Unit 1 - Cloudfront.net
advertisement
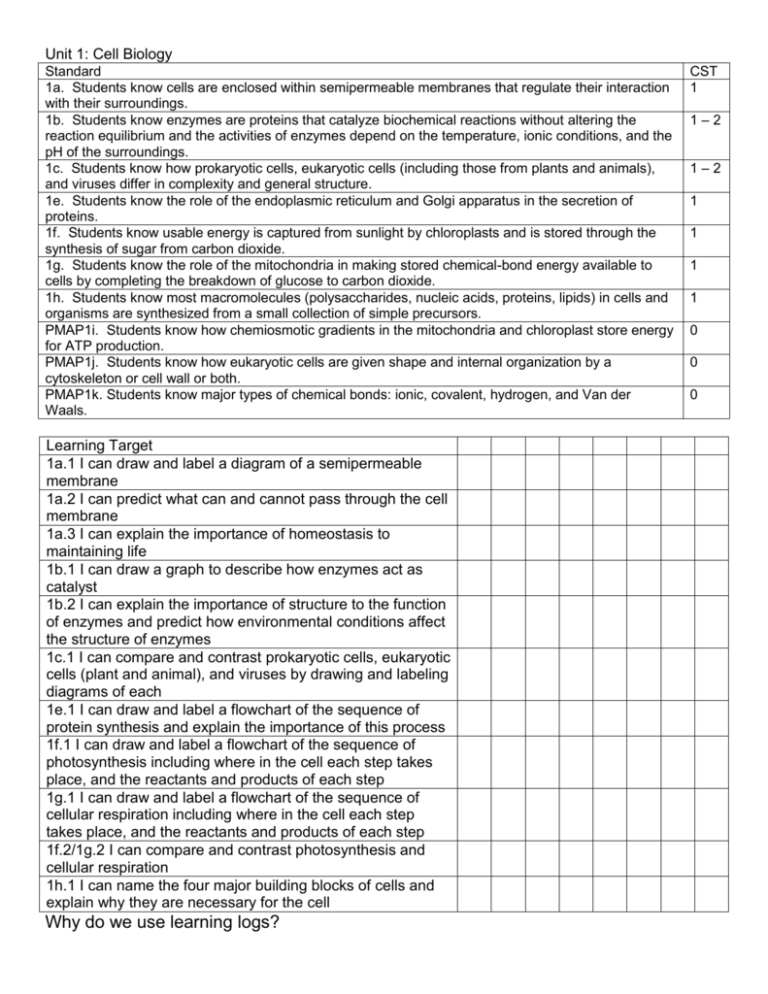
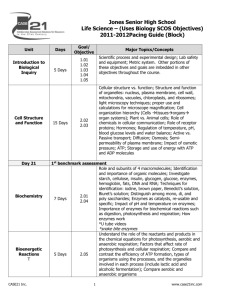
Unit 1: Cell Biology Standard 1a. Students know cells are enclosed within semipermeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. 1b. Students know enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium and the activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic conditions, and the pH of the surroundings. 1c. Students know how prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), and viruses differ in complexity and general structure. 1e. Students know the role of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the secretion of proteins. 1f. Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar from carbon dioxide. 1g. Students know the role of the mitochondria in making stored chemical-bond energy available to cells by completing the breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide. 1h. Students know most macromolecules (polysaccharides, nucleic acids, proteins, lipids) in cells and organisms are synthesized from a small collection of simple precursors. PMAP1i. Students know how chemiosmotic gradients in the mitochondria and chloroplast store energy for ATP production. PMAP1j. Students know how eukaryotic cells are given shape and internal organization by a cytoskeleton or cell wall or both. PMAP1k. Students know major types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, hydrogen, and Van der Waals. Learning Target 1a.1 I can draw and label a diagram of a semipermeable membrane 1a.2 I can predict what can and cannot pass through the cell membrane 1a.3 I can explain the importance of homeostasis to maintaining life 1b.1 I can draw a graph to describe how enzymes act as catalyst 1b.2 I can explain the importance of structure to the function of enzymes and predict how environmental conditions affect the structure of enzymes 1c.1 I can compare and contrast prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (plant and animal), and viruses by drawing and labeling diagrams of each 1e.1 I can draw and label a flowchart of the sequence of protein synthesis and explain the importance of this process 1f.1 I can draw and label a flowchart of the sequence of photosynthesis including where in the cell each step takes place, and the reactants and products of each step 1g.1 I can draw and label a flowchart of the sequence of cellular respiration including where in the cell each step takes place, and the reactants and products of each step 1f.2/1g.2 I can compare and contrast photosynthesis and cellular respiration 1h.1 I can name the four major building blocks of cells and explain why they are necessary for the cell Why do we use learning logs? CST 1 1–2 1–2 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 Learning logs help you to track your own progress throughout the unit. You will be able to identify what topics you really understand and what topics you need to work on. Do now questions, class work, quizzes, exit slips, etc. all tell you how well you understand the material. You should think about how you have been doing with those when you fill out your learning log. Each unit has 3 – 6 standards (these come from the state of California). Mr. Beckerman breaks down the standards by creating learning targets, which are written on the front of this learning log. The scores that you write in your learning log do not affect your grade, so be honest! Don’t be afraid to give yourself a 0 or a 1 if you really don’t understand something. Being honest on your learning log will help Mr. Beckerman see that you need help on that topic and it will help you to see what topics you need to study. How do I use my learning log? 1. Put today’s date at the top of the column. 2. Carefully read the learning target. 3. Give yourself a score from 0 – 4 in the box to the right of the learning target (make sure to use the box under the date you are scoring yourself). a. 0 means “I have no idea what this is even talking about.” b. 1 means “If somebody asked me about this, I would have to guess.” c. 2 means “I could probably answer a very easy question about this, but I don’t think I could do more than that.” d. 3 means “I almost get it, but there are a few questions I still have about this. I think I can correctly answer questions about this, but I might not always be able to explain my answer.” e. 4 means “I am so confident about this learning target that I could teach it to someone else” 4. Do not give yourself a score on learning targets that we have not covered yet. 5. Every time we fill out learning logs, give yourself a score on all learning targets we have covered. a. On the first day of the unit, you will give yourself a score from 0 – 4 on the first learning target. b. On the second day of the unit, you will give yourself another score from 0 – 4 on the first learning target and a score on the second learning target. By the end of the unit, you will have given yourself multiple scores on some learning targets. That’s good! This will let you see your progress. Maybe on the first day we learned something you were at a 2.5, then after the next class you understood it better and got to a 3.5, and after the review session before the test you completely understand the material and you got to a 4. You are ready for the test now! Day 1: Characteristics of life -> 1h (macromolecules) all living tings are made of cells, this is what cells are made of Day 2: -> 1a (membrane + homeostasis) cells need a special environment to live, membrane maintains those conditions Day 3 (50 min): -> 1b (enzymes) those conditions are so important because it lets cells do the reactions they need with enzymes Day 4 -> 1c (cell types + parts) different reactions + functions happen in different places in the cell Day 5 -> 1e (ER + golgi) making proteins keeps the cell alive because it keeps those reactions going + the structure of the cell Quiz! Day 6 (50 min) -> 1f (photosynthesis) all of those reactions require energy, which comes originally from the sun + photosynthesis Day 7 -> lab! Day 8 -> 1g (cellular respiration) energy must be converted to ATP to be used by the cell via cellular respiration Day 9 -> test











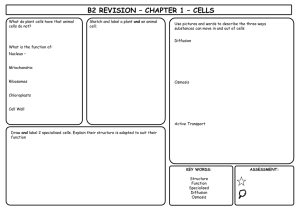
![Biology B2 revision sheet colour[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006699123_1-118546e1cf2edc78c83e680e8a2fb59f-300x300.png)