American History II Unit 2 Map
advertisement
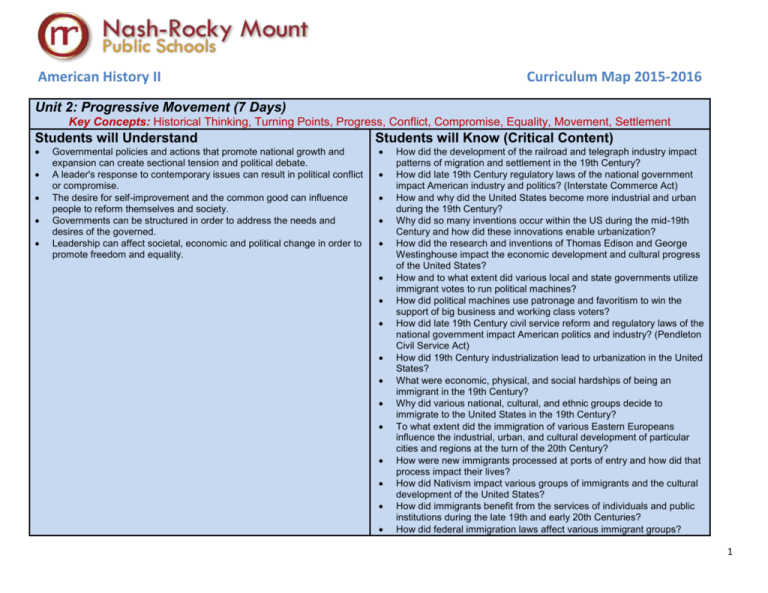
American History II Curriculum Map 2015-2016 Unit 2: Progressive Movement (7 Days) Key Concepts: Historical Thinking, Turning Points, Progress, Conflict, Compromise, Equality, Movement, Settlement Students will Understand Governmental policies and actions that promote national growth and expansion can create sectional tension and political debate. A leader's response to contemporary issues can result in political conflict or compromise. The desire for self-improvement and the common good can influence people to reform themselves and society. Governments can be structured in order to address the needs and desires of the governed. Leadership can affect societal, economic and political change in order to promote freedom and equality. Students will Know (Critical Content) How did the development of the railroad and telegraph industry impact patterns of migration and settlement in the 19th Century? How did late 19th Century regulatory laws of the national government impact American industry and politics? (Interstate Commerce Act) How and why did the United States become more industrial and urban during the 19th Century? Why did so many inventions occur within the US during the mid-19th Century and how did these innovations enable urbanization? How did the research and inventions of Thomas Edison and George Westinghouse impact the economic development and cultural progress of the United States? How and to what extent did various local and state governments utilize immigrant votes to run political machines? How did political machines use patronage and favoritism to win the support of big business and working class voters? How did late 19th Century civil service reform and regulatory laws of the national government impact American politics and industry? (Pendleton Civil Service Act) How did 19th Century industrialization lead to urbanization in the United States? What were economic, physical, and social hardships of being an immigrant in the 19th Century? Why did various national, cultural, and ethnic groups decide to immigrate to the United States in the 19th Century? To what extent did the immigration of various Eastern Europeans influence the industrial, urban, and cultural development of particular cities and regions at the turn of the 20th Century? How were new immigrants processed at ports of entry and how did that process impact their lives? How did Nativism impact various groups of immigrants and the cultural development of the United States? How did immigrants benefit from the services of individuals and public institutions during the late 19th and early 20th Centuries? How did federal immigration laws affect various immigrant groups? 1 American History II Curriculum Map 2015-2016 To what extent did rapid industrial development produce widespread poverty and poor working conditions in the United States? How did the immigration process at the beginning of the 20th Century and the work of various charitable individuals impact opportunity and mobility for new immigrants? How did late 19th Century regulatory laws of the national government impact American industry and politics? (Sherman Antitrust Act) How did Social Darwinism develop and how did intellectuals use it to justify the actions of industry and society at the turn of the century? How did Social Darwinism impact the development of American industry, government policies, and social customs during late 1800s? How did industrialists take risks during the late 1800s to develop and monopolize industries and how did their efforts impact the economic development and cultural progress of the United States? How did “Captains of Industry” defend their acquisition of wealth and power during the Gilded Age? To what extent did rapid industrial development produce widespread poverty and poor working conditions in the United States? How and why did labor unions form during the 19th Century and to what extent their leadership bred opposition and results? How and to what extent did various labor groups demonstrate and benefit from union tactics during the 19th Century? Essential Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. How can urbanization lead to political, economic and social reform? How can immigration lead to political, economic and social reform? How can the desire for power lead to corruption and an unbalanced distribution of wealth? Why do movements for political, economic, and social reform occur? Priority Standards Learning Outcomes (DO) AH2.H.1 Apply the four interconnected will be able to analyze the dimensions of historical thinking to the effects of the Social Gospel American History Essential Standards movement on urban in order to understand the creation and communities at the turn of the development of the United States over 20th Century time. I will be able to analyze the reasons for and effects of AH2.H.2 Analyze key political, the disenfranchisement and economic, and social turning points in segregation of AfricanAmerican History using historical Critical Content & Vocabulary by Strand Materials/Resources Progressive Era Students will read the excerpts of muckrakers, identify the social problem they are exposing, and the impact of the muckraker’s writings. Students will compare and contrast the beliefs of Booker T. Washington, WEB DuBois, and History Jane Addams Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) Wilmington race riot (1898) Great Migration Booker T. Washington Tuskegee Institute Atlanta Compromise Speech W.E.B. Du Bois 2 American History II Curriculum Map 2015-2016 thinking. AH2.H.3 Understand the factors that led to exploration, settlement, movement, and expansion and their impact on United States development over time. AH2.H.4 Analyze how conflict and compromise have shaped politics, economics, and culture in the U.S. AH2.H.5 Understand how tensions between freedom, equality, and power, have shaped the political, economic, and social development of the U.S. AH2.H.8 Analyze the relationship between progress, crisis and the "American Dream" within the U.S. American citizens. I will be able to compare and contrast the ideas of the civil rights leaders of the early 20th Century. I will be able to analyze the problems that led to, and effects of the Populist and Progressive movements at the turn of the 20th Century. Marcus Garvey and assess which person’s beliefs are more appropriate in dealing with the issues of segregation. Students will look at the actions of Roosevelt, Taft, and Wilson and judge which president in the most “progressive” based on the accomplishments of each president. Niagara Movement The NAACP Ida B. Well Robert LaFollette Carrie Nation Ida Tarbell Lincoln Steffens Upton Sinclair Jacob Riis Urban slums Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire Omaha Platform William Jennings Bryan “Cross of Gold” Speech Theodore Roosevelt Woodrow Wilson William Howard Taft Civics and Government Progressivism Democracy Capitalism Socialism Muckraking Civil rights Disenfranchisement Literacy test Poll taxes Grandfather clauses De jure segregation De facto segregation Jim Crow Laws Populism Greenbacks Munn v. Illinois (1877) Wabash v. Illinois (1886) Interstate Commerce Act Pendleton Act 3 American History II Curriculum Map 2015-2016 Sherman Antitrust Act U.S. v. E.C. Knight & Co. (1895) Anthracite Coal Strike Northern Securities v. U.S. (1904) Elkins Act Payne-Aldrich Tariff American Tobacco v. U.S. (1909) Mann Act (1911) Election of 1912 Progressive/Bull Moose Party Federal Reserve Act The Grange Economics Geography Culture Social Gospel Settlement houses Segregation Suffrage Social Gospel Gold standard Bimetallism 4