Final Study Guide Key
advertisement

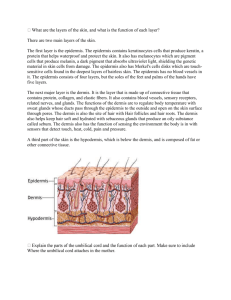
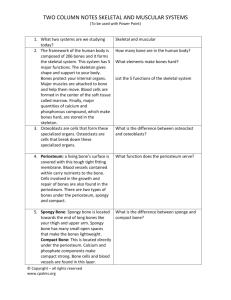
HBS Final Study Guide Systems o Integumentary o Skeletal o Muscular o Cardiovascular Integumentary System 1. What are the three layers of the skin Epidermis Dermis Hypodermis (Subcutaneous) 2. What is unique about the epidermis? a. What is the epidermis composed of? The Epidermis is composed of primarily dead skin 3. What features are found in the dermis? a. What purpose do those items serve? i. Sebaceous Gland Secrete Sebum (An oily substance) that helps protect the skin from pathogens and makes the skin smooth and soft ii. Sweat Glands Helps to cool down the skin through secreting sweat (A mixture of nutrients and water) iii. Nerve Endings/Pain Receptors Nerve endings help the skin to sense or feel pressure from their outside environment 4. What nutrient does the skin synthesize The skin synthesizes Vitamin D 5. What are some protective functions of the skin? Provide a physical barrier Provide a mechanical barrier 6. How does the skin help in excretion The skin helps to excrete sweat and sebum in order to help the body maintain homeostasis 7. How does the skin aid in thermoregulation? The skin aids in thermoregulation by secreting sweat, which helps to cool off the body The skin will help with radiation by releasing heat The smooth muscle of the arrector pili contracts, standing hair up, which traps warm air next to the body o The contraction of muscles also releases heat 8. What is the pigment that gives the skin color and aids in protection called? Melanin 9. What is Basal Cell Carcinoma? A type of skin cancer that is the lease malignant, but most common form 10. What is the difference in the different categorizes of burns a. 1st A burn that only affects the epidermis b. 2nd A burn that damages the dermis, but does not penetrate through the dermis c. 3rd A burn that penetrates throught the dermis into the hypodermis (Subcutaneous layer) 11. Which types of burn is the most damaging? 3rd Degree 12. What is it called when the dermis and the epidermis separate due to friction? Blister SKELETAL SYSTEM 13. What is the primary function of the skull? Protection of the Brain 14. Be able to pick out the bones found in the axial and appendicular skeleton 15. Where are red blood cells formed? Red Bone Marrow a. Where is that marrow found? Epiphysis of long bones Flat Bones 16. Why do bones contain attachment sites? For Skeletal muscles to attach 17. Where does the skeletal system store fat? Yellow Marrow a. Where is that marrow found? Diaphysis of long bones 18. List an example of a long bone Femur, Humerus, Ulna, Radius, Tibia, Fibula, Phalanges a. Short Bone Carpals, Tarsals b. Flat Bone Cranial Bones, Coxal, Scapula c. Irregular Bone Vertebra, Mandible, 19. What is the disorder called when there is a lack of calcium in the bones? Osteoporosis 20. What are the three abnormal curvatures of the spinal column called? Scoliosis Kyphosis Lordosis 21. What is the fracture called when the bone punctures the skin? Compound Fracture 22. Be able to list the three different categories of joints and an example of each a. (Synovial joint, ball and socket, found between the humerus and scapula) Synovial- Hinge- Femur &Tibia Fibula Cartilaginous- Pubic Symphysis Fibrous- Sutures- Frontal & Parietal MUSCULAR SYSTEM 23. What are the three types of muscle? Skeletal Smooth Cardiac a. What are their main functions Skeletal- Attach to bones to provide body movement Smooth- Contract the digestive tract to allow internal bodily movement Cardiac- Contract to pump blood out of the heart 24. What are the locations of the three different types of muscles Skeletal- Attach to bones Smooth- In the lining of the walls of the digestive tract Cardiac- In the heart 25. Which muscles are voluntary, Skeletal a. Which muscles are involuntary Smooth Cardiac 26. What types of muscles are striated? Skeletal Cardiac 27. What muscle is responsible for helping the heart beat Cardiac 28. What are antagonistic muscle pairs (Agonist vs Antagonist) Muscles that oppose and work against each other a. List an example Biceps Brachii and Triceps Brachii 29. What is the difference between a sprain and a strain a. (Think Location) Sprain- A stretching or tearing of a ligament Strain- A stretching or tearing of a tendon 30. How can someone slow down the process of aging on their muscles Proper Exercise Proper Diet 31. What is the term for muscle growth Hypertrophy a. Muscle loss/wasting away Atrophy 32. How are flexion and extension different Flexion is when the angle of the joint decreases Extension is when the angle of the joint increases a. Adduction vs Abduction Adduction is when the body part is brought towards the midline of the body Abduction is when the body part is brought away from the midline of the body CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 33. What are the different type of blood vessels Arteries Veins Capillaries a. How are they different Arteries are thick walled vessels that take blood away from the heart Veins are thin walled vessels that contain valves and bring blood back towards the heart Capillaries are small vessels where the site of gas exchange occurs 34. Which blood vessels contain valves and carry blood back towards the heart? Blood Veins 35. Which blood vessels have very thick muscular walls and bring blood away from the heart? Blood Arteries 36. What is the main function of the heart? Pump blood throughout the body 37. What is the purpose of the pulmonary vessels? To supply the blood with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide 38. What is the function of the entire cardiovascular system? To supply the body with oxygen and nutrients 39. What do red blood cells do? Red blood cells carry hemoglobin, which are iron containing proteins that carry oxygen from the lungs and give off to the body 40. Where does gas and nutrient exchange occur? Capillaries 41. What is a health blood pressure range? 120/80 is normal o 140>/90> is hypertension 42. What is the disease that is responsible for a buildup of fatty substances on the vessel wall, leading to a narrowing of the vessel? Atherosclerosis 43. How can someone maintain/create a healthy blood flow? Proper Diet Proper Exercise Don’t/Quit Smoking Maintain stress level 44. Be able to label a diagram of the heart