Feudal Advancements

Western Culture in Post-Classical Era
Christianity dominates philosophy and art, which causes conflict and change
Popular Religion
In early medieval times, people don’t necessarily understand the correlation between their actions and their religion
Over time, the ways in which people can express their faith increase
Ordinary people blend Christianity with their local culture
Religious Themes in Art and Literature
Western Europe is very extensive in religious art (crucifixion and nativity scene)
Artists paint on wooden panels
Artwork produced on key religious figures
(Christ, Mary, various St.s)
Architectural schemes change from
Romanesque to Gothic
Gothic architecture consists of taller windows, and church spires that point toward the heavens
Medieval music and literature reflects strong religious interest (hymns and poems)
Religious texts still written in Latin, but everyday music/literature/conversations are in vernacular
Changing Economic and Social Forms in Post-
Classical Centuries
Under manorial system, most regions produce for local consumption
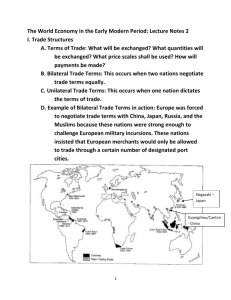
Italian merchants trade for cloth from
Netherlands and Belgium, England trades timber for Scandinavian furs
Strains on Rural Life:
Agriculture increases, and peasants escape manorialism in order to improve their own economic situations, lords end up taxing the lower
classes these conflicts remain until the 19 th century religion prompts egalitarian sentiment among lower classes, which doesn’t necessarily make those in power happy
Growth of Trade and Banking
as agriculture increases, many people are able to specialize skilled workers produce goods that they trade
banking system is brought to Europe to help facilitate long-distance trade
wealthy merchants invest in ships and goods in hope that a profit is earned
Christian thinkers, such as Thomas Aquinas, oppose profit-making sell at a “just” price
Western Europeans trade luxurious goods
(silk, spices) used for preservation of meat, and medicine
North Germany and Southern Scandanavia join together in the Hasneatic League to encourage trade
Merchants are less accepted in Europe than they are in India and China
Aside from taxation and from loans, the royal government lets merchants conduct their own business little interference
In ascending to a more powerful role in society, the merchant class creates their own law
Guilds- organizations of like-skilled workers
Their goals were security and quality, not necessarily maximization of profit
Guilds give their members a voice in society
Europeans are excellent clock-makers
In Italy and in Germany, workers are employed by capitalists who pay them based on production contradictory teachings in
Europe
After living in a city for 366 days, a serf can gain his freedom from the manor