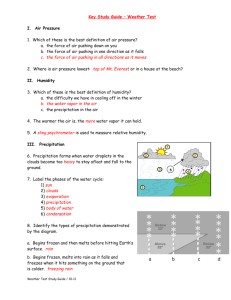
student fill in weather notes

Weather Notes
I. Wind- moving air caused by differences in ______________________ (uneven heating of the earth)
A. Instruments used my Meteorologist
1. wind vane- weather vane (______________)
2. Anemometer- wind from any direction will catch one arm and start it moving. (_____________ and direction)
3. weather balloons- winds in ______________ atmosphere
- ________________ changes in speed and direction
- move faster
B. Jet stream
- located near _________________ at latitude 30 o N and 30 o S are high-speed bands of wind.
-_______________, sizes, ________________, and shapes vary from day to day, and season to season.
Summer – jet stream is near U.S./Canadian border. ____________________masses pushed North.
Winter – jet stream moves south ____________________ moves south.
Coriolis effect- northern hemisphere wind deflected to the ____________________.
___________________ hemisphere wind deflected to the left.
II. Front – boundary between ____________ air masses.
- air masse change temp. and humidity at the front.
Signs of fronts.
1. a line of clouds
2. falling barometer
3.change in wind _________________
4. temperature change
-numbers 2 through 4 show a front is ________________________.
-fronts are drawn in regions of great change in ____________ and wind ______________. This is where ___________________ tend to bend. (shape is generally a wedge)
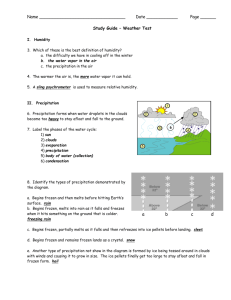
1. Warm Front: warm air slides over departing cold air- large bands of precipitation form
(___________).
This is the symbol on a map for a warm front
2. Cold Front: cold air pushes under a warm air mass. Warm air rises quickly=narrow bands of violent storms form(_______________________).
This is the symbol for a cold front
3. Occluded Front: 2 air masses merge and force warm air between them to rise quickly. Strong winds and heavy precipitation will occur(________________________________)
This is the weather map symbol for an occluded front
4. Stationary Front: warm or cold front stops moving. Light wind and precipitation may occur across the front boundary (________________________)
This is the weather map symbol for a stationary front
III. Weather Maps – overall picture of weather across the earth.
-local conditions to national weather service _________times a day.
-Station Model- group of symbols, shows weather
- measures the following from ground to make surface maps:
_____________________ * Dew Point
Air pressure * _______________________
Wind speed * Cloud cover
Wind direction * _______________________
____________________
A. Conditions measured for forecast (Weather Stations)
1. Air pressure
- if _______________, air mass moves over. (improving weather)
-if _________________, a front or low pressure is approaching, often precipitation. (a change in weather)
2. Wind direction
-winds shift from southwest to northwest a ______________ front is located.
-winds shift from east to southeast a__________________ front is located.
3. Clouds
-cirrus to cirrostratus and altostratus is a ______________ front and rain for a long time.
-cirrus to dark cumulonimbus is a _____________ front and a violent storm but not
for a long time.
4. Wind speed
5. Temperature
-dropping temperature is a clue to a ____________ front.
-rising temperature is a clue to a ________________ front.
III. Forecasting-
A. Steps to produce a surface map.
1. station models printed on map
2. _____________ are drawn a. circled areas that represent lowest pressure and labeled lows b. smaller circled areas that represent highest pressure and labeled highs
3. isotherms are drawn in occasionally.
4. meteorologist analyze map, mark the line for fronts and _____________ precipitation.
B. Movement of weather systems- are in _________________ lines unless acted upon by another air mass.
1. pattern of movement shows both _______________ and ________________of system.
2. _________________ based on prediction of position of system.
-forecast only accurate for about _________ hours.
-long-range forecasts- very general based on seasonal averages of temperature and pressure and winds in upper troposphere.
C. How can we find information on weather patterns?
1. ground readings
2. ___________ take radio readings
3. ships report conditions
4. satellites
5. ______________________
6. Doppler radar
IV. Storms-
A. Thunderstorm-violent weather system
-Produces- Cumulus clouds; Strong winds; Heavy rain; Lightning; Thunder; Hail; Tornadoes
-more than ___________people a year killed by lightning from thunderstorms.
-Form- cold front, warm air is pushed _________ by an advancing cold mass.
-Storm moves- growth of clouds, speed of wind increases and _________________ clouds form.
-high winds of upper troposphere push top of cloud forward making an – ________________ top.
1. Lightning- discharge of electricity from a thunder cloud to the ______________ or to another ______________________.
- temperature of a lightning flash reaches 28,000 _______
2. Thunder- sudden expansion of the air.
-Rumbling- sound is spread out in time or echo in a mountain.
-Heat lightning- glow of lightning so far away that its ______________ can not be heard.
B. Tornadoes- small funnel-shaped whirlwind that spins in a ______________________direction around an area of very low pressure.
- wind speeds can be greater then ______________________
- pressures are so low that a closed building will explode
- develops with in a cumulonimbus cloud
- forms during spring and early summer in middle of country
- travels at speed of ____________ to ________________
- only lasts a ___________ minutes
Conditions: layer of warm moist air with cooler drier air above it.
How does it start?
1. hypothesis: lightning helps by heating air making it less dense, causing air to rise.
2. hypothesis: extreme differences in temperature between air on ground and air in upper troposphere start air rising.
C. Hurricane – large tropical cyclone that develops in the doldrums, usually during the _________ summer.
- Western Pacific Ocean called a _____________ and in Indian ocean called a _______________.
- hurricanes form in areas where air is normally gently rising.
- 70% of hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean form along west coast of _________________.
-Water is the fuel that causes a hurricane to increase in _____________ and ______________.
- hurricanes are speeds of _________km/ hr and up
- tropical storms are speeds of ________km/hr to _______km/hr
-more dangerous than the wind and rain is the _____________________ ( bulge in ocean under the light air) this raises the ocean level by 8 meters.
How it Forms:
1. the faster the air moves over the ocean, the more water vapor it picks up
2. the more water vapor in the air releases more heat increasing the winds.
3. the longer the storm stays over water, the more this cycle continues and the _________________ the storm.
Eye- center area of _____________
- the air is slowly sinking and the sky is clear
- fastest winds found in a ____________ around the eye
Naming Hurricanes
- _________ year cycle
-named alphabetically with male and female alternating
V. Watch and Warning
National severe storms forecast center is in __________________, Missouri.
Watch- covers an area of 100 km by 200 km.
- gives time when they are ____________________
Warning- when one has actually been ___________________.
- gives location and area where it is likely to go