Earth Science Semester 1 Exam Study Guide S6E5a. Compare and
advertisement
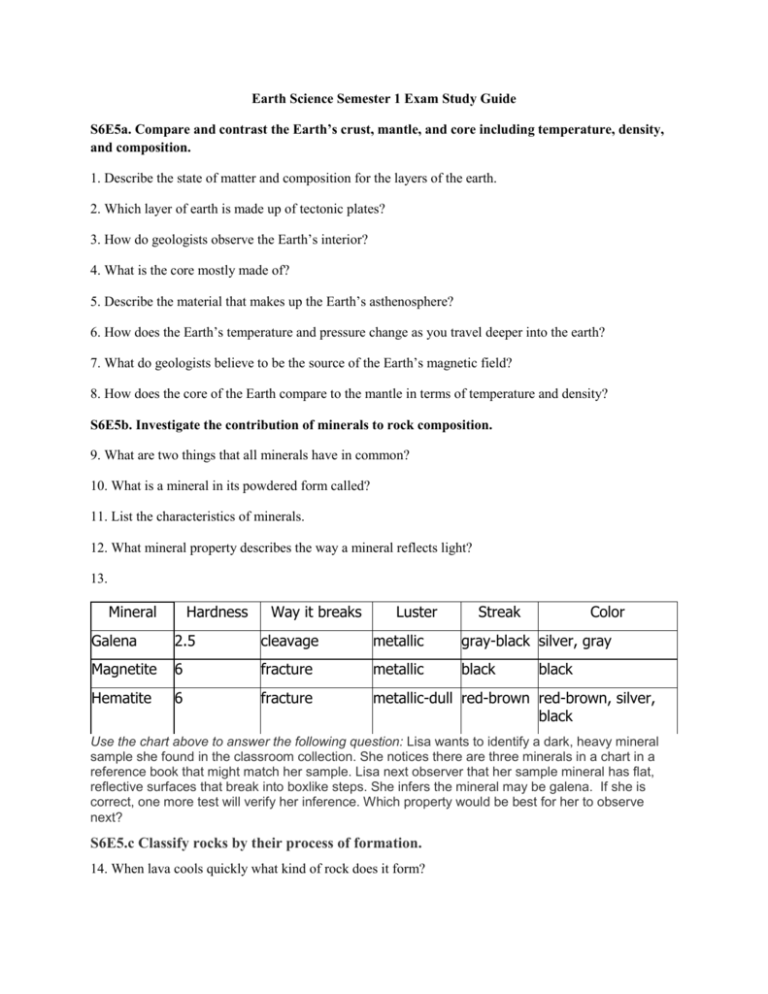
Earth Science Semester 1 Exam Study Guide S6E5a. Compare and contrast the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. 1. Describe the state of matter and composition for the layers of the earth. 2. Which layer of earth is made up of tectonic plates? 3. How do geologists observe the Earth’s interior? 4. What is the core mostly made of? 5. Describe the material that makes up the Earth’s asthenosphere? 6. How does the Earth’s temperature and pressure change as you travel deeper into the earth? 7. What do geologists believe to be the source of the Earth’s magnetic field? 8. How does the core of the Earth compare to the mantle in terms of temperature and density? S6E5b. Investigate the contribution of minerals to rock composition. 9. What are two things that all minerals have in common? 10. What is a mineral in its powdered form called? 11. List the characteristics of minerals. 12. What mineral property describes the way a mineral reflects light? 13. Mineral Hardness Way it breaks Luster Streak Color Galena 2.5 cleavage metallic gray-black silver, gray Magnetite 6 fracture metallic black Hematite 6 fracture metallic-dull red-brown red-brown, silver, black black Use the chart above to answer the following question: Lisa wants to identify a dark, heavy mineral sample she found in the classroom collection. She notices there are three minerals in a chart in a reference book that might match her sample. Lisa next observer that her sample mineral has flat, reflective surfaces that break into boxlike steps. She infers the mineral may be galena. If she is correct, one more test will verify her inference. Which property would be best for her to observe next? S6E5.c Classify rocks by their process of formation. 14. When lava cools quickly what kind of rock does it form? 15. What is the order of events in the formation of sedimentary rocks? 16. What characteristic is common to metamorphic rocks? 17. What characteristic is found in sedimentary rock? 18. Why do some igneous rocks have holes? 19. What type of rock is tan in color, fine-grained, and contains fossils? S6E5.f Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). 20. Which layer(s) of the Earth is a combination of the crust and the upper mantle? 21. Why was Alfred Wegener’s idea of continental drift rejected? 22. What is the process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle? 23. Where are the results of the plate movement seen at? 24. What is the main reason that the continents look very different than they did 100 million years ago? 25. What causes the movement of the Earth’s tectonic plates? 26. What is not used as evidence to support the theory of continental drift? 27. What are U-shaped valleys formed by? 28. What causes sediment and rock to move to lower elevations through time? S6E5.h Describe soil as consisting of weathered rocks and decomposed organic material. 29. What does organic matter break down into? 30. What is humus? 31. How does soil receive the nutrients that it gets to be healthy soil? 32. Al wants to determine in which horizon an unknown type of soil is found. He finds out through testing that it is dark and contains a lot of decomposed organic matter. He determines that this kind of soil is found in _________________________________ 33. How are minerals carried from the A horizon to the B horizon? S6E6. Students will describe various sources of energy and their uses and conservation. 34. When people practice conservation, they _____________________________________. 35. What can be burned to produce biomass? 36. List the energy resources that are used as alternatives to or instead of fossil fuels. 37. Places where magma is close to the Earth’s surface may be suitable for generating what? 38. I am used mainly in the western US. My energy comes from the heat within the Earth. I can be used for home heating. Water that is piped down to me is turned into steam to turn turbines and generate energy. What am I? S6E6.b Identify renewable and nonrenewable resources. 39. A resource that after being used can be replaced in a short amount of time is said to be what?