Chapter 5 “The Young Republic”
advertisement

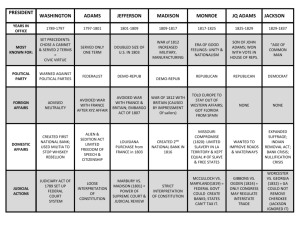
Chapter 5 “The Young Republic” 1787- Northwest Ordinance enacted -establishes governments in the NW Territory (present day Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Wisconsin, Michigan) -5,000 people = assembly (legislature) -60,000 people= you can become a state in the Union, your state will be equal to original states - PLAN for how U.S. will grow, expand, etc. - SLAVERY IS FORBIDDEN IN THE NW TERRITORY!!!!! Themes of 1790s -Establishment of a new government -executive departments (Cabinet) -Judiciary Act (establishes lower court system) - Bill of Rights (1st 10 Amendments of the Constitution, 1791) -establishing precedent -Asserting National Powers (Federalism) -Development of Political Parties - 1st American Party System Federalists “Hamilitonians” – Alexander Hamilton, John Adams Want a strong national government Democratic Republicans “Jeffersonians”- Thomas Jefferson Want a weaker national government (more states’ rights) Foreign policy doesn’t favor British By the 1830’s- Federalists become Whigs Republicans become Democrats By the 1850’s- Whigs become Republicans (GOP)- don’t want slavery in new territories 1799- George Washington dies of strep throat 1800- John Adams is defeated; Thomas Jefferson becomes 3rd President. 1803- Louisiana Purchase - purchased from France - basically the inner 1/3 of US -$15 million - almost guarantees “continental nation” - removes France from continent 1803- Marbury v. Madison (judicial review- John Marshall) Thomas Jefferson as a President - 1st term more successful than 2nd -Sec. of State is James Madison - judiciary act (circuit courts) -impeachment of Supreme Court Justices - small army, small navy (will be a problem later…) -Louisiana Purchase - sends Meriwether Lewis and George Clark (1804- leave from St. Louis) -Jefferson opposes Aaron Burr, who happens to be tried for treason- Vice Presidentgrandson of John Edwards… Burr kills Alexander Hamilton in a DUEL in 1804! Europe (Jefferson- foreign policy) 1803- British and French are fighting again; U.S. is neutral and trading with both countries. 1807- “Chesapeake Incident”- American ship is boarded by the British (within view of the American coast) 1807- Response to CI- Embargo (no trade with Europe)- American trading vessels cannot got to foreign ports (downside- American produce can’t be traded… American farmers are hurt) 1808- Madison is elected President 1809- Embargo repealed; “Non-Intercourse Act” (Americans can trade with everyone except France and Britain) 1811- Battle of Tippecanoe (near Lafayette, IN) - William Henry Harrison - War Hawks (Congressmen- KY- Henry Clay, SC- John Calhoun) -American settlers are being attacked by Indians (Native Americans) at the urging of the British(who are still in Canada) Madison is a weak leader, pressured into war by Clay, Calhoun, and others. War of 1812 - versus British (aka War w/ Britain, Mr. Madison’s War, the 2nd War of Independence) - British attack Washington, DC (Madison flees, buildings burned- including White House), Baltimore, Ft. McHenry (inspired The Star Spangled Banner) -December, 1814- Treaty of Peace, Treaty of Ghent - negotiated by Henry Clay and John Quincy Adams -no real resolution about trading rights -“Status Quo Antebellum” – the way things were before the war -United States didn’t really know the war was over. - January 1815- General Andrew Jackson - Battle at New Orleans (Jackson Square) 1815 - Peace is restored in Europe, Napoleon defeated at Waterloo -Americans reopen foreign trade -American focus changes to Westward Expansion 1815-1824 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS -James Monroe (Madison’s Sec. of State, President after Madison) -John Quincy Adams (Monroe’s Sec. of State)- very well educated, experienced -John Marshall (Chief Justice of the Supreme Court) - other new leaders: Henry Clay (KY), John C. Calhoun (SC), Gen. Andrew Jackson (TN), Daniel Webster (Mass.) - New issues: problems with westward expansion, renewal of the Bank, tariff (fee or tax on imported), internal improvements (roads, harbors, canals, ports) - growing nationalism, sectionalism (specifically North v. South- 1830s) - generation of politicians… BORN in the USA! “Founding Fathers” dying off… -increased controversy about slavery -Women’s Rights become an issue -Abolitionism “Land Resolutions” - Convention of 1818 -John Quincy Adams is Sec. of State - North border of LA Purchase is set at 49th parallel - Joint occupation of the Oregon Country- 42 degrees- 54 degrees, 40 seconds (w/ Britain), both Americans and British can settle (1818-1846) -Florida becomes part of the US. - US boundary all the way to the Pacific Ocean. The Monroe Doctrine - says the Americas (North America, Central America) are no longer open to new colonization by Europe. - largely written by John Q. Adams The Missouri Compromise -1819 - James Tallmadge, Jr. (NY) -proposes that no slaves are allowed in Missouri -Missouri is admitted to the Union as a slave state. - Maine is admitted as a free state… Balance of slave and free states is maintained in the Senate. -What about the LA Purchase? - 36 degrees, 30 seconds - to the North is free, to the South is slaves -South is ok with this because they didn’t think anyone would settle in the LA Purchase area- the “Great American Desert” Election of 1824 - John Quincy Adams - Andrew Jackson - William Crawford * no candidate wins the majority… - Election goes to the House of Representatives. - Henry Clay - “Corrupt Bargain” - John Quincy Adams becomes President, JQC makes Henry Clay his Sec. of State Andrew Jackson- 7th President of the United States - 1828 elected, 1829-1837 (presidency) -“the common man,” from Tennessee, first President from “The West” -attorney, owns plantation (The Hermitage, in Nashville) and slaves - 3 main issues: 1. Nullification- right claimed by state to declare a federal law void 2. Indian Removal- moved Native Americans west 3. U.S. Bank (federal bank)- Jackson wants to destroy it - member of modern day Democratic party