Name: Period: _____ Oceanography Exam III: Chemical and
advertisement

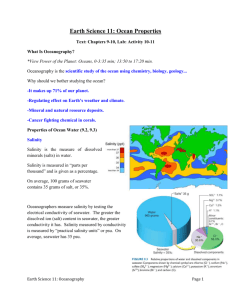
Name: _______________ Period: _____ Oceanography Exam III: Chemical and Physical Oceanography This exam will cover the material that has been covered in class since the last exam. The items below are a summary of what has been taught but labs, videos, homework assignments and notes from lecture are your most complete sources of information. Use them to answer the questions on this study guide. This guide will be due on the day of the exam as a homework assignment You may use a page of notes on this test (8 ½” X 11” - front side only) Your test will be on Tuesday 11/24 for 1th period and Wednesday 11/25 for 2th period. Chemical Oceanography: Chemistry of seawater Why is chemical oceanography the most interdisciplinary of the branches of oceanography? What does a chemical oceanographer study and what tools do they use to accomplish this? Since the most common molecule in the ocean is water, what are its unique properties? Review the following terms: hydrogen bonding, cohesion, adhesion, surface tension, solubility. What are the unique thermal properties of water? How does this influence earths heat budget? What is the marine effect? What is the continental effect? How does these relate to the ocean? How do temperature, salinity and pressure affect the density of water? What is a pycnocline, a halocline and a thermocline? How does the ocean stratify by density in the Tropical region? Temperate region? Polar region? What is normal ocean salinity? ppt (o/oo) Is all the “salt” in the ocean NaCl? Why does it vary? Physical Oceanography: Air-sea interactions, waves, currents, tides, shoreline dynamics How does the physics of water affect sound and light travel in the ocean? Why does it matter? What is sonar and how do oceanographers use it to study the ocean? What relationship exists between the climate, weather and the ocean? Patterns? What causes uneven solar heating on earth and how does this affect the atmosphere and ocean? What are atmospheric Circulation cells? What are the largest cells? (be able to draw/label them) What is a Walker cell? Where are they found? How does atmospheric circulation cells relate to convection cells in the mantle and thermohaline circulation in the ocean? What are the global wind patterns? Trade winds? Easterlies and Westerlies? ITCZ? What is the Coriolis Effect and what influence does it have on wind, currents, and storms? Northern vs. Southern hemisphere? What are the main surface circulation currents in each ocean? What is the great ocean “conveyer belt” model of ocean currents? What is a deep sea current? What causes upwelling and downwelling? Why does this matter? What causes waves? How do they change in the surf zone along the coast? Label a wave: wave height, wavelength, crest, and trough. What is a tide? What causes them? Why do they vary? What is the difference between a spring tide and a neap tide?