Final Exam Review (le
advertisement

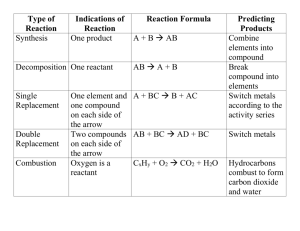
Final Exam Review (level 2) 2011-12 Lab 1) 5.1 g of copper (II) carbonate is added to a test tube that has a mass of 42.30g. The substance is heated, cooled, and a final mass is taken. The final mass is 45.90g. a. What is the mass of the final substance? b. How much mass was lost (as a gas)? 2) Two clear, colorless solutions are added together. The final result is a substance that appears cloudy and white. a. What are two indicators of a chemical change for this reaction? b. What type of reaction has occurred? Determining Chemical Formulas (Holt: chapter 7) 1) Determine the molar mass of aluminum fluoride. 2) Determine the molar mass of copper (II) sulfate. 3) Determine the molar mass of ammonium phosphate. 4) What is an empirical formula? 5) What is the empirical formula for P4O10? 6) What is the empirical formula for a substance that has a percent composition of 40.00% C, 6.72% H, and 53.29% O? 7) Calculate the empirical formula for caffeine given the following percent composition: 49.5% C, 5.15% H, 28.9% N, and 16.5% O. 8) What is a molecular formula? 9) What does “molecular mass” represent? 10) If the empirical formula is 11) A certain substance was used as a grain pesticide until it was banned. Calculate the molecular formula for ethylene dibromide given its approximate molar mass of 190 g/mol and its percent composition: 12.7% C, 2.1% H, and 85.1% Br. 12) TNT (trinitrotoluene) is a white crystalline substance that explodes at 240ºC. Calculate the percent composition of TNT, C7H5(NO2)3 13) Chemical Equations (Holt: chapter 8) 1) What is a “diatomic molecule”? 2) What are the diatomic molecules? 3) What state of matter is Na at normal temperature and pressure? 4) What state of matter is Ti at normal temperature and pressure? 5) What state of matter is Cl2 at normal temperature and pressure? 6) What state of matter is iodine at normal temperature and pressure? 7) What state of matter is carbon at normal temperature and pressure? 8) The solubility rules determine the state of matter for what type of compounds? 9) What is the term for a substance that has been dissolved in water? 10) What is the term for an insoluble substance that forms when 2 solutions mix? 11) What is the state of matter for magnesium carbonate? 12) What is the state of matter for barium sulfide? 13) What is the state of matter for silver chloride? 14) What is the state of matter for lead (II) nitrate? 15) What is the state of matter for potassium phosphate? 16) What is the symbol for heat? 17) Where is a “catalyst” placed in a chemical equation? 18) What must be the same on opposite sides of a yield sign? 19) Please balance the following equations: a) Al2(SO4)3 + Ca(OH)2 ---> Al(OH)3 + CaSO4 b) C2H2 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O c) H3PO4 ---> H4P2O7 + H2O d) Hg2CO3 ---> Hg + HgO + CO2 e) C4H10 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O f) Hg(OH)2 + H3PO4 ---> Hg3(PO4)2 + HOH g) P4 + O2 ---> P2O5 f) C7H16 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O g) Au2S3 + H2 ---> Au + H2S h) SrBr2 + (NH4)2CO3 ---> SrCO3 + NH4Br i) AlBr3 + Cl2 ----> Br2 + AlCl3 j) Ca3(PO4)2 + H2SO4 ---> CaSO4 + Ca(H2PO4)2 Chemical Reactions (Holt: chapter 8) 1) What is/are the reactant(s) of a decomposition reaction? 2) What is/are the reactant(s) of a single-replacement reaction? 3) What is/are the reactant(s) of a double replacement reaction? 4) What is/are the reactant(s) of a combustion reaction? 5) What is/are the product(s) of a combustion reaction? 6) What is/are the product(s) of a synthesis reaction? 7) What is/are the product(s) of an acid/base neutralization reaction? 8) How can you recognize an acid from its compound formula? 9) How can you recognize a base from its compound formula? 10) What type of reaction is represented by each of the following: a) Al2(SO4)3 + Ca(OH)2 ---> Al(OH)3 + CaSO4 b) C2H2 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O c) H3PO4 ---> H4P2O7 + H2O d) Hg2CO3 ---> Hg + HgO + CO2 e) C4H10 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O f) Hg(OH)2 + H3PO4 ---> Hg3(PO4)2 + HOH g) P4 + O2 ---> P2O5 f) C7H16 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O g) Au2S3 + H2 ---> Au + H2S h) SrBr2 + (NH4)2CO3 ---> SrCO3 + NH4Br i) AlBr3 + Cl2 ----> Br2 + AlCl3 j) Ca3(PO4)2 + H2SO4 ---> CaSO4 + Ca(H2PO4)2 11) What type of chemical reaction releases heat? 12) What type of chemical reaction absorbs heat? 13) Please complete the following reactions: a) FeBr3 + AgNO3 b) H3PO4 + Mg(OH)2 c) AlBr3 + Fe d) MgCO3 e) Ca + P4 f) Zn + NiC2H3O2 g) C3H8 + O2 h) K + HOH Stoichiometric Problems (Holt: chapter 9) 1) Why are mole ratios used in stoichiometric problems? 2) Explain why the conversion factor cannot be used for the reaction represented by the equation 3) m 4) How many moles of Ag can be produced if 350. g of Cu are reacted with excess AgNO3 according to the equation Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) 2Ag(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq)? 5) Limiting Reactant Problems (Holt: chapter 9) 1) What is a “limiting reactant”? 2) Comparing limiting and excess reactants, explain why the flame would go out in the Bunsen burner shown below if either of the indicated valves were tightened too much. 3) 4) Determine the maximum number of moles of product that can be produced from 7.0 mol Al and 8.0 mol Cl2 according to the equation 2Al + 3Cl2 2 AlCl3. 5) What mass of PCl3 forms in the reaction of 75.0 g P4 with 275 g Cl2 ? 6) Gas Theory (Holt: chapter 10) 1) What type of collisions to gas molecules experience and what does it mean? 2) Express 699mmHg in kPa Gas Laws (Holt: chapter 11) 1) What is the relationship between pressure and temperature?