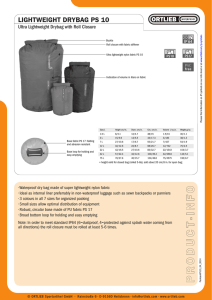
Fabric Fault Corrective Action Corrective Recipe
advertisement

Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad 8. Q.A.D: The full abbreviation of Q.A.D. is Quality Assurance Department which is needed for the purpose of checking the quality of the fabric. Quality is mainly checked for ensuring that the fabric is suitable to meet all the requirements according to the customer’s specified order. The quality can be classified by four types which are discussed below: 1. Product based quality: Product based definition of quality mainly depends on the quality. Product based quality is more related to manufacture. More the number of units in specified time more is product based quality. From the user point of view more number of units in a specific cost is called product based quality. 2. User based quality: The user based quality simply means the quality, whatever the customer says or wants. In short, meeting or exceeding customer’s requirement and expectations. 3. Manufacturing based quality: The definition of this quality means, meeting specifications or conformance to requirements. It is nothing but manufacturing based quality. Any deviation from meeting the requirements means poor quality. 4. Value based quality: In this type of quality, there is more consideration of cost of a product or service. 149 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 8.1. Organogram of Quality Assurance Department: Quality Control Manager Sample Incharge Senior Quality Control Inspector Quality Inspector Quality Control Inspector Sample Chaser Quality Control Trainee Sample Helper 8.1.1. Inspection Process: Inspection of the fabric is done by the quality inspectors intended for ensuring proper quality of the fabric at various sections of the dyeing, Knitting and finishing section. The System which is used by the ECHOTEX textile industry is 4Point inspection system. The inspection process of ECHOTEX textile industry is discussed below: 8.1.2. 4-Points system: The 4-points system are called American Apparel Manufacturers Association (AAMA) Point grading system for determining fabric quality is widely used by the department of defense in the united state and endorsed by the AAMA as well as the ASQC (American Society of Quality Control) In this system fabric faults are identified with defect point in the scale of i.e. maximum defect point is 4. 150 Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad 8.1.3. Pointing System for Fabric faults: The faults are pointed acceding to the size of the defect and the size of the hole in the knitted fabric. For fault pointing system according to the size of defect is as follows: Fabric defect size Penalty point Up to 3” 1 Points More than 3” but less than 6” 2 Points More than 6” but less than 9” 3 Points More than 9” 4 Points For fault pointing system according to holes and opening is as bellow: Size of hole Penalty points less than 1” 2 Points More than 1” 4 Points Knot (4 types) less than 3” 1 Points Slubs- less than 3” 1 Points Total defect points per 100 square yds are calculated and normally those fabric roll containing more than 40 points/100 yds are considered seconds however a garments manufacture based on the price line and type of garments produced may use more or less than 40 points / 100 yds as an acceptance criteria. For example, a fabric rolls 120 yds long and 48 in width contains the defect: Defects seen on the fabric sample A. 2 defects up to sample Defect points of every faults 2 1=2 points B. 5 defect over 3 in but less than 6 in. 5 2=10 points C. 1defect over 6in but less than 6 in 1 3=3 points D. 1 defects over 9 in. 1 4=4 points Total defects point =19 points Therefore, Total Points Scord in The Roll ×3600 Inch×Total Yards Inspected 19×3600 = 48×120 Points/100 yd2 = Fabric Width In = 11.9 defect points/ 100 yd2 So if the acceptance criteria are 40 points/100 yd2 then this roll is acceptable. The maximum number of defect points to be counted against any one linear yard is points. 151 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Overall fabric quality is assessed on the basis of the number of defect points per 100 yd2 of fabric. 8.2. General Rules for Inspection: Some general rules are followed for inspecting a fabric which should be maintained during inspecting a finished or grey fabric. During inspecting a fabric the rules which should be followed is given below: Only one meter of fabric cannot be penalized more than 4 points. Any defect occurring repeatedly throughout the entire fabric should be marked. Combination of warp and weft defect running in one meter should not be penalized more than 4 points in them. Fabric should always be inspected on face side only if it is not specified for back side inspection. 8.2.1. Points for various Types of Fabric Faults: The points are also different for different types of fault occurring in the fabric. During inspecting a fabric in the Quality Control section of the ECHOTEX Dyehouse the various common faults are pointed as below: Faults Points Any size Hole White Specks Oil Stain Chemical Spot Water Drop Fly Yarn Slub Rub Mark Rust Stain Yarn Contamination 4 points 1 points 1 points 1 points 1 points 1 points 1 points 1 points 1 points 1 points As the above given faults are commonly found in the Finishing and Knitting Section of the ECHOTEX Dyehouse, so these faults are regularly pointed but other than these type of faults of the fabric, the fabric should be sent to the higher authority or be rejected. 152 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 8.2.2. Inspection Machine: Fabric inspection is usually done on fabric inspection machine. These machines measures rolls of fabric by placing them over the inspection table under adequate light source and rerolled as they leave the table. The amount of fabric rolls passed on the inspection machine is measured by the metering roll on the machine. This inspection machine is either power driven or the inspector pulls the fabric over inspection table. The defect are tracked, marked and recorded on an inspection sheet. Such machine are also equipped with equipments to control the length of the fabric is delivered from the back and also monitor the back side of the fabric. The width of the fabric is most important for manufacture of basis garments. Inspecting light Metering roller Figure: QAD grey inspection machine. 153 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 8.3. ECHOTEX Final Inspection report: 50 60 70 80 90 100 Wa4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Penalty Point Legend H= Hole OS=Oil Stain CH=Chemical Spot WD=Water Drop FY=Fly Yarn WS=White specks S=Slubs R=Rub Mark RS=Rust Stain Yc=Yarn Contamination IS: Insect Spot Faulty Appearance Four Points System: US: Uneven shade,Np= Napes Cr= Crease mark, P=patches, G/H=GSM Hole, HR=Hairy, MS=Machine Stoppage, N/L=Needle line,BR= Barre Mark,CM=Crimple mark,BW=Bowing,DC=Dead Cotton, SN=Snagging/M=Line Mark,P/H=Pin hole Size of Defect Penalty 0-3" 1 Points 3-6” 2 Points 6-9” 3 Points Over 9 inch 4 Points Reject Qty: 40 M/C DIA XGG 30 Shift: 20 Yarn Lot: 10 Inspection By: Buyer:………….Batch:………………Shade:………………Style:……………..Date : Roll 1- 11- 21- 31- 41- 51- 61- 71- 81- 91- A/Dia A/GSM Pts/Mtr Class Checked By: Shade: Inspect: Dryer/Comp/Stenter Test Report: Inspection Time: Req.Width: Req. GSM: Grey Weight: Final Inspection Report Work Order: Acceptance Calculation Factor=Roll Yardage (A) =Total Point, Roll (B) Formula=B/A× 100 =Points/100 Yards < 40 PTSA 41-60 PTSB 61-80 PTSC 80 Above Reject 154 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 8.4. Grey Inspection report: M/C DiaX GG Finished GSM Finished Dia Grey GSM/ St.Length 1-10 1120 2130 3140 4150 5160 6170 7180 8190 91100 Pts/ Mtr Roll Wt. Cl as s Inspection Time: Grey Dia Faulty Appearance GSM Hole=GH, Lycra out=LY, Barre mark=BM ,Drop stitch=DS, Crease mark= CR, Sinker mark=SM, Yarn Conta=CY, Fly conta=FC, Slubs=S, Oil spots=OS, Press off=PO, Wrong design=WD, Oil line=OL, Uneven yarn=UY, Naps=N, Thick/Thin=T/T Four Point System Acceptable Calculation Size of defect Penalty Up to 40 point = A 0-3” >3-6” >6-9” >9” Hole <1” Hole <1” 1 Points 2 Points 3 Points 4 Points 2 Points 4 Points 41 to 60 point = B Remark: Inspection By: Total Qty: Formula Point = Total point ×100 Total length(in meter) 61 to 80 point = C Above Reject Qty: Checked By: Roll Insp = Rejected 155 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 8.5. Faults of fabric during Knitting: The ECHOTEX has a renowned inspection section where not only internally knitted fabric faults are detected but also the fabrics knitted in other industries are also inspected. In the inspection section there are various faults found of the knitted fabrics. Some of the faults found during knitting are discussed below: Hole. Lycra out. Lycra drop. Barre mark. Needle mark. Drop stitch. Crease mark. Sinker mark. Yarn contamination. Fly contamination. Slub. Oil spot. Press off. Wrong design. Oil line. Miss yarn. Uneven yarn. Naps. Thick and Thin. Needle broken. Loop. Stare. Yarn mixed. Patta. Color contamination. Wheel mark. Dirty yarn. 1. Hole: During yarn breakage from yarn passage from the wheel to the feeder if the joining of the yarn is done by normal binding process then hole could be produced in the fabric. Hole 156 Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Causes: Using old lubricant or knitting oil which has been oxidized. Longer needle latch holding time of the loop. Unwanted sharp objects in the knitting machine. If binding of broken yarn is not properly done. Using yarns having knots slubs etc. Using yarns having no moisture. Yarn running in too high tension. If the dial and cylinder does not work together Remedies: Check the lubricants used for oiling the knitting machine. Make sure all the loops are produced at a same speed. Check for any unwanted sharp objects in the machine. Using good quality yarn during knitting. Check the tension of the yarn passage. Check the speed of the running yarn. Check if cylinder and dial of knitting machine is working together. 2. Lycra out: If a yarn is torn during the passage of lycra yarn from the lycra stand to the feeder or if one of the yarns are missing during passage than lycra out occurs. The lycra out is normally a gap mark present throughout the fabric. Lycra Out Causes: If any lycra yarn is missed during knitting. If lycra yarn feeder arrangement is not proper. If lycra yarn tension is not proper. Remedies: Lycra yarn should be passed to the maintaining proper tension Broken ends of the lycra yarn should be immediately fixed. Proper cleaning of the lycra knitting machine should be done. 157 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 3. Color contamination: After the production of the fabric if there is presence of another colored yarn then this fault is known as color contamination. Color Contamination Causes: It consists of single fibre, bunch of fibre or yarn pieces in varying colors. Presence of yarn during knitting having different color. Remedies: It is very difficult to remove. So need to be careful in process. Fly preventive cover can be used. Before knitting of new fabric the machine should be cleaned by applying air flow. 4. Miss yarn: If a yarn is missed by the needles during fabric loop formation then miss yarn is occurred. This miss tarn is normally caused if any yarn is not passed from the feeder while the yarn passage. Miss Yarn Causes: If any yarn is missed during knitting. If yarn feeder arrangement is not proper. If yarn tension is not proper. Remedies: Yarn should be passed to the maintaining proper tension Broken ends of the yarn should be immediately fixed. Proper cleaning of the knitting machine should be done. 5. Wrong Design: If an unwanted design is occurred with the buyer specified design in the fabric then it is known as wrong design. Normally this fault is caused while knitting dyed yarns as a result if there is a cause of miss yarn or extra yarn supplied to the knitted fabric. 158 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Wrong Design Causes: If the number of feeders for any individual yarn is not proper. If the produced stripe is not occurred according to measurement. 6. Thick and Thin: When thick or thin place is found in the fabric design then this sort of fabric faults are normally known as thick and thin. Generally thick and thin occurs if there is a passage of yarn having uneven thickness. Thick Place Causes: Thick and thin places in the yarn. Fabric takes up too weak. Irregular present of slubs of yarn. Remedies: Controlling take-up speed in the knitting machine. Checking yarn before using for knitting. Checking thickness regularity of slubs yarn. 7. Fly contamination: During knitting if any dirt, dust or any foreign particles pass into the yarn or the fabric and the fabric is knitted with the fabric then that dirt or dust on the knitted fabric is called fly contamination. 8. Yarn mixture: If there is a presence of another yarn in the knitted fabric which is not identical to the yarns of the knitted fabric then it is called yarn mixture. This fault is normally seen while dyed yarn knitting or if a yarn dyed fabric is knitted previously on the knitting machine. 9. Slub: If any uneven yarn is used during knitting of the fabrics which has both thick and thin place in the yarn then the thick places found in the knitted fabric is called slub. 159 Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Slub yarn Causes: Usually caused by a thick or heavy place in yarn or by ling getting onto yarn feeds. Remedies By using good yarn quality. Checking the supply yarn of the store. Make sure that all the yarn packages are of same count and particular lot. 10. Loop: If the needle is unable to catch the yarn in the needle latch then there occurs a gapping effect in the fabric similar to the effect of needle broken but in this case instead of yarn breakage a gapping effect in the fabric. 11. Wheel mark: At the time of yarn passage from the wheel if the wheel is misplaced from its actual position then a mark is produced throughout the fabric which is called wheel mark. 12. Needle broken: Needle broken is normally caused when the needle is broken which causes tear in a particular place of the fabric in the loops of that certain place. Needle Broken Causes: Due to dirt deposition in needle this problem occurred. This problem also can occur due to yarn tension variation. 13. Drop stitch: 160 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics If any problem occurs in the latch of the needle while catching the yarn then it could result in drop stitch. If the miss stitch is seen in the fabric in a small area of the fabric then it is called drop stitch. Drop Stitch Causes: Yarn guide properly set. Defective needle latch. Yarn tension is not sufficient or too long stitches Take down to high. Wrong yarn treading. Cylinder dials system too high. Bad take up. Very dry material. Insufficient yarns tension. Broken needle hooks. Yarn feeder wrongly threaded-in. Remedies: Precise yarn guide resetting. Needle change. Yarn composition and collier re adjustment. Take down re adjustment. Dial position re adjustment. Yarn threading through the right bore. Use of fabric fault detector. 14. Oil spot: When small circular oil marks are seen in the knitted fabric then it is called oil marks. Normally oil spots occur during oiling the cylinder from the residual oils remaining in the needle. 161 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Oil Spot Causes: During lubricating the machine if more needle oil poured on the machine. If excess oil is present on the cylinder and needles of the fabric. Remedies: Carefully using needle oil during oiling the machine. 15. Oil line: Oil line is the vertical oil mark seen throughout the knitted fabric. Normally if more oiling is done to a particular cam then oil marks occur. 16. Barre mark: Barre mark is caused due to excess tension on the yarn while knitting the fabric. This excess tension can whether cause elongation or shrinkage of the fabric. 17. Stare: Stare is caused on the fabric when the needle latch is unable to grab the yarn and produces small hole like star marks on the fabric. Pin Stare Mark Causes: When needle latch is bent due to long time usage, then this problem occurred. Remedies: Needle must be changed. 18. Sinker mark: Sinker mark is caused when the sinker is broken or it contains dirt on the sinker then the sinker mark is seen on the fabric. This sinker mark is slightly larger than the needle mark. 162 Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Sinker Mark Causes: Sinker not clean. Defected or broken sinker. Incorrect depth of sinker which causes the stitch length to change while the needle knocks over during its movement towards rest position. When dirt’s deposited in sinker, it is raised and causes the faults. Remedies: Sinker has to be clean. It should be checked that the sinker having correct thickness and depth. Replacement of defected sinkers. 19. Lycra drop: Lycra drop is similar to Lycra out but in this case the gap mark in the fabric takes a small area or space in the fabric, but not throughout the fabric. Lycra Drop Causes: If any lycra yarn is missed during knitting. If lycra yarn feeder arrangement is not proper. If lycra yarn tension is not proper. Remedies: Lycra yarn should be passed to the maintaining proper tension Broken ends of the lycra yarn should be immediately fixed. Proper cleaning of the lycra knitting machine should be done. 163 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 20. Yarn contamination: Presence of any other foreign yarn in the knitted fabric is known as yarn contamination. 21. Patta: Patta is caused when the yarn tension in the fabric is not proper, which causes the fabric to either shrink or expand unexpectedly to a particular place of the fabric. 22. Wheel free: If the tension of the yarn passage is less than the yarn passage tension of the wheel then it causes wheel free problem on the knitted fabric. 23. Dirty yarn: If the yarn used for knitting the fabric is dirty then the fault occurred in the fabric is that the fabric has a dirty appearance which is called dirty yarn. 24. Press off: When there is a larger hole in the fabric which causes the loops of the knitted fabric to tear up inside the fabric is known as press off. Pressoff Causes: Yarn breaks before the yarn feeder. Yarn package winding faults, poor package build-up. Fibre fly block the yarn guides, feeders etc. Remedies: Carefully feeding the yarn by the feeder. Carefully yarn winding. Choosing the yarn very carefully. 25. Uneven yarn: Uneven yarn is responsible for various fabric faults. Such as, slub, needle broken, thick thin, naps, etc. 164 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Uneven Yarn 26. Naps: If there are thick places present in the yarn then that is known as naps. 8.6. Faults of fabric after dyeing: In the Finishing section of ECHOTEX Dyehouse there is another inspection section where all the finished fabrics are regularly inspected before reaching the garments section and the also various corrective actions are taken for the proper buyer recommended appearance of the finished fabric. The faults which are mainly occurred in the finishing section of the dyehouse are discussed below: Hole Oil Stain Chemical Spot Water Drop Fly Yarn White specks Slubs Rub Mark Rust Stain Yarn Contamination Insect Spot Uneven shade Napes Crease mark Patches GSM Hole Hairy Machine Stoppage Needle line Barre Mark Crimple mark Bowing 165 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Dead Cotton Snagging Line Mark Pin hole 1. Rust Stain: The stain mark which is caused by excess heat of the burners while passing through the conveyer of the machines. Rust Stain Causes: During passing the fabric through the Stenter or dryer machine if the temperature of dyeing the fabric is too high. If the blower of the tenter frame is unable to spread the fire coming from the nozzle throughout the fabric. Remedies: The speed and temperature of the tenter frame should be properly maintained while passing the fabric through the tenter frame. Make sure the blower has the capability to pass the hot air uniformly throughout the fabric. 2. Chemical Stain: The stain mark which is caused by improper application of finishing chemicals and also due to improper dissolving of the finishing chemicals. Chemical Stain Causes: 166 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics The knitting industry unlike weaving uses oil to lubricate machinery where the fabric is being produced. Such oil mixed with dust and metallic powder can, cause stain on the fabric being knitted. Remedies: Control of the oil itself, by applying it in minimum quantities and delivering it continuously so that present in the fabric but does not show up in any build up of solid material. Using oils that are readily mixed with water so called securable or clean oils. The majority of knitted piece goods are wet finished before cutting and therefore little oil staining will remain in finished fabric. On stitch shaped garments tight control is needed as they are not wet finished stain are dealt with during examination by solvent based spotting guns. 3. Oil Stain: The stain mark which is caused by applying needle oil in the knitting machine. Oil Spot Causes: Storage condition. Core pH before drying. Packing used for while goods free from BHT [Butyl hydroxyl toluene]. Remedies: Packing material used for while goods free atmospheric pollutants like oxides and dimity etc. Packing material free from phenolic antioxidant. While good core pH should be 6.0-6.5. 4. Fly Yarn: Fly yarn is also a knitting fault which is caused due to presence of dust particles on the supplied yarn while knitting the fabric. 167 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Fly Contamination Causes: It is caused if flying dust particles or colored yarn knitted with the fabric. By using dirty yarn. Remedies: By using good quality yarn. Proper cleaning of the machine before knitting. 5. Dead Cotton: The presence of dead cotton fibers in the fabric causes very small white spots on the fabric surface which occurs as there is no dye absorbency in the dead fiber contained areas of the fabric. Dead Cotton Causes: Poor cotton quality. More abrasion during process. Remedies: Try to maximize the abrasion during process. Use acid cellulose softener. 6. Uneven Shade: If color difference or shade difference is seen on the fabric surface then the color or shade of the fabric is called uneven shade. 168 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Uneven Shade of Remazol Reactive dyes Causes: Very rapid addition of dyes and chemicals. Uneven pretreatments (Scouring, Bleaching, Desizing). Lack control of dyeing machine like Machine speed. Temperature. Dosing time. Circulation pump. Plating device. Material: Liquor ratio. Remedies: Check addition of dyes and chemicals at a steadily increasing rate. Proper pretreatments. Proper control of dyeing machine. Check the rope turn over time. Verify rope speed and chamber loading calculations. 7. White Specks: White specks are the white mark seen on the fabric surface when it is passed through the rollers as a result of presence of unwanted dust particles on the fabric surface. 8. Insect Spot: During storing the fabric if dead insects are found on the fabric which causes mark on the fabric surface then that is called insect spot. 9. Rub Mark: Rub mark has a white mark appearance which is caused due to passage through the squeezer machine or other rollers in the finishing machine as a result of excess friction. 10. Yellow Spot: If there is yellowish color seen on a particular area of the dyed, bleached or softener treated fabric then that specific spot on the fabric surface is termed as Yellow spot. 169 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Yellowish spot in the fabric Causes: Storage condition. Core pH before drying. Packing used for while goods free from BHT [Butyl hydroxyl toluene]. Remedies: Packing material used for while goods free atmospheric pollutants like oxides and dimity etc. Packing material free from phenolic antioxidant. While good core pH should be 6.0-6.5. 11. Dia Mark: During the passage of the knitted fabric through the take down roller the fabric passes over two pointed blades causing needle mark at one side and on the other side there is also a line mark produced which is called the Dia mark. Dia Mark Causes: During passing the fabric through the spreader of the circular knitting machine if the fabric passes at an irregular tension. If the spreader has contains very sharp blades on both sides the needle mark and dia mark both are caused. Remedies: To avoid dia mark the fabric should be carefully passed through the spreader. The tension of take down mechanism of take down rollers should be properly maintained. 12. Crease Mark: 170 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics The presences of unwanted line marks on the surface of the fabric due to presence of mechanical pressure during fabric processing are called crease marks. Crease mark in the fabric Causes: More cycle time. Faulty plaiting device. Incorrect set bowed expender. Variation of heating and cooling rate. Improper fabric movement. Remedies: Anti-creasing agent are used to avoid crease mark problem. 13. Crample mark: Crush mark or crample mark is mainly caused during reeling the fabric into the Dyebath which a result of unbalanced speed of loading to the dye bath is reeling. Crample mark can also be caused during passing the fabric through the finishing machines due to the uneven pressure of the rollers. Crample mark in the fabric Causes: Lower fabric speed. Lower liquid ratio. Higher rate of cooling. Remedies: Running with a higher fabric speed. Increasing the liquor ratio. A slower rate of cooling. 14. Pin Hole: When small holes are seen in the fabric after dyeing which is occurred in the dye bath or in the finishing section is called pin hole damage. 171 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Pin Hole Damage Causes: Oxidation of the knitting oil/lubricant on the fabric stored for a long duration. Presence of heavy metal ions in peroxide bath. Presence of sharp metallic part in some parts in machine. Remedies: Check presence of any sharp object in machine. Provide magnetic filter in water or steam line. Provide magnetic filter in water or steam. Check if the used water for dyeing is properly softened. 15. GSM Hole: The hole which is caused by cutting the fabric with GSM cutter while measuring the GSM of the fabric. GSM Hole Causes: Continuous cutting of the fabric using GSM cutter for measuring GSM. Remedies: For GSM measuring applying calculated value and indentifying the whole weight and length to measure GSM. 16. Bowing: If spirality occurs in the design or loop construction towards length and width direction of the fabric then it is called bowing. 172 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics Bowing Causes: This structure consist of plain and lacost design where stitch where stitch length for tuck stitch is kept same as all knit loops As a result waviness has produced in lacost part. Remedies: Different SL for tuck stitch must be kept by adjusting VDQ pulley. 17. Snags: Snags mainly occur while processing filament yarns. The tendency towards snagging can be reduced by using yarns with a coarser single filament count, lesser crimp elasticity and higher twist. During knitting all mechanical influences, caused by rough surfaces on yarn guide elements, yarn feeders, needles, fabric take-up, etc. have to be avoided. Even after knitting some snags can appear especially during fabric setting, if its storage and further processing has not been undertaken carefully. 173 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 8.7. Corrective Actions taken for removing faults: Fabric Fault Corrective Action Corrective Recipe Chemical Stain Anti Staining Anti Staining: 1gm/l Oxalic Acid: 3gm/l Temperature Time : 800C 15min Yellow Spot Washing Wetting Agent & Detergent: 0.5gm/l Temperature Time : 900C 10min Chemical Stain on White Fabric Bleaching Half Bleach Caustic: 2gm/l Hydrogen Peroxide: 2gm/l Optical Brightening Agent: 0.1gm/l Temperature Time : 950C 30min Yellow Spot on White Fabric Bleaching Half Bleach Caustic: 2gm/l Hydrogen Peroxide: 2gm/l Optical Brightening Agent: 0.1gm/l Temperature Time : 950C 30min Oil Stain Anti Staining Anti Staining: 1gm/l Temperature Time : 900C 15min Band Line Anti Staining Anti Staining: 1gm/l Oxalic Acid: 3gm/l Temperature Time : 800C 15min Line Mark Washing Soaping Agent(Dekol SN): 0.5gm/l Temperature Time : 650C 15min Crease Mark Softener Spot Anti Creasing Washing Dirty Spot Anti Staining Anti Staining: 1gm/l Temperature Time : 900C 15min Rub Mark Washing Soaping Agent: 0.5gm/l Temperature Time : 650C 15min Hairiness Enzymatic Treatment Enzyme: 1% of Fabric weight Temperature Time : 550C 40min Uneven Shade Bleach & Re-dye Wetting Agent & Detergent: 0.5gm/l Acid: 3gm/l Temperature Time : 900C 10min Bleaching Temperature Time : 950C 30min Cotton Dyeing Temperature Time : (600C -800C) 30min Polyester Dyeing Temperature Time : 1300C 30min 174 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 8.8. Flow Chart of Quality Control of Grey Fabrics: Fabric inspection On-line inspection Off-line inspection Outside Inside Outside production Fabric rolls checkfabric quality Every machine checkfabric quality Inside production Check with yarn count, Stitch length, Dia & Gauge Fabric inspection 100%Fabric quality First Bulk (first roll) Approved Sample (Solid & Dyed Yarn) Pass Fail Grey Store 100% inspection for quality fabric Approval card (Knitting) Pass Fail Grey Store Reject -immediately inform to executiveOutside factory Approval card (Finishing) Pass Fail Grey Store Reject -immediately inform to executiveOutside factory 175 Engr. Khandaker Sakib Farhad Quality Assurance of Knit Fabrics 8.9. Flow Chart of Quality Control of Dyed and Finished Fabrics: Receiving fabric from Finishing Section Matching Fabric Shade in Light box Shade OK Shade not OK Separating from one roll to another Passed to Dyeing & Finishing Section Determining the Fabric Faults Visually and by Machine Calculating the Fabric Faults Fabric not OK Fabric OK Determining if the Fabric is treatable Passed to the Storage Section Pass to Dyeing & Finishing Section for Re-processing Untreatable Rejected 176