Chapter 4 Plate Tectonic TEST
advertisement

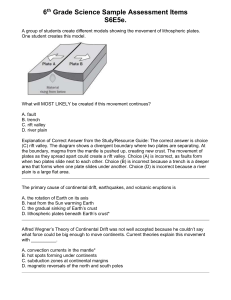
Plate Tectonics TEST Chapter 4 Name: ____________________ Period:__ Modifications: 1. Which of the following is the densest layer of the solid Earth? a. mantle b. core c. atmosphere d. crust 2. What is the term used to describe the area where thin oceanic plates spread apart, releasing magma and creating new oceanic crust? a. convergent boundary b. normal fault line c. mid-ocean ridge zone d. subduction zone 3. The outer layer of the Earth – including both the continents and the ocean basins – is divided into separate plates. About how much do crustal plates move each year? a. 5-10 kilometers b. 5-10 miles c. 5-10 centimeters d. 5-10 meters 4. Geologic evidence shows that Earth’s lithosphere plates can move thousands of kilometers across the Earth’s surface. These movements a. do not change the Earth’s surface at all. c. occur due to human activity. b. occur gradually over millions of years. d. occur in one sudden movement. 5. How might two lithosphere plates interact with each other? I. II. III. a. I and III only They can collide with each other. One plate may slide under another plate. They can slide past each other. b. I, II, and III c. II and III only d. II only 6. Base you answer to the following question on the map below. The map represents the movement of tectonic plates that resulted in the collision of India with Asia. Scientists believe that 71 million years ago, India was at position A. Which present –day geologic feature in Nepal resulted from this collision? a. a rift valley b. a mountain range c. an ocean ridge d. ocean trench 7. Locations A, B, C, and D are shown on the accompanying map. Which location is closest to a tectonic plate boundary? Use page 125 in your textbook. a. A b. B c. C d. D 8. Which two tectonic plates are separated by a mid-ocean ridge? Use page 125 in your textbook. a. Indian-Australian and Eurasian c. North American and South American b. Indian-Australian and Pacific d. North American and Eurasian 9. When a continental crustal plate collides with an oceanic crustal plate, the continental crust is forced to move over the oceanic crust. What is the primary reason that the continental crust stays on top of the oceanic crust? a. continental crust is less dense. c. continental crust melts at higher temperatures. b. continental crust deforms less easily. d. continental crust contains more mafic minerals. 10. Base you answer to the following questions on the map, which shows the location of mid-ocean ridges and the age of some oceanic bedrock near these ridges. Letters A through D are locations on the surface of the ocean floor. The age of oceanic bedrock on either side of a mid-ocean ridge is supporting evidence that at the ridges, tectonic plates are a. diverging b. converging c. locked in place d. being subducted 11. The movement of tectonic plates is inferred by many scientists to be driven by a. tidal motions in the hydrosphere c. convection currents in the asthenosphere b. density differences in the troposphere d. solidification in the lithosphere 12. What is the only entirely liquid layer of the earth? a. the upper mantle b. the outer core c. the inner core d. the lower mantle 13. The deep interior of the Earth can be mapped using a. seismic waves b. sonar c. information from drilling expedition d. ocean waves 14. What do scientists use the global positioning system for? a. to measure plate motion c. to make images of tectonic plates b. to measure the Earth’s thicknesss d. to locate fossils 15. Which of these did NOT provide evidence for continental drift? a. sea-floor spreading b. oceanic plate theory c. the fossil record d. magnetic reversals c. reverse fault d. strike-slip fault 16. When compression pushes rocks together, it creates a a. normal fault b. fold 17. The breaking of rock layers due to stress in the Earth’s crust is known as a. uplift b. folding c. faulting d. subsidence 18. The northern portion of Pangaea that broke apart about 180 million years ago is known as a. Pangaea. b. Panthalassa. c. Gondwana. d. Laurasia. 19. The Earth’s core is made of two parts – the inner and outer core. The inner core is made mostly of a. nonmetallic liquid b. nonmetallic gas c. solid metal d. liquid metal 20. Which best summarizes the composition of Earth’s core? a. b. c. d. it contains a solid outer region surrounding a liquid iron core. it contains a liquid outer region surrounding a solid iron core. it contains a semi-liquid rock outer region surrounding a liquid core. it contains a basalt, semi-liquid outer region surrounding a solid core. 21. Which best describes Earth’s crust? a. it is stationary and unable to move. c. it is located between the outer core and inner core. b. it is thicker than the mantle and the core. d. it is composed of continental and oceanic plates. 22. Which causes the movement of tectonic plates? a. gravitational pull between Earth and the moon c. energy produced by earthquakes within the Earth b. convection occurring beneath the Earth’s crust d. rotation of liquid rock found within the core 24. Which most likely occurs when two continental plates are pushed into one another? a. the plates stop moving c. the plates will form a mountain b. the plates will form a trench d. the plates break into pieces Look at the following concept map. On the back of your bubble sheet, you should number 25-29. For each number, fill in the missing information to complete the chart. Answer the following questions on the back of your bubble sheet. Please note that question 33 has two parts. Make sure you respond to both questions and put your answer in a complete sentence. Earth’s crust is described as “constantly shifting and moving.” Give three examples of evidence that supports the theory of Continental Drift. Write your answers on the back of the bubble sheet. 30. 31. 32. 33. Why did most scientists discredit Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift? Was validity in The Theory of Continental Drift ever realized by Alfred Wegener?