Science Subject Knowledge Audit
advertisement

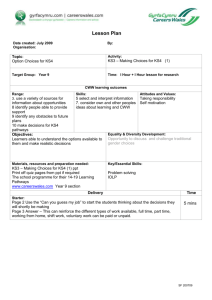
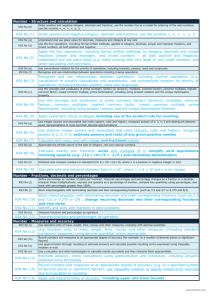
Ratings S Secure R Refreshment needed D Development needed PGCE Science KS3/4 subject knowledge audit Name: ……………………………………………. Area Level and year of previous study Rating Action taken Working scientifically Accuracy, precision, repeatability and reproducibility Development of theories: publishing results and peer review Scientific enquiries: independent, dependent and control variables Techniques, apparatus, and materials for fieldwork and laboratory work 1 Sampling techniques Data presentation methods, including tables and graphs SI units and IUPAC chemical nomenclature Simple statistical techniques Use and derive simple equations and carry out appropriate calculations 2 Area Level and year of previous study Rating Action taken Energy Motion and forces Physics KS3 Waves Electricity and electromagnetis m Matter Space physics 3 Physics KS4 Motion: Newton’s laws and momentum Energy: conservation, transfer, transformation, dissipation (and associated economic and environmental implications, including efficiency) Energy: transfers, work done, KE and gravitational PE, relationship between work and energy Kinetic theory and atomic structure as models to explain physical phenomena 4 Motion: Newton’s laws and momentum Energy: conservation, transfer, transformation, dissipation (and associated economic and environmental implications, including efficiency) Energy: transfers, work done, KE and gravitational PE, relationship between work and energy Electricity: generation, distribution and use; the relationship between power, energy and time 5 Area The particulate nature of matter Level and year of previous study Rating Action taken Atoms, elements and compounds Chemistry KS3 Pure and impure substances Chemical reactions Energetics The periodic table Materials Earth and atmosphere 6 Chemistry KS4 The chemical elements: atomic structure and the periodic table The chemical elements and compounds: structure and bonding (metallic, ionic, covalent and forces between molecules) Materials: How the properties can be explained in terms of their structure and bonding; how the properties determine the uses Chemical reactions: patterns and types of reaction (redox, neutralisation, electrolysis and polymerisation) 7 Chemical reactions: patterns and types of reaction (redox, neutralisation, electrolysis and polymerisation) Chemical reactions: controlling chemical reactions – rates of reaction and reversible reactions) Energy changes in chemical reactions 8 Area Cells and organisation Level and year of previous study Rating Action taken Biology KS3 Skeletal and muscular system Nutrition and digestion (including plants) Gas exchange systems (including plants) Reproduction (including plants) Health 9 Area Level and year of previous study Rating Action taken Classification Biology KS4 Plant biology (growth; photosynthesis; reproduction; internal regulation; response to environment) Human biology (factors affecting health; reproduction; growth and development; organ systems: circulatory, digestive, nervous; internal regulation) Cells (structure, animal plant microbial, division, specialisation) 10 Biochemistry (cell; respiration; photosynthesis; proteins; enzyme action; DNA; protein synthesis) Genetics (inheritance, mono and dihybrid cross; recessive, dominant and codominance Ecology (interdependence, ecosystems; energy flow; nutrient cycling; environmental change; indicators; reducing human impact on environment) Changes over time (Evolution; selection; adaptation) 11 Biochemistry (cell; respiration; photosynthesis; proteins; enzyme action; DNA; protein synthesis) Fieldwork (sampling techniques) 12