VOCABULARY asexual reproduction A type of reproduction
advertisement

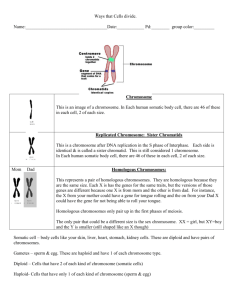
VOCABULARY asexual reproduction A type of reproduction involving only one parent that produces genetically identical offspring by budding or by the division of a single cell or the entire organism into two or more parts autosome A chromosome that is not directly involved in determining sex, as opposed to a sex chromosome binary fission The type of cell division by which prokaryotes reproduce. Each dividing daughter cell receives a copy of the single parental chromosome cancer cells Do not have a properly functioning cell-cycle system; instead, they divide excessively and can invade other tissues of the body cell cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a eukaryotic cell, from its origin in the division of a parent cell until its own division into two; composed of the M, G1, S, and G2 phases cell cycle control system A cyclically operating set of molecules in the cell that triggers and coordinates key events in the cell cycle crossing over The reciprocal exchange of genetic material between nonsister chromatids during synapsis of meiosis I cyclin A cellular protein that occurs in a cyclically fluctuating concentration and that plays an important role in regulating the cell cycle. cyclin dependent kinases A protein kinase that is active only when attached to a particular cyclin diploid cell A cell containing two sets of chromosomes (2n), one set inherited from each parent G0 A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle. G1 The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins. G2 The second gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs. genetic recombination The general term for the production of offspring with new combinations of traits inherited from the two parents genome The complete complement of an organism's genes; an organism's genetic material growth factor A protein that must be present in the extracellular environment (culture medium or animal body) for the growth and normal development of certain types of cells haploid cell A cell containing only one set of chromosomes (n) homologous chromosomes Chromosome pairs of the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern that possess genes for the same characters at corresponding loci. One homologous chromosome is inherited from the organism's father, the other from the mother. Also called homologues or homologous pair. independent assortment A general rule in inheritance that when gametes form during meiosis, each pair of alleles for a particular characteristic segregate independently; also known as Mendel's second law of inheritance kinetochore A structure of proteins attached to the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle. maturation promoting factor (MPF) Maturation-promoting factor (M-phasepromoting factor); a protein complex required for a cell to progress from late interphase to mitosis. The active form consists of cyclin and a protein kinase. meiosis A two-stage type of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that results in cells with half the chromosome number of the original cell mitosis A process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells conventionally divided into four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis conserves chromosome number by equally allocating replicated chromosomes to each of the daughter nuclei mitotic phase The phase of the cell cycle that includes mitosis and cytokinesis mitotic spindle An assemblage of microtubules and associated proteins that is involved in the movements of chromosomes during mitosis nondisjunction An accident of meiosis or mitosis, in which the members of a pair of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to move apart properly S phase The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated. sex chromosomes One of the pair of chromosomes responsible for determining the sex of an individual sexual reproduction A type of reproduction in which two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the gametes of the two parents sister chromatids Replicated forms of a chromosome joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis or meiosis II somatic cell Any cell in a multicellular organism except a sperm or egg cell zygote The diploid product of the union of haploid gametes in conception; a fertilized egg