EDSE4275_PortfolioRubric_Fall2011
advertisement
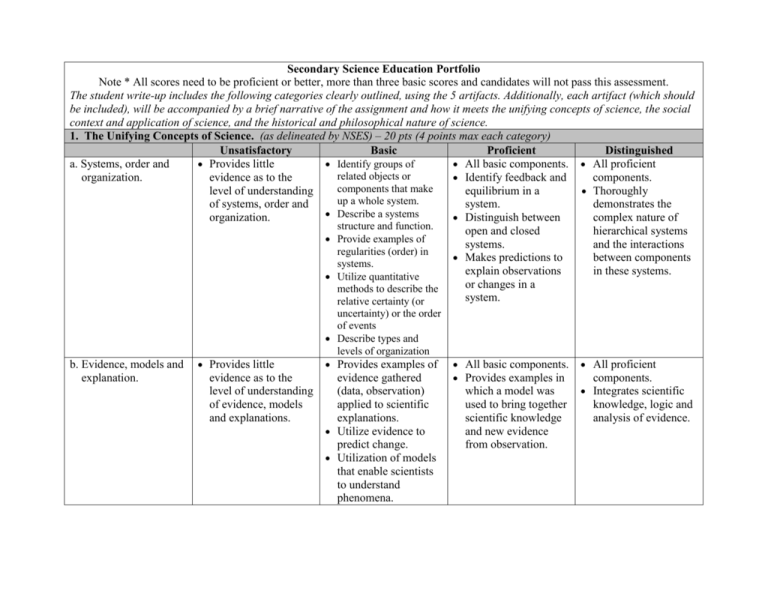
Secondary Science Education Portfolio Note * All scores need to be proficient or better, more than three basic scores and candidates will not pass this assessment. The student write-up includes the following categories clearly outlined, using the 5 artifacts. Additionally, each artifact (which should be included), will be accompanied by a brief narrative of the assignment and how it meets the unifying concepts of science, the social context and application of science, and the historical and philosophical nature of science. 1. The Unifying Concepts of Science. (as delineated by NSES) – 20 pts (4 points max each category) Unsatisfactory Basic Proficient Distinguished Identify groups of a. Systems, order and Provides little All basic components. All proficient related objects or organization. evidence as to the Identify feedback and components. components that make level of understanding equilibrium in a Thoroughly up a whole system. of systems, order and system. demonstrates the Describe a systems organization. Distinguish between complex nature of structure and function. open and closed hierarchical systems Provide examples of systems. and the interactions regularities (order) in Makes predictions to between components systems. explain observations in these systems. Utilize quantitative or changes in a methods to describe the system. relative certainty (or b. Evidence, models and explanation. Provides little evidence as to the level of understanding of evidence, models and explanations. uncertainty) or the order of events Describe types and levels of organization Provides examples of evidence gathered (data, observation) applied to scientific explanations. Utilize evidence to predict change. Utilization of models that enable scientists to understand phenomena. All basic components. Provides examples in which a model was used to bring together scientific knowledge and new evidence from observation. All proficient components. Integrates scientific knowledge, logic and analysis of evidence. c. Constancy, change and measurement. Provides little evidence as to the level of understanding of constancy, change and measurement. Provides examples of constancy. All basic components. Examples are Provides examples of change. Provides an example of measurement related to constancy or change. d. Evolution and equilibrium. Provides little evidence as to the level of understanding of evolution and equilibrium. Provides an example of evolution. Provides an example of equilibrium. e. Form and function. Provides little evidence as to the level of understanding of form and function. Provides an example of form and function (e.g. organisms, systems, objects). Explains how form and function are related. relevant, clear and directly connected to area of content expertise. An example in which change or constancy has been measured. Utilizes graphs and other visual interpretations of data to show change. All basic components. Evolution example provides evidence that current organisms, compounds, systems, etc. come from past forms. More than one example of equilibrium is provided. All basic components. Provides example of form and function in: organisms, systems and objects. Further elaborates on each example above relating the form to its function. All proficient components. Provides evidence demonstrating an understanding of the relationship between change and constancy in a system. All proficient components. More than one evolutionary example is provided beyond a biological application. Equilibrium examples demonstrate an understanding of balance and homeostasis. All proficient components. Provides more than one example relating form and function in: organisms, systems and objects. 2. Social context and application of science. 20 points (4 points max each category) Unsatisfactory Basic Proficient a. Personal and Provides little Provides some Provides evidence of community health. evidence as to the evidence benefits of physical level of understanding demonstrating basic fitness. of personal and knowledge of fitness, Provides an example community health. nutrition, of nutritional communicable knowledge. disease, Demonstrates noncommunicable knowledge of disease, disease communicable and prevention and noncommunicable environment hazards. diseases. Identifies risk behaviors related to disease prevention. Provides an example of environmental hazards. b. Socially important Provides little Provides example of All basic components. issues, science and evidence as to the how science and For examples given, technology. level of understanding technology affect demonstrates of social issues related issues related to understanding of the to science and human activity. influence science and technology. Provides examples of technology have on the relationship policy, economics, between science and ethics and politics. technology. Distinguished All proficient components. Provides details and documents demonstrating a thorough understanding of the topics listed under proficient. All proficient components Describes how funding sources influences science and technology. c. Environmental quality and population growth. d. Human and natural induced hazards. Provides no evidence related to the environment or population growth. Gives an example of environmental change. Provides no evidence Provides example of related to human and natural hazards. human induced hazard. Provides example of natural hazard. All basic components Provides more than All Proficient one example of environmental change. Describes the effect of an environmental change on populations. Provide an example of population growth on the environment. Distinguishes All basic components. Explains how human components. induced hazards effect populations. Explains how natural hazard effect populations. e. Natural resources. Provides no mention of natural resources. Provides examples of some natural resources. All basic components. Identifies natural resources with evidence of finite or cyclical natural of resources described. between human and natural changes in the environment and their effect on populations. Provides examples of a natural systems ability to maintain balance. Provides detailed examples of population growth and the negative impact on the environment. All proficient components. Provide examples of natural catastrophic events and costs of and impact on populations. For human and natural examples given, provide evidence of risk assessment and/or benefit of hazards. All proficient components. Demonstrates understanding of conservation of resources given as examples. 3. The historical and philosophical nature of science. 10 points (5 points max each category) Unsatisfactory Basic Proficient a. Historical and cultural Provides no evidence Provides an example All basic components. development of of historical or of a scientific event Provides an example science. cultural development that influenced where culture has of science. history. contributed to Provides an example scientific knowledge. of science as a human Provide an example endeavor. of an ethical scientific issue. Provide an example of a scientist who was influence by culture, societal or personal beliefs. b. Scientific inquiry. Provides no evidence Provides an example All basic components. Provide examples that of scientific inquiry. of how scientific science distinguishes knowledge is itself from other ways distinguished from of knowing through the non-scientific use of empirical knowledge. standards, logical arguments, and skepticism. Examples of scientific explanations that are consistent with experimental and observational evidence about nature. Examples of scientific ideas that have been subjected to several reviews. Distinguished All proficient components. Provide an example where science was influenced by social, cultural and/or personal beliefs. Provides several example of scientists who were influenced by society, culture and personal beliefs. All proficient components. An example of an issue where two scientists differ in their interpretations of the evidence or theory. Attachment NSTA Teaching Standards Portfolio Scoring Sheet Student’s Name: ________________________ Date Completed: ________________________ Instructor: ____Dr. Andrea Burrows____ Section 1. The unifying concepts of science – 20 pts a. Systems, order and organization. b. Evidence, models and explanation. c. Constancy, change and measurement. d. Evolution and equilibrium. e. Form and function. 2. Social context & application of science – 20 pts a. Personal and community health. b. Socially important issues, science and technology. c. Environmental quality and population growth. d. Human and natural induced hazards. e. Natural resources. 3. The historical & philosophical nature of science – 10 pts a. Historical and cultural development of science. b. Scientific inquiry. Score Comments