06 EL STORE Lab - CA Climate Change
advertisement

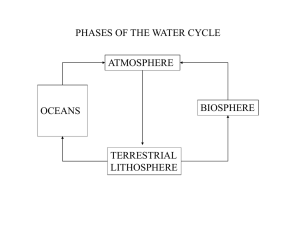
AP Environmental Science Name: Period: SRI STORE Project Day 2 – Not In My Back Yard (How Will Climate Change Affect Northern California) Directions: Using Google Earth and the STORE data set, you will be asked to evaluate the climate change impact to California between now and 2050. Purpose: • Learn how GIS (Graphical Information Systems) tools (Google Earth) collect and display temperature, precipitation and vegetation data • Learn about climate change models • Use GIS databases to study climate pattern changes in California • Gather current and projected data about temperature and rainfall changes in California • Analyze the impact of projected climate change on various types of vegetation in California Background Information about Our Computer Simulation Geographical Information Systems (GIS) such as ArcGIS or Google Earth allow scientists and students to display sets of different data such as rainfall, temperature and plant populations in one map format. In this lab activity, you will incorporate layers of data onto a map of the California Study Area, a region stretching from San Jose eastward to the Sierra foothills. The map format allows you to easily visualize the relationship between temperature, rainfall and vegetation types. Our data about current vegetation types and their locations is collected by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). Current average temperature and precipitation data is collected by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and National Climate Data Center (NCDC). These data can be layered onto our map of the California Study Area and you can see how vegetation types vary by region. We can study eight different vegetation types whose current tolerance for altitude, rainfall and temperature are shown below: Tolerance Ranges for Various California Vegetation Types Vegetation Type Annual Precipitation (rain and snow fall) (in/yr) July Daily High Temperature ( oF ) W inter Low Temperature ( oF) Elevation (ft) Crops 5-30 80-100 32-40 0-1500 Deciduous Forest 20-40 90-100 25-40 100-2800 Evergreen Forest 20-70 60-100 0-50 100-7500 Mixed Forest 12-50 80-100 32-50 100-1700 Grassland 5-100 60-100 15-50 100-3300 Shrub 12-100 80-100 15-40 100-3300 Herbaceous Wetland 5-30 70-80 32-50 0-2700 Wooded Wetland 5-20 90-100 32-50 0-1900 However, in order to predict how vegetation patterns will be affected by climate change, we will need information about temperature and rainfall patterns in the future. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an international scientific organization that has produced several scenarios about climate change, and our lab activity uses one of the more severe of those scenarios (IPCC A2). In the U.S, the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Community Climate Change Model (CCSM) uses the IPCC-A2 scenario to make predictions about how climate change affects local temperature and rainfall patterns. This activity involves using current and projected rainfall and temperature data to analyze the impact of climate change in our local California Study Area. Using Google Earth as well as the classroom reference sheets, begin filling in your data on the tables provided. Analysis of Precipitation Patterns 1. Compare the change in precipitation among the 5 weather stations. Is there a trend or is the result variable? Cite specific data as evidence to support your conclusion. (2 Points) 2. Will the predominant vegetation surrounding each weather station remain similar from now to the year 2050? Use specific data as evidence to support your conclusion. (2 Points) 3. Examine the Sierra Nevada regions near the Sonora and Twin Lakes weather stations. What do you think will happen to the snow pack and reservoirs in these regions by the year 2050? What impact will this have on California’s water supply? Use specific data as evidence to support your conclusion. (2 Points) Data Table 2: Temperature Data Collection and Assessment Refer to the instruction sheet at your lab station for tips to find and access the necessary data. Find the relevant data and fill in the information in your data table. (2 Points) Analysis of Temperature Data 1. Evaluate the projected change in January and July temperatures between now and 2050 among the 5 weather stations. Is the change in July consistent? Give numerical evidence to support your conclusion. (3 Points) 2. Making an assumption that the range of tolerance for each vegetation type does not change between now and the year 2050, evaluate how the projected temperature changes will affect vegetation in each region. Discuss and describe which regions will have vegetation changes, and give numerical evidence to support your conclusions. (2 Points) 3. Of course, organisms do adapt to changes in environment through their ability to migrate to more suitable regions and via the process of natural selection. In this case: a. Describe the process by which plants “migrate” to other regions. Do you think there will be enough time for vegetation to migrate to a more suitable climate while climate change is occurring? (2 Points) b. When considering traits of “r” and “k” selected organisms as studied earlier in the year, describe specific organism traits will be selected for if climate is changing at a rapid pace? (2 Points) c. Briefly describe how selection pressure changes the vegetation’s gene pool. How does an organisms “range of tolerance” play a part in this. What type of selection would you predict to play a major role in organisms adapting to climate change in the California Study Areas? Explain your answer. Refer to the diagram at the right showing different types of natural selection (Disruptive, Stabilizing & Directional). (2 Points) 4. Do you think there will be enough time to allow for adaptation to the changed climate? Cite specific evidence and data to support your conclusion. (2 Points) 5. Based upon the expected change in vegetation, describe the impact to food webs in habitats near each of the 5 weather stations. Give specific examples to support your conclusion. (2 Points) Analyze Regional Variability 1. Was the impact of precipitation and temperature change consistent from one weather station to another? Cite specific evidence from each station to support your conclusion. (2 Points) 2. How are crops different than other vegetation types? Thinking about advances in biotechnology, specifically that of GMO’s (Genetically Modified Organisms) and irrigation (drip irrigation), how might the expected scenarios for 2050 values not account for the reality of how crops will be affected? (2 Points) 3. Now, look at the reference sheets showing world maps and global predictions for sea level, precipitation and temperature changes under the IPCC A2 scenario. What part or parts of the world shows the greatest impact? Will very many people notice this change? What challenge will Europe face with both increased temperature and less rainfall? What will the impact be in Asia? (2 Points) 4. Based upon the variability in impact of climate change, would citizens of each region agree on the importance of trying to minimize climate change? Explain and justify your conclusion. Use specific countries in your justification. (2 Points) SRI STORE Project Day 2 – Not In My Backyard (How Will Climate Change Affect Northern California) Weather Station Data & Calculation Table 1: Precipitation Data Collection and Assessment (2 Points) Refer to the instruction sheet at your lab station for tips to find and access the necessary data. Find the relevant data and fill in the information in your data table. T win Lakes Sonora Modesto Mount Hamilton San Jose Data Location 3 Predominant Vegetation Type(s) Vegetation Precipitation Tolerance Range (in/yr) Current Annual 2050 Precipitation Precipitation Precipitation Difference (in/yr) (in/yr) (in/year) (AnnPrecip) Google Earth Data Layer STORE Activity #2 Google Earth Weather Station Google Earth Data Layer Calculation Percent Change in Precipitation (%) Calculation Is 2050 Precipitation Within Vegetation Tolerance range? Student Inference SRI STORE Project Day 2 – Not In My Backyard (How Will Climate Change Affect Northern California Weather Station Data & Calculation Table 2: Temperature Data Collection and Assessment (2 Points) Refer to the instruction sheet at your lab station for tips to find and access the necessary data. Find the relevant data and fill in the information in your data table. Vegetation Vegetation 3 Temperature Temperature Current Jan. Predominant Tolerance Tolerance A vg. Low Vegetation Range Range July Temp ( oF) Type(s) o o January ( F ) ( F) T win Lakes Sonora Modesto Mount Hamilton San Jose Google Earth Data STORE Activity Data Layer #2 Location STORE Activity #2 2050 January A vg. Daily Low Temp ( oF) Current July A vg. Daily High Temp ( oF) 2050 July Avg. Daily High Temp ( oF) Google Earth Google Earth Data Google Earth Google Earth Data Weather Station Layer Weather Station Layer January Difference ( oF) Calculation Is 2050 Is 2050 July July January Temp Within Difference Temp Within the tolerance the tolerance ( oF) range? range? Calculation Student Inference Student Inference