Lab Report: Photosynthesis
advertisement

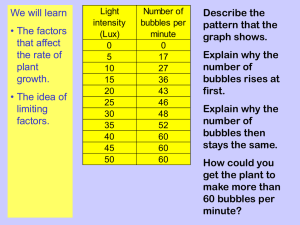
Lab Report: Photosynthesis Purpose of this Lab What is the goal of this lab? What question are you trying to answer, or what problem are you trying to explain? Exp 1 & Exp 2:In this experiment we will be investigating the effect of sunlight on the rate of photosynthesis. Exp 3: To prove that light is needed for photosynthesis Exp 4: To investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis Hypothesis After reading the lab instructions (but before starting the lab) record your best educated guess about what will happen in the experiment. Explain what lead you to this hypothesis. Exp 1 & Exp 2: If sunlight is present then there is a higher rate of photosynthesis Exp 3: If sunlight is prevented from reaching a part of the leaf then photosynthesis will not occur in that region Exp 4: If temperature increases then the rate of photosynthesis also increases. Experimental Design List the materials used in this lab, and a brief explanation of the procedures you followed. (You do not need to retype the procedure; simply summarize your procedures). Add #’s where necessary. Materials:Hydrilla, water with carbon dioxide added to it, beaker, pH meter, conical flask, testube, source of flame, splint 1. Measure out 30ml of water and carbon dioxide mixture into the beaker 2. Measure and record pH of the water 3. Submerge the hydrilla plant in the beaker 4. Place an upside down conical flask to seal the hydrilla and place an inverted testube over it's mouth to complete the seal, the testube will also be used to collect the oxygen produced 5. Measure the pH of the water every hour for five hours and record the results 6. At the completion of 5 hours remove testube frome over conical flask and place a lighted splint inside, simultaneously start the stop watch and measure how long it takes for the glow to die out completely 7. Repeat experiment in the absence of light Note: to ensure that you are conducting a fair experiment make sure that temperature and light intensity remain constant through out the course of the experiment Materials:Leaf, water, bunsen burner, beaker, tongs, ethanol, dropper, iodine solution 1. Boil Water on bunsen burner 2. Place leaf in boiling water to soften it 3. Warm ethanol in water bath 4. Dip leaf in ethanol to decolorize it 5. Using a dropper, drop a few drops of iodine solution on the leaf 6. Record any color change Data Experiment 1 Data and Observations Step 4 Record the initial pH value of the water in the beaker: 5.7 Step 8 Record the pH value of the water in the beaker at: 1:00 pm: 2:00 pm: 3:00 pm: 4:00 pm: 5:00 pm: 5.9 6.1 6.3 6.5 6.6 Step 12 Record the behavior of the glowing splinter after it’s placed in the test tube: The Glowing splint bursts into flame Record the duration of the burn: 9s Experiment 2 Data and Observations Step 3 Record the initial pH value of the water in the beaker: 5.7 Step 7 Record the pH value of the water in the beaker at: 8:00 am: 9:00 am: 10:00 am: 11:00 am: 12:00 pm: 5.5 5.3 5.1 4.9 4.7 Step 11 Record the behavior of the glowing splinter after it’s placed in the test tube: The splints glow died out Record the duration of the burn: 1s Experiment 3 Data and Observations Step 3 Record your observations of the leaf after being removed from the boiling water and being dipped in ethanol: The leaf had been softened and decolorized, the enzymes in the leaf have also been denaturized preventing any further photosynthesis from occurring and thereby changing the results What was accomplished by boiling the leaf in ethanol? This allowed any change in color caused by the iodine solution would show clearly Step 5 Record your observations of the leaf after staining it with iodine: The section on the leaf that was not covered by the foil turned blue, while the section that had been covered by the foil remained colorless What does this test indicate about the two sections of the leaf? In other words, what is present in most of the leaf that is absent in the area which was foil covered? Starch was present in the part of the leaf that remained uncovered. Starch wasn't produced in the covered section because of photosynthesis not taking place due to lack of sunlight Experiment 4 Data and Observations Step 3 Record the initial pH value of the water in the beaker: 5.7 Step 7 Record the pH value of the water in the beaker at: 8:00 am: 9:00 am: 10:00 am: 11:00 am: 12:00 pm: Steps 8, 11, and 15 (multiple trials) Hot plate temperature 1pm pH value 2 pm pH value 3 pm pH value 4 pm pH value 5 pm pH value Observations of splinter in test tube Duration of burn 5.7 5.7 5.7 5.7 5.7 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 3 25 degrees 28 degrees 31 degrees 34 degrees 6.0 6.3 6.5 6.8 7.1 6.0 6.3 6.5 6.8 7.1 6.0 6.4 6.7 7.1 7.4 6.0 6.3 6..5 6.8 7.1 Bursts into flame Bursts into flame Bursts into flame Bursts into flame 7.00s 7.00s 8.50s 7.00s Conclusion After conducting the experiment, how would you now explain the problem(s) or answer the question(s) raised when you described the purpose of the lab? Be sure to base your answer on the data you collected. Consider whether your conclusion is the only explanation for the data you collected or if there could be alternate explanations. the conclusion to exp 1 and 2: In conclusion photosynthesis occurs in the presence of sunlight or light. The plant takes up carbon dioxide which was dissolved in the water, thereby increasing the pH. In the absence of sunlight there was no photosynthesis occurring, however the plant continued to respire, producing carbon dioxide. This carbon dioxide dissolved in the water, further decreasing the PH. In conclusion to exp 3, the part of the leaf that was covered by the foil, did not receive any sunlight and therefore did not photosynthesize. Because photosynthesis did not take place, glucose was not produced in that region, so there was no starch formed This was indicated by no iodine staining taking place in that region, Thus proving photosynthesis does not occur in the absence of light. In conclusion to exp 4, increasing temperature caused an increase in the rate of photosynthesis, until 31 degrees, which was the optimum temperature, after which the rate of increase decreased I due to the denaturing of enzymes. Recall the discussion of the characteristics of life at the beginning of the class. What characteristic of life does this lab deal with? Mentabolism Think About It What is your familiarity with the terms infrared and ultraviolet? What uses and/or risks do they pose to humans? Infrared: (of electromagnetic radiation) having a wavelength just greater than that of the red end of the visible light spectrum but less than that of microwaves. Infrared radiation has a wavelength from about 800 nm to 1 mm, and is emitted particularly by heated objects. Ultraviolet: (of electromagnetic radiation) having a wavelength shorter than that of the violet end of the visible spectrum but longer than that of X-rays.