Chapter 6 Jones
advertisement

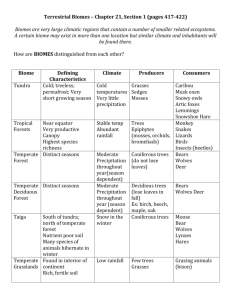
Chapter 6 Summary APES Campbell Jones Major Ecosystems of the World Biome- a large, relatively distinct terrestrial region with similar climate, soil, plants, and animals, regardless of where it occurs in the world Biomes around the World Arctic Tundra- The treeless biome in the far north that consists of boggy plains covered by lichens and small plants such as mosses; has harsh, very cold winters, and extremely short summers (50-160 days) o Occurs in the extreme northern latitudes o Alpine Tundra-similar ecosystem located in the higher elevations of mountains, above the tree line, and can occur in any latitude o Tundra has a layer of permafrost, permanently frozen ground that varies in depth and thickness. This limits root penetration depth o Has a Low species richness (number of different species), and a low primary productivity (rate at which energy is accumulated) o Animals include lemings, voles, weasels, arctic foxes, snowshoe hares, ptarmigan, snowy owls, and musk oxen Boreal Forests-A region of coniferous forest in the northern hemisphere, located just south of the tundra, but not in the southern hemisphere o Winters are severe, but not as bad as tundra o Permafrost is patchy, and where it is found, is often deep under the soil o Black and white spruces, balsam fir, eastern larch, and other conifers dominate the boreal forest o Animals include caribou, wolves, bears, and moose. o Not suited to agriculture because of its short growing season and mineral poor soil. However, the forest yields lumber and pulpwood Temperate Rain Forest-a coniferous biome with cool weather, dense fog, and high precipitation o 50 in. of rain per year o Trees include western hemlock, Douglas fir, western red cedar, Skita spruce, and western arborvitae o Squirrels, wood rats, mule deer, elk, bird species, sever amphibian species and reptiles are common in temperate rain forest o Temperate rain forest is a rich wood producer, giving lumber and pulpwood o Also one of the world’s most complex ecosystems in terms of species richness o Loggers replant the area after harvest with a monoculture (a single species) of trees Temperate Deciduous Forests-A forest biome that occurs in temperate areas with a moderate amount of precipitation o Precipitation ranges from about 30-60 in. annually o Soil is rich in organic material o Trees form a dense canopy that overlies saplings and shrubs. These include oak, hickory, maple, and beech o Animals include deer, bears, and many small mammals and birds o These were among the first biomes to be converted to agricultural use Temperate Grasslands-a grassland with hot summers, cold winters, and less rainfall than the temperate deciduous forest biome o Precipitation averages about 10-30 in. annually o Soil has considerable organic material o Covered mostly with grass, although trees grow near rivers and streams. Periodic wildfires help maintain grasses as the dominant vegetation in grasslands o Tallgrass Praries-moist temperate grasslands, occur in Midwest Originally covered with herds of grazing animals such as pronghorn elk and bison Smaller animals included prairie dogs and foxes o Shortgrass Prairies-temperate grasslands that receive less precipitation. This occurs in Montana, South Dakota, and other Midwestern states Grasses grow about knee high Chaparral-a biome with mild, moist winters and hot, dry summers; vegetation is typically small-leaved evergreen shrubs and small trees o Have Mediterranean climates o Vegetation looks strikingly similar all over the world o Usually has a dense growth of evergreen shrubs but may contain short, drought-resistant pine or scrub oak trees o When a fire occurs, it doesn’t kill the underground parts of the plants, and the spring back up in the winter o Animals include mule deer, wood rats, chipmunks, lizards, and many species of birds Deserts-A biome in which the lack of precipitation limits plant growth; deserts are found in both temperate and subtropical regions o About 10 in. annually of precipitation o Plants include cacti, yuccas, Joshua trees, and sage brushes o Plants have adapted to need little water o Animals tend to be small, and include frogs and toads, tortoises, iguanas, Gila monsters, and Mojave rattlesnakes o Mammals include gerbils, jerboas, and kangaroo rats. Also, mule deer, jackrabbits, oryxes, and kangaroos Savanna-a tropical grassland with widely scattered trees or clumps of trees o Annual precipitation is 30-60 in. o Soil is rich in aluminum, which resists leaching o Animals include wildebeest, antelope, giraffe, zebra, elephants, lions, hyenas o Savannas are rapidly being converted into rangeland for cattle Tropical Rain Forest-a lush, species-rich forest biome that occurs where the climate is warm and moist throughout the year o Annual precipitation ranges from 80-180 in. o Plants capture a lot of energy by photosynthesis. The trees are typically evergreen flowering plants with shallow roots o Rain forest has 3 layers of vegetation 1) Topmost story consists of the crowns of occasional, very tall trees who get direct sunlight 2) Middle level forms a continuous canopy that lets in a little sunlight to the lower level 3) Smaller plants specialized for life in the shade occupy the bottom level o Most animals live in the trees, which include reptiles, amphibians, insects, sloths, monkeys. There are large ground animals such as elephants Vertical Zonation o The distribution of vegetation on mountains o Base is covered by deciduous trees o At higher elevations, there are coniferous subalpine forests o The top of the mountain might have a permanent ice or snow cap Aquatic Life Zones o Plankton- small or microscopic organisms that are relatively feeble swimmers o Zooplankton-nonphotosynthetic organisms that include protozoa, shrimplike crustaceans, and larval stages of many animals o Nekton-larger strongly swimming organisms such as fishes, turtles and whales o Benthos-bottom dwelling organisms that fix themselves to one spot such as sponges, or oysters o Rivers and Streams o Flowing Water Ecosystem-a freshwater ecosystem such as a river or stream in which water flows in a current o o Standing Water Ecosystems- A body of fresh water that is surrounded by land and that does not flow o Littoral Zone-a shallow-water area along the shore of a lake or pond where light reaches the bottom o Limnetic Zone- the open water beyond the littoral zone o Profundal Zone-beneath the limnetic zone of a large lake o Thermal Stratification-temperature of a lake changes sharply with depth o Turnover-Water shifts in order to spread O2 and nutrients throughout the lake. It shifts between the limnetic and profundal zone. o Freshwater Wetland o Land that shallow freshwater covers for at least part of the year and that has a characteristic soil and water-tolerant vegetation On every continent except Antarctica Average of 7 in. of rainfall annually include marshes( grass like plants) and swamps ( woody trees or shrubs) Animals include bird species, beaver, otters, muskrats, game fishes, amphibians, alligators, turtles, snakes o Estuaries-a coastal body of water, partly surrounded by land, with access to the open ocean and a large supply of fresh water from a river o Water levels rise and fall with the tide, while salinity fluctuates with tidal cycles o Greatly ranges in temperature seasonally and even daily. Seasonal changes in the temperature o Animals include oysters, shrimp and crabs, and worms o Salt Marshes- shallow wetlands dominated by salt-tolerant grasses o Mangrove Forests- the tropical equivalent of salt marshes Marine Ecosystems o Intertidal Zone-the area of shoreline between low and high tides o Benthic Environment-the ocean floor, which extends from the intertidal zone to the deep ocean trenches (Photobenthic) o Seagrass Beds- flowering plants adapted to complete submersion in salty ocean water o Kelp Forests- the largest brown algae o Coral Reefs-built from accumulated layers of calcium carbonate Fringing Reef-directly attached to the short of a volcanic Other Terms island or continent and has no lagoon associated with it Atoll-a circular coral reef that surrounds a central lagoon of quiet water o Pelagic Environment-consists of all ocean water o Euphotic Zone- extends from the surface to a depth of 150m in the clearest ocean water o Neritic Province-the part of the pelagic environment that overlies the ocean floor from the shoreline to a depth of 200m o Zooplankton-feed on phytoplankton in the euphotic zone o Nekton- consume zooplankton, such as herring, sardines, squid, manta rays o Oceanic Province-The part of the pelagic environment that overlies the ocean floor at depths greater than 200m Seagrass Beds- flowering plants adapted to complete submersion in salty ocean water Kelp Forests- the largest brown algae Coral Reefs-built from accumulated layers of calcium carbonate, located in