File
advertisement
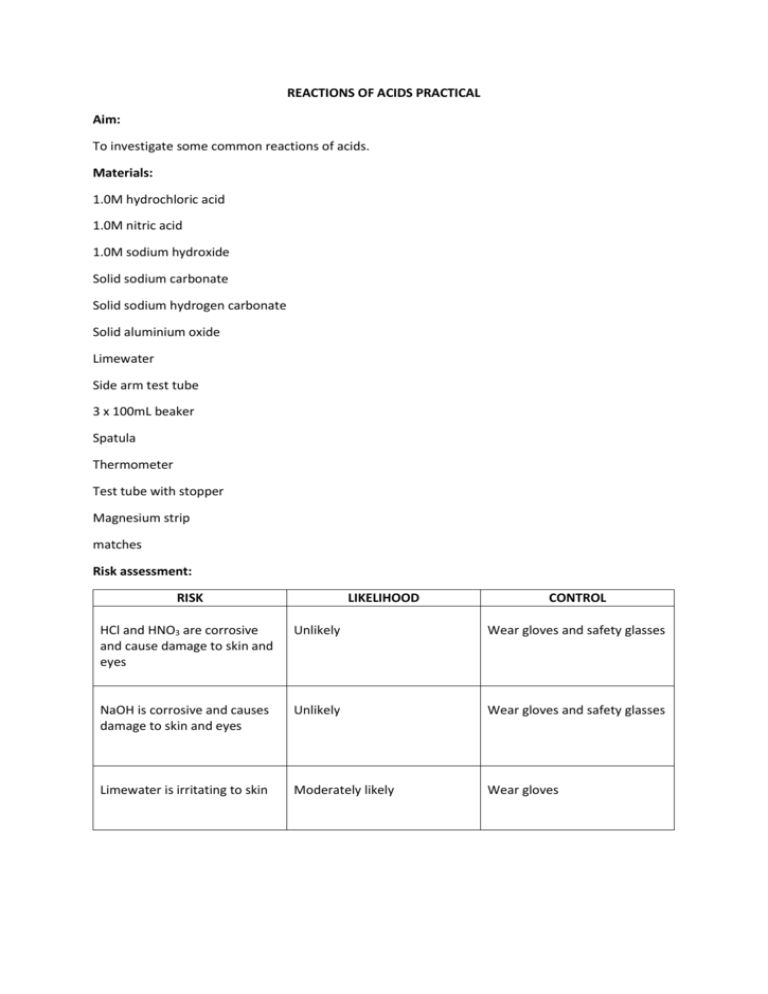
REACTIONS OF ACIDS PRACTICAL Aim: To investigate some common reactions of acids. Materials: 1.0M hydrochloric acid 1.0M nitric acid 1.0M sodium hydroxide Solid sodium carbonate Solid sodium hydrogen carbonate Solid aluminium oxide Limewater Side arm test tube 3 x 100mL beaker Spatula Thermometer Test tube with stopper Magnesium strip matches Risk assessment: RISK LIKELIHOOD CONTROL HCl and HNO3 are corrosive and cause damage to skin and eyes Unlikely Wear gloves and safety glasses NaOH is corrosive and causes damage to skin and eyes Unlikely Wear gloves and safety glasses Limewater is irritating to skin Moderately likely Wear gloves Results: Experiment number 1 2 3 4 5 What to do Place a piece of magnesium in a test tube with 3cm of hydrochloric acid and stopper. Hold the stopper on for about a minute then test the gas with a lit match. Place about 10mL of hydrochloric acid in a small beaker and take the temperature. Add about 10mL of sodium hydroxide and take the temperature again. Place a spatula of sodium carbonate into a small beaker and add 10mL of nitric acid. Record any temperature changes. Place a spatula of aluminium oxide into a small beaker and add 10mL of nitric acid. Record any temperature changes. Place a spatula of sodium hydrogen carbonate into a side arm test tube. Add 10mL of nitric acid. Stopper the tube and place the delivery tube into a small beaker of limewater. Observations Tube got hot; gas formed; gas made popping sound with match. Temperature increased by 5°C Temperature decreased 3°C, gas produced, solid dissolves Temperature increased by 4°C, dissolution not obvious Gas produced; makes limewater turn white/milky Discussion: In the first reaction, a metal reacts with an acid to produce salt and hydrogen gas: Magnesium + hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride + hydrogen General reaction: acid + metal salt + hydrogen Hydrogen makes a popping sound with a lit match due to this reaction: Hydrogen + oxygen water (+ energy) In the second reaction, this reaction occurs: Sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid sodium chloride + water General reaction: acid + base salt + water In the third reaction, nitric acid reacts with a carbonate: Nitric acid + sodium carbonate sodium nitrate + water + carbon dioxide General reaction: acid + carbonate salt + water + carbon dioxide The fourth reaction is the reaction of an acid and an oxide: Aluminium oxide + nitric acid aluminium nitrate + water General reaction: acid + oxide salt + water The fifth reaction is another acid/carbonate reaction, but this time the gas produced was bubbled through limewater using a side arm test tube and a delivery tube. The limewater turned milky white. Sodium hydrogen carbonate + nitric acid sodium nitrate + water + carbon dioxide General reaction: acid + hydrogen carbonate salt + water + carbon dioxide Limewater is a solution of calcium hydroxide. It reacts with carbon dioxide to form a white calcium carbonate precipitate: Calcium hydroxide + carbon dioxide calcium carbonate + water The only problem encountered in this task was that the limewater was already a bit cloudy to start with, so you had to observe carefully to see the precipitation occurring. Conclusion: Acids react with other substances in a variety of ways.