Plate Tectonic Theory notes
advertisement

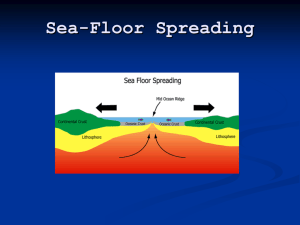
Plate Tectonic Theory I. History A. Three stages to get there 1. Continental Drift 2. Seafloor Spreading 3. Plate Tectonic Theory B. What did people believe about the earth before Plate Tectonics? 1. The continents were in fixed positions 2. The map of the earth was unchanging a) Same past, present, and future locations of continents II. Continental Drift A. Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) 1. German Astonomer/Meteorologist/climatologist/geologist a. First to use weather balloons b. Wrote a textbook on Geology that Germans LOVED c. Just wanted to be a professor somewhere! 2. Proposed that continents have slowly drifted to current locations 3. All land masses were once joined together in a single large mass called “Pangea”-Greek for “All Land” 4. Pangea split apart and the continents gradually moved to their current positions= Continental Drift 5. Most of the evidence was already known. a) Wegener just assembled it and proposed the theory b) "Scientists still do not appear to understand sufficiently that all earth sciences must contribute evidence toward unveiling the state of our planet in earlier times, and that the truth of the matter can only be reached by combing all this evidence. . . It is only by combing the information furnished by all the earth sciences that we can hope to determine 'truth' here, that is to say, to find the picture that sets out all the known facts in the best arrangement and that therefore has the highest degree of probability. Further, we have to be prepared always for the possibility that each new discovery, no matter what science furnishes it, may modify the conclusions we draw." The Origins of Continents and Oceans (4th edition) B. Evidence for Continental Drift 1. Continents fit together like a puzzle a. Atlantic Coastlines of South America and Africa 2. The same fossils are found on separate continents a. Plants (Glossopteris) and Animals (Mesosaurus, Cynognathus, Lystrosaurus) b. These plants and animals couldn’t fly or swim that far 3. Similar rock sequences in separate areas a. In South America, Africa, India, Antarctica, Australia b. Basalt lava on top, then sandstone/shale, then glacial till 4. Evidence of different climates in the fossil record a. Antarctica has fossilized plants…somewhere warmer b. Africa has glacial till….it was somewhere colder C. Rejected 1. The continents didn’t have a perfect fit, and most didn’t fit at all 2. Land bridges…big ones… could have allowed crossings 3. Coincidence or widespread events 4. Polar wandering- the earth’s polar locations may have changed 5. Most importantly…wouldn’t we feel them move? a. Couldn’t measure it b. Couldn’t explain the cause of movement. 6. Alfred was ridiculed, but finally got a professorship a. Soon after, he reluctantly went on his 4th trip to Greenland b. Died collecting Ice samples III. Seafloor Spreading A. Harry Hess 1. Naval Rear Admiral. Served in WWII 2. Post-WWII, helped map the seafloor a. Worried about the Soviets and subs 3. Discoveries by others of the undersea ridges and mountains a. He reviewed the data again and made a hypothesis B. Seafloor Spreading 1. Sonar allowed mapping of sea floor a. “Scar” encircles the whole globe. Mid-ocean ridge 2. A mirrored profile emerged a. Undersea mountains with a rift in the middle b. Mountains led to low abyssal plains on both sides c. Ended with continental slope and shelf on each side d. Not perfectly symmetrical though 3. Proposed that hot, less dense mantle material rises toward the mid-ocean ridges 4. Some material solidifies. Some flows sideways and drags the seafloor along with it in both directions a. As the seafloor spreads apart, new seafloor is created b. Older seafloor moves away in opposite directions c. This could explain how the crust moved! Supports Continental Drift Theory. C. Evidence for Seafloor spreading 1. Mid-Ocean Ridge System encircles globe 2. Less sediments and fossils around the mid-ocean ridges (Younger) 3. 1968- Glomar Challenger Expedition a. Collected rock samples to see ages b. Younger rocks near mid-ocean ridges. Older near continents. c. Ocean floor age mirrored on each side of mid-ocean ridge 4. Paleomagnetism a. When rocks form, they take on the magnetic profile of the earth at that time b. Magnetic field switches every so often though. c. Pattern mirrors on ocean floor as well 5. Seafloor spreading explains how continental drift can occur. IV. Plate Tectonic Theory A. It’s a combination of continental drift and seafloor spreading 1. The lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates. 2. They move across the upper mantle (Asthenosphere) 3. They collide and divide to create the major landforms on Earth today B. Caused by convection currents 1. Heated Asthenosphere flows upwards (less dense) 2. When it hits the crust it spreads outwards 3. Flowing Asthenosphere drags lithosphere with it 4. Asthenosphere material cools, sinks. 5. Cycle repeats C. Tectonic Plates 1. Explains a. Mountains b. Earthquakes c. Volcanoes d. Other geologic patterns and features 2. Can use these features to find the plates Plate Tectonic Theory I. History A. Three stages to get there 1. ____________________________ ________________________ 2. ___________________________ __________________________ 3. Plate Tectonic Theory B. What did people believe about the earth before Plate Tectonics? 1. The continents were in ______________________ positions 2. The map of the earth was ________________________________ a) Same past, present, and future locations of continents II. Continental Drift D. ______________________ ________________________________ (1880-1930) 6. German Astonomer/Meteorologist/climatologist/geologist a. First to use weather balloons b. Wrote a textbook on Geology that Germans LOVED c. Just wanted to be a professor somewhere! 7. Proposed that continents have slowly ______________________ to current ____________________________ 8. All land masses were once joined together in a single large mass called “________________”-Greek for “All ___________________” 9. Pangea ____________ _____________ and the continents gradually moved to their current positions= Continental Drift 10. Most of the evidence was already known. a) Wegener just _______________ it and proposed the theory b) "Scientists still do not appear to understand sufficiently that all earth sciences must contribute evidence toward unveiling the state of our planet in earlier times, and that the truth of the matter can only be reached by combing all this evidence. . . It is only by combing the information furnished by all the earth sciences that we can hope to determine 'truth' here, that is to say, to find the picture that sets out all the known facts in the best arrangement and that therefore has the highest degree of probability. Further, we have to be prepared always for the possibility that each new discovery, no matter what science furnishes it, may modify the conclusions we draw." The Origins of Continents and Oceans (4th edition) E. Evidence for Continental Drift 5. Continents ___________ together like a __________________________ a. Atlantic Coastlines of South America and _______________ 6. The same __________________ are found on separate continents a. Plants (Glossopteris) and Animals (Mesosaurus, Cynognathus, Lystrosaurus) b. These plants and animals couldn’t fly or swim that far 7. Similar _____________ _________________________ in separate areas a. In South America, Africa, India, Antarctica, Australia b. Basalt lava on top, then sandstone/shale, then glacial till 8. Evidence of different ___________________ in the fossil record a. Antarctica has fossilized _________…somewhere _________ b. Africa has glacial till….it was somewhere _______________ F. Rejected 7. The continents didn’t have a __________________ ____________, and most didn’t fit at all 8. ___________ _________…big ones… could have allowed crossings 9. Coincidence or widespread events 10. __________ __________- the polar locations may have changed 11. Most importantly…wouldn’t we ___________________________? a. Couldn’t measure it b. Couldn’t explain the ___________ of ________________________. 12. Alfred was ridiculed, but finally got a professorship a. Soon after, he reluctantly went on his 4th trip to Greenland b. Died collecting Ice samples III. Seafloor Spreading D. _______________ _________________ 4. Naval Rear Admiral. Served in WWII 5. Post-WWII, helped _____________ the __________________________ a. Worried about the Soviets and _______________ 6. Discoveries of the undersea ridges and _______________________ a. He reviewed the data again and made a hypothesis E. _______________________ ________________________________ 5. ______________________ allowed mapping of sea floor a. “Scar” encircles the whole globe. _________________________ 6. A mirrored profile emerged a. Undersea mountains with a _____________ in the middle b. Mountains led to low abyssal plains on both sides c. Ended with continental slope and shelf on each side d. Not perfectly _______________________________ though 7. Proposed that hot, ____________ ___________________ mantle material rises toward the mid-ocean ridges 8. Some material ________________. Some flows sideways and __________________ the seafloor along with it in both directions a. As the seafloor spreads apart, new seafloor is created b. Older seafloor moves away in opposite directions c. This could explain how the crust moved! Supports _______________________________ ____________________ theory. F. Evidence for Seafloor spreading 6. Mid-Ocean Ridge System encircles globe 7. Less sediments and fossils around the mid-ocean ridges (_____________________) 8. 1968- Glomar Challenger Expedition a. Collected rock samples to see ____________________ b. ___________________ rocks near mid-ocean ridges. Older near ____________________________. c. Ocean floor age mirrored on each side of mid-ocean ridge 9. ______________________________ a. When rocks form, they take on the magnetic profile of the earth at that time b. Magnetic field switches every so often though. c. _______________________ mirrors on ocean floor as well 10. Seafloor spreading explains how continental drift can occur. IV. Plate Tectonic Theory D. It’s a combination of ___________________________ ________________ and ________________________ ________________________ 4. The lithosphere is broken into ___________________ _____________. 5. They move across the upper mantle (_________________________) 6. They __________________________ and divide to create the major landforms on Earth today E. Caused by __________________________ _________________________ 5. Heated Asthenosphere flows _____________________ (less dense) 6. When it hits the crust it spreads outwards 7. Flowing Asthenosphere ___________________ lithosphere with it 8. Asthenosphere material cools, _____________________. 5. Cycle repeats F. Tectonic Plates 3. Explains a. Mountains b. Earthquakes c. Volcanoes d. Other geologic patterns and features 4. Can use these features to find the plates