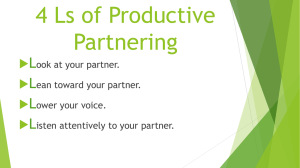
Chapter1 Teaching Aids
advertisement
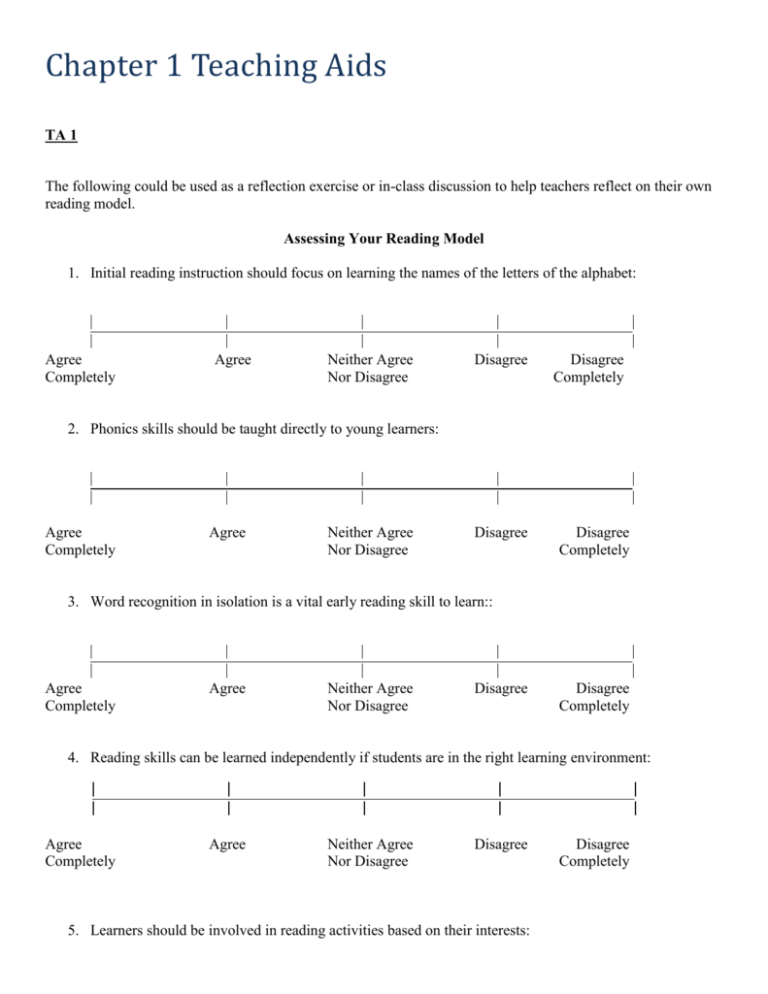
Chapter 1 Teaching Aids TA 1 The following could be used as a reflection exercise or in-class discussion to help teachers reflect on their own reading model. Assessing Your Reading Model 1. Initial reading instruction should focus on learning the names of the letters of the alphabet: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 2. Phonics skills should be taught directly to young learners: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 3. Word recognition in isolation is a vital early reading skill to learn:: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 4. Reading skills can be learned independently if students are in the right learning environment: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree 5. Learners should be involved in reading activities based on their interests: Disagree Completely Agree Completely 6 Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely Scripted reading instruction is superior to unscripted reading instruction: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 7. Students learn phonics through their independent reading activities: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 8. Whole-language instruction provides students opportunities to learn reading skills independently: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely Disagree Disagree Completely Disagree Disagree 9. Phonics skills should be taught directly and systematically: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree 10. Beginning ESL students benefit from direct skills instruction: Agree Agree Neither Agree Completely Nor Disagree Completely 11 Workbook activities help students learn the reading skills they need to read: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 12 There is an important sequence to learning reading skills from letter names to comprehension: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 13 A reader’s background knowledge helps her/him to predict and understand text: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 14 ESL(ELL) students learn to read English best when skills such as phonics are taught in a systematic sequential fashion: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 15 Bilingual instruction results in cognitive confusion for students: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 16 Results of the National Reading Panel show that systematic phonics instruction is important: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 17 Reading good children’s literature helps learners develop knowledge of phonics, word recognition, and comprehension skills: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 18 Teaching ESL(ELL) students to recognize words in isolation is a valuable instructional approach: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 19 Having ESL(ELL) students read and write from their first day in school is a good pedagogical approach: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely 20 ESL(ELL) students should learn to read first in their first languages: Agree Completely Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Disagree Completely TA 2 Write a paragraph that Articulates your own personal view of the second language reading process. Also discuss how your views influence your classroom practice. Compare your ideas with colleagues and see if you can come to some common agreements about theories beneficially affect classroom practice. TA 3 Work with your partner to complete the grid below. Rank from 1 to 5 how each of these instructional approaches addresses each aspect of the “big five” Ideas in reading instruction. Number one would be the most effective approach for addressing a particular aspect of reading and number five would be the least effective. After you finish, get together with another pair and discuss your rankings as well as your reasons for your rankings. Instructional approach DRTA Language experience Initial teaching alphabet Whole language Critical literacy Multiliteracies Phonemic awareness Alphabetic principle Fluency Comprehension Vocabulary TA 4 Compare these two classrooms below. How do you think these pictures reveal how literacy instruction has changed over the past hundred years? TA 5 Some Informal Classroom Observations When you have a chance to visit a classroom or you can make observations in your own classroom. Please do not sit in the back of a room and write notes or answer the following. (1) What kind of reading program, if any, do you see in your classroom? (2) What kinds of language are on the walls? Student work? (3) Do you see any kind of phonics program? If so, what is it? (4) Do you see any kind of vocabulary program? If so, what is it? (5) How does the teacher manage the classroom? Are there instructional groups? (6) What surprises you most about the classroom? (7) What kind of lesson plan(s) did you see? (8) What good tips did you learn about teaching, if any? (9) What is the model of reading the teacher (or you hold)? How is it evident in classroom activities?