4.1 Notes Follow Up
advertisement

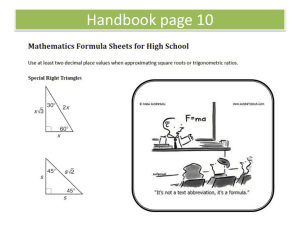
4.1 Triangles Notes Follow Up Honors Geometry Name: ________________________________ The Triangle Sum Theorem states the following: The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. Complete the following proof of the Triangle Sum Theorem below. Begin the proof by sketching a line passing through D and parallel to AC . (p.219) Given: # ABC Prove: m1 m2 m3 180 PLAN FOR PROOF: a. Draw an auxillary line through B and parallel to ̅̅̅̅ 𝑨𝑪 b. Show that m∠𝟒 + m∠𝟐 + m∠𝟓 = 180°, ∠𝟏 ≅ ∠𝟒, and ∠𝟑 ≅ ∠𝟓 c. By substitution, 𝐦∠𝟏 + 𝐦∠𝟐 + 𝐦∠𝟓𝟑 = 𝟏𝟖𝟎 STATEMENTS REASONS 1. What is a Polygon? What is a triangle? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is an auxiliary line and how was it used in the first proof? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ The Exterior Angle Theorem states the following: The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles. Complete the following proof of the Exterior Angle Theorem below. In the figure, 4 is the exterior angles and 1 & 2 are the nonadjacent interior angles. Given: # ABC Prove: m1 m2 m4 STATEMENTS REASONS 1. ∆ABC 1. Given 2. 2. Triangle Sum Theorem 3. ∠3 and∠4 are supp 3. 4. m∠3 + m∠4 = 180° 4. 5. 5. Substitution 6. m∠1 + m∠2 = m∠4 6. Subtraction 3. How many different exterior angles does every triangle have? __________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is a corollary to a theorem? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 2 Corollary to the Triangle Sum Theorem states ____________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Prove the Corollary to the Triangle Sum Theorem below. Given: # ABC Prove: mB mC 90 STATEMENTS REASONS 1. ∆ABC 1. Given BASIC TRIANGLE REVIEW 5. Triangles can be classified by side and by angle. Describe the different classifications by side. Include a sketch of each classification. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 3 6. Describe the different classifications by angle. Include a sketch of each classification. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 7. Explain why an obtuse triangle cannot have two obtuse angles. ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. An isosceles triangle is defined as a triangle with at least two congruent sides. What does this imply about an equilateral triangle? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 4