Greek and Latin Roots
advertisement
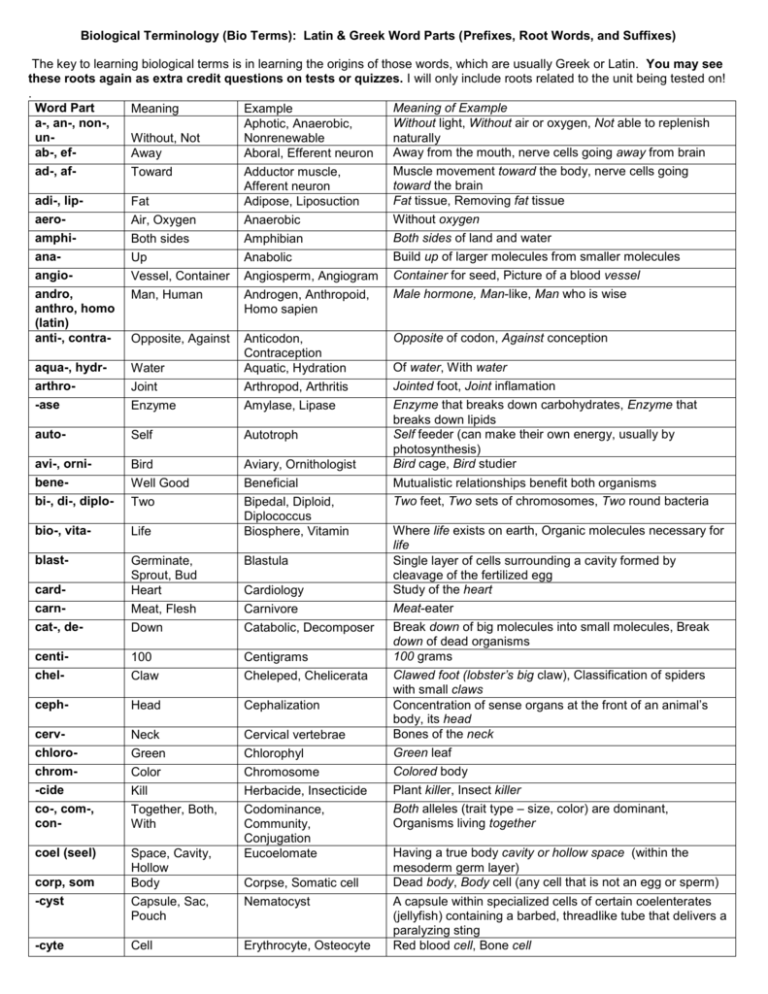
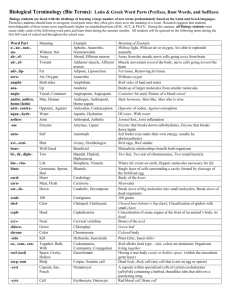
Biological Terminology (Bio Terms): Latin & Greek Word Parts (Prefixes, Root Words, and Suffixes) The key to learning biological terms is in learning the origins of those words, which are usually Greek or Latin. You may see these roots again as extra credit questions on tests or quizzes. I will only include roots related to the unit being tested on! . Word Part Meaning of Example Meaning Example a-, an-, non-, Without light, Without air or oxygen, Not able to replenish Aphotic, Anaerobic, unWithout, Not Nonrenewable naturally ab-, efAway from the mouth, nerve cells going away from brain Away Aboral, Efferent neuron ad-, afMuscle movement toward the body, nerve cells going Toward Adductor muscle, toward the brain Afferent neuron adi-, lipFat tissue, Removing fat tissue Fat Adipose, Liposuction aeroWithout oxygen Air, Oxygen Anaerobic amphiBoth sides of land and water Both sides Amphibian anaBuild up of larger molecules from smaller molecules Up Anabolic angioVessel, Container Angiosperm, Angiogram Container for seed, Picture of a blood vessel andro, Male hormone, Man-like, Man who is wise Man, Human Androgen, Anthropoid, anthro, homo Homo sapien (latin) anti-, contraOpposite of codon, Against conception Opposite, Against Anticodon, Contraception aqua-, hydrOf water, With water Water Aquatic, Hydration arthroJointed foot, Joint inflamation Joint Arthropod, Arthritis -ase Enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates, Enzyme that Enzyme Amylase, Lipase breaks down lipids autoSelf feeder (can make their own energy, usually by Self Autotroph photosynthesis) avi-, orniBird cage, Bird studier Bird Aviary, Ornithologist beneWell Good Beneficial Mutualistic relationships benefit both organisms bi-, di-, diplo- Two Two feet, Two sets of chromosomes, Two round bacteria Bipedal, Diploid, Diplococcus bio-, vitaWhere life exists on earth, Organic molecules necessary for Life Biosphere, Vitamin life blastGerminate, Blastula Single layer of cells surrounding a cavity formed by Sprout, Bud cleavage of the fertilized egg cardStudy of the heart Heart Cardiology carnMeat-eater Meat, Flesh Carnivore cat-, deBreak down of big molecules into small molecules, Break Down Catabolic, Decomposer down of dead organisms centi100 grams 100 Centigrams chelClawed foot (lobster’s big claw), Classification of spiders Claw Cheleped, Chelicerata with small claws cephHead Cephalization Concentration of sense organs at the front of an animal’s body, its head cervBones of the neck Neck Cervical vertebrae chloroGreen leaf Green Chlorophyl chromColored body Color Chromosome -cide Plant killer, Insect killer Kill Herbacide, Insecticide co-, com-, Both alleles (trait type – size, color) are dominant, Together, Both, Codominance, conOrganisms living together With Community, Conjugation coel (seel) Having a true body cavity or hollow space (within the Space, Cavity, Eucoelomate Hollow mesoderm germ layer) corp, som Dead body, Body cell (any cell that is not an egg or sperm) Body Corpse, Somatic cell -cyst Capsule, Sac, Nematocyst A capsule within specialized cells of certain coelenterates Pouch (jellyfish) containing a barbed, threadlike tube that delivers a paralyzing sting -cyte Red blood cell, Bone cell Cell Erythrocyte, Osteocyte deca-, decideciddendro-, arbordent, dont 10 Cut Off Tree derm Skin Decameter, Deciliter Deciduous Dendrochronology, Arboretum Dental plaque, Orthodontist Epidermis, Ectoderm deutero- Second Deuterostome dia-, dif-, dissdors-, noto- Through, Apart, Across The Back Diarrhea, Dissect, Diffusion Dorsal fin, Notochord echineco- Echinoderm, Echidna Ecology ecto-, exo- Spiny Where one lives, Home Out, Outside -emia Blood Condition entomo-, insect epi- Insect Equ-, iso- Equal, Same Hyperglycemia, Sickle cell anemia Entomologist, Insectivore Epidermis, Epicardium, Epiphytes Isotonic, Equilibrium erthreu- Red True ex-, extra-, exogastrgeo hapl-, mono-, uni- Out, Outside, Beyond Stomach Earth One herb-, -phyte homo (greek) hyper- Plant Same More, Excessive hypo-, sub- Less, Below lingu gnath (nath) gram, -graph Tongue Jaw Written or Picture helix hemhepato- Spiral, Coil Blood Liver herphetero- Reptile Different, Other ichthyes Fish interintra-, endo-itis Tooth or Teeth Upon, Over, Atop Ectoderm, Exoskeleton Erythrocyte Eukaryote, Eucoelomate Extinct, Extracellular, Extrapolation Gastrointestinal (GI) Geotropim Haploid, Monosaccharide, Unicellular Herbivore, Epiphyte Homozygous Hypertonic, Hypertension Hypotonic, Hypotension, Subatomic Sublingual Agnathan Electrocardiogram, Sonography Double helix Hemorrhage Hepatitis 10 meters, 10 liters Deciduous trees lose their leaves in the fall Counting tree rings to determine its age, Place where many different trees grow Teeth with patches of bacterial growth, Dr. who straightens teeth Top skin layer, Outer layer of tissue/skin during embryo development Mouth develops second (the anus develops first) Flow through, Cut apart, Across (cell membrane) Fin on the back of a fish, A embryonic structure that will become vertebrae Spiny skin (sea star), (spiny anteater) Study of where organisms live Outer layer of tissue during embryo development, Skeleton on outside of body High blood sugar levels, Sickle shaped red blood cells (should be circular) Insect studier, Insect eater Upon the dermis (skin), Over the heart, Atop a plant Solute levels are equal on both sides of a membrane (inside & outside the cell) Red blood cell True nucleus (protective membrane around DNA), True body cavity Died out, Outside the cell, Beyond known values (on a graph) Stomach and intestines A plant’s response to the earth’s gravity One set of chromosomes, One unit of sugar (glucose), one celled organism Plant eater, Atop a plant Same alleles (form of a gene); More solute (something dissolved in water), Excessive blood pressure Less solute, Below normal blood pressure, Below atoms (protons, neutrons, electrons) Under the tongue A fish without a jaw Print out of the heart’s electrical activity, Taking pictures using sound waves Two strands in a spiraled shape Bleed heavily Inflammation of the liver Study of reptiles (lizards, croc’s, turtles, and snakes) Offspring gets different forms of same trait (Tt), Other feeder (ex. herbivore) Fish with a cartilage skeleton, Fish with a bony skeleton Between Inside Herpetologist Heterozygous, Heterotroph Chondrychthyes, Osteichthyes Intercellular Intracellular, Endoderm Inflammation of Dermatitis, Laryngitis Inflammation of the skin, Inflammation of the larynx Between cells Inside a cell, Inside layer of a developing embryo karyo, caryo kilo-, millleuco-, leukoloc logy Cell Nucleus 1000 White Place Study or Science of To break Prokaryote, Procaryotic Kilogram, Milliliter Leucocyte Locus Mycology, Virology macro-, megaMal, dis, dys Large marmedi-, mesometa- Sea Middle Change meter Measurement micro- Small morph Shape, Form multi, myria, polymutamyo- Many Macromolecule, Megafauna Malnutrition, Disease, Dystrophy Marine Biology Medial, Mesoderm Metamorphosis, Metastasis Spirometer, Sphygmomanometer Microsporangia, Microbiology Mesomorph, Metamorphosis Multicellular, Myriapod, Polysaccharide Mutation Myofibril, Fibromyalgia nasal, rhin, probosc neonephr-, renal Nose New Kidney Nasal septum, Rhinoplasty, Proboscis Neonatal Nephron, Renal vein nomoct- Name 8 Binomial nomenclature Octopus oma omni-, toti- Tumor, Swelling All Carcinoma, Lymphoma Omnivore, Totipotent oo-, ov- Egg orth- Straight Oogonia, Oviduct, Oviparous Orthoptera, Orthodontist ose, gly, sacchar -osis oste- Sugar Glucose Act, Condition Bone paleo-, archeoparapatho- Old, Ancient Acidosis Osteoarthritis, Osteocyte Paleontology, Archeology Parallel, Parapodia Pathogens ped, pod pentperiphago, troph, vore phore Feet, Foot 5 Around To Feed or Eat lys- Bad or Ill Change Muscle Beside Disease Carry, To Bear Lyses, Cytolysis Centipede, Tetrapod Pentradial, Pentose Pericardium Phagocyte, Autotroph, Carnivore Chromatophore (voicebox) Cells without a nucleus 1000 grams, 1000th of a liter White blood cell Place on a chromosome where a specific gene is found Study of Fungi, Study of Viruses Process of breaking up or digesting a cell membrane causing cell death Large molecules (lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids), Big animals The tumor was malignant. Study of life in the Sea or Ocean Middle, Middle layer of tissue during embryo development Change in shape or location; Cancer cells that change location (spread), Measures inhalation & exhalation, Measures blood pressure Small spore carriers (male), Study of microbes (bacteria, viruses, etc.) Middle form, Change in shape (tadpole to frog) Organism made of many cells, Organism w/many feet, Many monosaccharides Change in the # or sequence of DNA Muscle cell, Muscle pain Wall dividing nasal cavity, Surgery of reshaping the nose, Elephant’s trunk Newborn Part of the kidney that filters/cleans blood, Vessel taking blood to the kidney Two-name naming system (Homo sapien = Humans) 8 feet Cancer-causing tumor, Tumor of the lymphatic system Eats all – plants & animals, All important cell (zygote) – becomes all cells Egg stem cells, Egg carrying tube, Eggs that are hatched outside the mother Straight-winged insect order (grasshoppers), Dr. who straightens teeth A simple sugar or monosaccharide made by photosynthesis in autotrophs Too much acid in body fluids Inflammation where bones meet (joint), Bone cell Study of fossils and the history of earth, Study of ancient civilizations Side by Side, Feet to the side Disease-causing organisms (some bacteria, some viruses, etc.) 100 feet, 4 feet 5 spokes or rays (sea star has 5 rays/arms); 5 carbon sugar Around the heart Eating cell (white blood cells), Self-Feeders (photosynthesizers), Meat eater Color or pigment carrying cell photo-, lumin Light Using light to make glucose, Organisms that can create light Plant Photosynthesis, Bioluminescence Epiphyte phyte, phyto pinn-, plum-, -pter pino- Wing, Feather, Fin Drink Pinnepedia, Plummage, Hymenoptera Pinocytosis platyploid Flat Chromosome Platyhelminthes Haploid, Diploid Using fins for feet (seals), Feather shape & patterns, Straight membraned wings Process of a cell engulfing/drinking liquids or dissolved substances Flatworm, Flat foot One set of chromosomes, Two sets of chromosomes pneumo-, pulmopost- Lungs Pneumonia, Pulmonary artery Post mortem Infection of the lungs, Vessel taking blood from the heart to the lungs After death pre-, pro prim-, prot- Before, Forward First Before birth 1st organisms to eat producers (herbivores), 1st animal pseudo- False quat-, quad, tetrarerhea, rrhea 4 Again Flow/Discharge Prenatal Primary consumer, Protozoa Pseudocoelomate, Pseudopodium Quarternary, Quadiceps, Tetrapod Reproduce Diarrhea sal sapr- Salt Rotten Saline Saprotroph schizo- Split scope View, See sect, -tom semi-, hemi- Cut One-Half sperm spir Seed Breathe Schizocoely, Schizophrenia Microscopic, Macroscopic Bisect, Anatomy Semipermeable, Hemisphere Spermacide, Spermatid Inspire, Spiracle stas, stat stom-, ora Unchanging Mouth Homeostasis Stomata, Oral cavity sym-, syn,sys tax- With, Together Symbiosis, Synthesize, System Taxonomy teloterr tert-, tritherm End Land 3 Heat toxic trans-, per- Poison Across, Through trop, volv Turn, Change Telophase, Telomeres Terrestrial ecosystem Tertiary, Trisomy Thermophile, Thermometer Neurotoxin, Hemotoxin Transport, Transdermal, Permeable Phototropism, Evolution Full of salt or salt containing Feeds on Rotting organic matter/dead organisms (also called decomposers) Cavity formed at the split of the endo- & ectoderm (protostomes), Split mind To see or view something small, To see or view something w/o using a scope Cut in two, To cut up Allows some (1/2), but not all things through, One-half a sphere (ball-shape) Sperm killer, A small or immature sperm To breathe in, Hole found on insects for air to enter and leave (breathing) Unchanging chemical conditions in healthy organisms Hole or mouth in leaves allowing gas exchange (O2 & CO2), Mouth space Organisms living with each other, Put together, Working together A system used to arrange or classify a large number of organisms End of mitosis, End or tip of chromosomes All living and nonliving things in a designated area on land 3rd, 3 bodies (chromosomes) Bacteria that live in hot areas, Heat measuring instrument troph ventr- To feed, eat Belly Autotroph, Heterotroph Ventral vore zo zyg Devour Animal Yoke (egg + sperm) Carnivore Zoology Zygote, Homozygous After Arrange A plant that grows atop of another plant False body cavity (between ecto- & endoderm), False foot (found in amoeba’s) 4th, 4 heads, 4 feet Produce again Frequent passage of loose, watery, soft stools Poison to the nervous system, Poison in the blood Across a cell membrane, Through the skin, Through a cell membrane Plant’s response of turning toward light, How organisms change over time Self feeders (Autotrophs); Other feeder (Heteroptroph) Belly portion of an organism (portion of a worm that touches the ground) Carnivores devour meat or flesh Study of animals Union of egg & sperm