Language Guided Lecture
advertisement
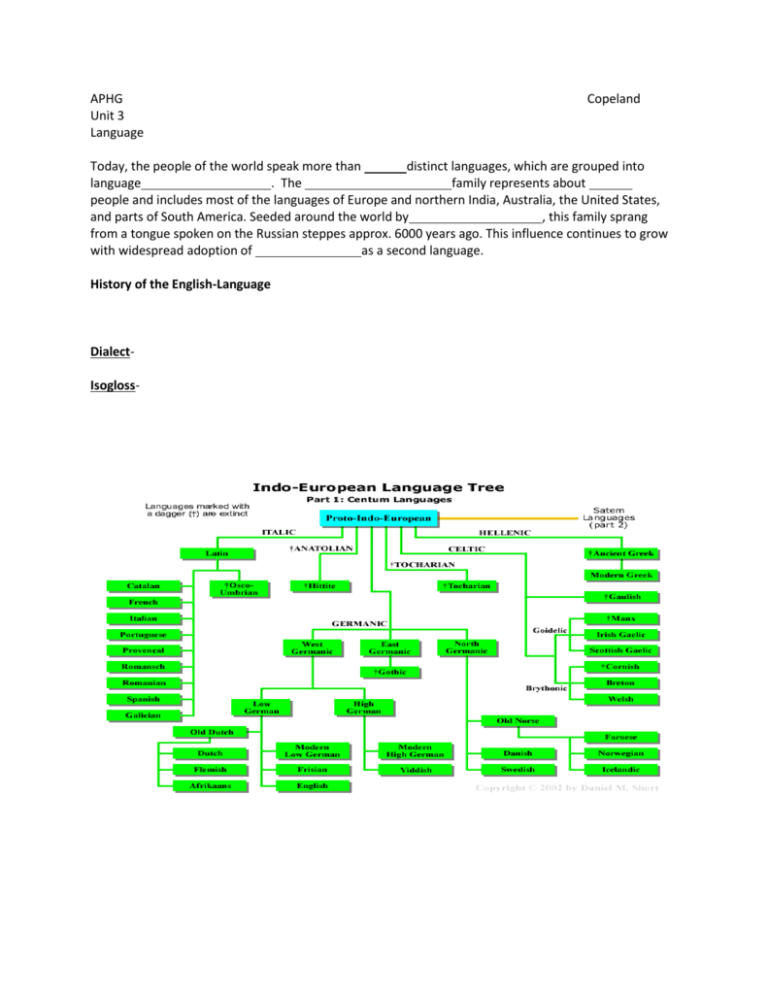
APHG Unit 3 Language Copeland Today, the people of the world speak more than distinct languages, which are grouped into language . The family represents about people and includes most of the languages of Europe and northern India, Australia, the United States, and parts of South America. Seeded around the world by , this family sprang from a tongue spoken on the Russian steppes approx. 6000 years ago. This influence continues to grow with widespread adoption of as a second language. History of the English-Language DialectIsogloss- Native American languages are spoken throughout the Americas, although the precise number of languages in this classification is not known. More than 300 native languages were once spoken in the U.S. and Canada. Two-thirds survive, but the few speakers left are aging. Even as native languages fade, their sounds echo in place-names such as Chicago and Massachusetts. Are Native Languages Surviving Today? Why or why not. American Indian-Meso and , Mayan languages, are the region’s strongest indigenous tongues. Most languages faded after European contact, but a few were documented by missionaries. African Languages African languages are grouped into four families: Niger-Congo, Nilo-Saharan, Khoisan, and Afro-Asiatic. : With more than 1400 languages – almost one-fourth of the world’s total – NigerCongo is one of the largest language families. It includes Swahili, used by 35 million East Africans as a lingua franca. Swahili: Where are you going? : About 200 Nilo-Saharan languages are spoken by ethnic minorities in their home countries. Only Dongolawi, a Nubian language of the southern Nile in Sudan, has a long written record. : Famous for clicking sounds, Africa’s Khoisan languages may be the continent’s oldest. Several have vanished; most have fewer than a thousand speakers. : The languages of ancient Babylon, Assyria, Egypt and Palestine belonged to this family. Still thriving, the largest living Afro-Asiatic language, Arabic, spreads in tandem with Islam. Eurasian Languages The languages of Eurasia are classified as members of either the or language families, which include over 70 related languages. Also found in Asia are three further groups— 1) Austro-Asiatic languages, spoken by 45 million people in South East Asian countries, 2) Dravidian family, which includes the main languages of India and Sri Lanka. 3) The Austronesian (formerly known as Malayo-Polynesian) language family is the main language grouping of the Pacific, spoken from Madagascar to Easter Island and Hawaii. : Finnish, Hungarian, and Estonian are safeguarded by their status as national languages. Other Uralic languages have declined in the past 100 years, many crowded out by Russian. : Some linguists think Mongolian, Tungusic, and Turkic languages are linked by kinship. Others attribute similarities to linguistic borrowing between traditionally nomadic peoples. Austro-Asiatic: Now distributed from to , this family’s languages may once have dominated most of SE Asia. Dravidian: Pockets of these language speakers live in and , but most are found in southern , where linguistic independence movements in the 1950’s led to the birth of several language-based states, such as Andhra Pradesh, home of Telugu. Austronesian: Island-hopping seafarers spread these languages across the and Indian Oceans from Hawaii to Madagascar. More than 1200 languages remain-about a hundred on the tiny Pacific islands of Vanuatu alone. Languages that do not belong to any of these families include language isolates such as and , the languages of New Guinea, and the Athabascan and Algonquian languages of sub arctic Canada. There are dozens of other rare languages, such as in Spain and France, Burushaski in Pakistan, persist as . Despite decades of research, links to known language groups have yet to be verified. , spoken in Siberia, is an example of a member of an isolated small language family. , now mostly spoken by Thai and Laotians, may have come from southwest China. Korean and Japanese: Both of these languages may be related. Both were influenced by Chinese. Many words are Chinese loans, and Japanese writing still uses Chinese characters. Basque Australian-Indigenous Languages Top Ten World Languages georgia Population: 8,186,453 Number of Counties: 159 Counties With the Most Languages Spoken Rank County Languages 1 DeKalb County 74 2 Fulton County 73 3 Cobb County 72 4 Gwinnett County 69 5 Clayton County 38 6 Chatham County 33 7 Clarke County 31 8 Richmond County 27 9 Muscogee County 25 t-10 Cherokee County 23 t-10 Fayette County 23 12 Columbia County 22 13 Henry County 21 14 Liberty County 19 15 Forsyth County 18 t-16 Bibb County 17 t-16 Douglas County 17 t-16 Houston County 17 19 Hall County 16 t-20 Carroll County 15 t-20 Lowndes County 15 t-22 Bulloch County 14 t-22 Glynn County 14 24 Floyd County 13 t-25 Dougherty County 12 t-25 Rockdale County 12 t-25 Whitfield County 12 Most Common Languages Spoken Rank Language Speakers 1 English 6,843,040 2 Spanish 426,115 3 French 42,630 4 German 32,760 5 Vietnamese 27,670 6 Korean 25,815 7 Chinese 19,390 8 Gujarathi 11,135 9 Kru, Ibo, Yoruba 9,770 10 Arabic 8,555 11 Japanese 8,255 12 Hindi 7,595 13 Tagalog 7,310 14 Russian 7,175 15 Urdu 7,110 16 Portuguese 6,875 17 Italian 5,825 18 Persian 5,480 19 Amharic 5,210 20 Laotian 5,180 21 Serbocroatian 5,010 22 French Creole 4,965 23 Cushite 4,075 24 Bengali 3,665 25 Mon-Khmer, Cambodian 3,545 26 Greek 3,320 27 Romanian 2,930 28 Hebrew 2,870 29 Polish 2,775 30 India, n.e.c. 2,730 31 Dutch 2,690 32 Thai 2,660 33 Tamil 2,560 34 Telugu 2,405 35 Mandarin 2,055 36 Swahili 1,770 37 Turkish 1,655 38 Miao, Hmong 1,360 39 Formosan 1,215 40 Czech 1,185 41 Cantonese 1,155 42 Malayalam 1,075 43 Ukrainian 1,035 44 Marathi 980 45 Fulani 945 46 Swedish 910 47 Hungarian 850 48 Panjabi 795 49 Kannada 790 50 Bulgarian 765 Languages in Georgia • DeKalb County’s 74 languages tied for the 52nd highest number recorded in any county in the United States. Other Georgia counties that were highly ranked included: Fulton County (57), Cobb County (t-59), and Gwinnett County (t-73). • Georgia has the third highest percentage of speakers of Caucasian, Cushite and Gujarathi in the United States. The Peach State also ranks fourth in the percentage of Efik and Sindhi speakers and fifth in the percentage of African, Fulani, Krio and Mayan language speakers. • DeKalb County has the third highest percentage of Amharic speakers of any county in the nation. Other counties that rank highly in a given language include: Habersham County (fourth, Laotian), DeKalb County (fourth, Cushite), Gwinett County (fifth, Romanian) and Clayton County (sixth, Kru/Ibo/Yoruba). 118 Languages spoken