of Pizarro 2. Human sacrifice C. Civilizations in North America 1. Anasazi 2. Iroquois 3. The Mound Builders VI. Flowering of Civilizations Essential Question: What are the basic beliefs and practices of Islam, as taught by Muhammad, and how did the Islamic state spread? Essential Question: Why do stereotypes develop about people or religion? Essential Question: How has the physical geography of East Asia affected the development of the region? A. The Islamic World 1. Muhammad’s teachings, Mecca, Medina 2. The Quran, Role of Archangel Gabriel 3. 5 Pillars of Islam, Jihad 4. Baghdad, to present-day terrorism 5. Islamic Contributions a. Medicine, astronomy b. Arts and Architecture 1. Mosques, Taj Mahal, Dome of Rock B. Early African Civilizations 1. Africa’s geography, trade a. Camel caravans across Sahara 2. Southern Africa a. Nubia 3. Kingdoms of West Africa a. Ghana b. Mali 1. Mansa Musa 2. Timbuktu c. Songhai 1. Center of Learning C. Civilizations of East Asia 1. Japan’s isolation, geography 2. Rise of the Japanese State a. Shogunate System b. Samurai, Code of Ethics, 47 Ronin c. Social structure, Polygyny 3. Korea a. Chinese influence b. Mongol influence 4. The Rise of the Great Viet a. Chinese influence b. Strong sense of national identity, Vietnam War VII. European Middle Ages Essential Question: How was Feudalism an economic, political, and social system? Essential Question: What influence did the Roman Catholic Church have on art, politics, and education in Medieval Europe? Essential Question: What impact did the Bubonic Plague have on Medieval Europe? A. Rise of Feudalism 1. Social, Political, Economic system B. Power of Roman Catholic Church 1. Pope’s power over Aristocracy 2. Church abuses 3. Holy Crusades and their impact C. New Kingdoms emerge 1. Charlemagne 2. France 3. England a. William the Conqueror, Henry II, John I, Magna Carta D. Impact of the Bubonic Plague E. Art and Architecture of the Middle Ages 1. Religious paintings 2. Cathedrals and Castles VIII. Transition to a Modern World Essential Question: Why did the Renaissance begin in Italy? Essential Question: How did humanism and secularism differ from previous Medieval beliefs? Essential Question: Who were the key reformers during the Protestant Reformation and how did they contribute to change ? A. The Italian Renaissance 1. Petrarch’s contribution to the Renaissance 2. The impact of humanism and secularism 3. Contributions of Renaissance writers, artists, and thinkers 4. The impact of the printing press on the Renaissance B. The Protestant Reformation 1. Church abuses 2. Martin Luther’s teachings and impact 3. King Henry VIII and the English Reformation 4. The Catholic Reformation/Inquisition C. The Scientific Revolution 1. Advances in science 2. Contributions of Copernicus, Galileo, Kepler, Isaac Newton, and Francis Bacon