station 1: optics vocabulary
advertisement

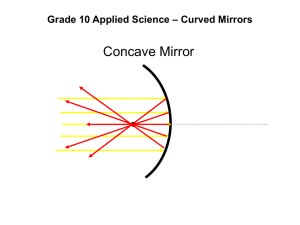
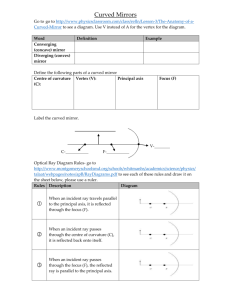
OPTICS REVIEW BELL RINGER STATIONS 1. Optics Definitions 2. Diagram and Properties of a Plane Mirror 3. Pinhole Camera Problem 4. Curved Mirror Calculation 5. Curved Mirror Diagram 6. Refraction 7. Lens Calculation 8. The Human Eye STATION 1: OPTICS VOCABULARY Write the word that corresponds to each definition or statement. a) The name of the ray that strikes a surface. b) The location where reflected rays cross the principal axis on a concave mirror. c) The angle where total internal refraction will occur (angle of refraction is 90o). d) The ratio of image height to object height. e) A type of light source produced by some chemical reactions (e.g. glowsticks) f) A type of light source produced by very hot objects (e.g. the Sun). g) The characteristic that distinguishes different forms of electromagnetic waves (e.g. red, blue, X-rays etc.) STATION 2: PLANE MIRRORS a) Sketch this diagram on your page. Construct a ray diagram to show how your eye sees an image in a flat (plane) mirror. b) State 5 properties of the image formed by this mirror. STATION 3: PINHOLE CAMERA PROBLEMS a) Sketch a pinhole camera diagram and label the diagram as to locate do (distance to object), di (dstance to image), ho (height of object) and hi (height of image). b) On the west coast of British Columbia, the giant Sitka spruce can grow to a height of 100m (the length of the football field!). If a 20 cm long pinhole camera takes a picture of a 100 m tall Sitka spruce from a distance of 2 km away, how large is the image? STATION 4: CURVED MIRROR CALCULATIONS a) A mirror with a focal length of -5 cm produces an image of an object 25 cm away. Calculate the image distance. b) Is this a converging or diverging mirror? c) Is this a convex or concave mirror? d) What is the magnification of the image? e) Is the image real or virtual? f) Is the image upright or inverted? STATION 5: CURVED MIRROR DIAGRAM a) Draw a ray diagram of a concave mirror with a focal length of 5 cm and an object at 4 cm. b) State 3 properties of the image. c) Draw a ray diagram of a convex mirror with focal length – 5 cm and an object at 4 cm. d) State 3 properties of the image. STATION 6: REFRACTION a) A ray of light in air enters a square piece of cubit zirconia (n = 2.15) with an incident angle of 20o. Calculate the angle of refraction for light entering and leaving the zirconia crystal. b) Draw a ray diagram to represent what is happening in part a). c) What is the critical angle for light travelling from zirconia back into air? STATION 7: LENS CALCULATIONS a) A student placed a candle 25 cm from a convex lens and produced a real, inverted image that was 75 cm from the lens. What is the focal point of this lens? b) What is the magnification of the lens? c) If the candle flame was 5 cm tall, how tall is the image? STATION 8: THE HUMAN EYE a) What part of the eye form refracts light? b) What part of the eye is the site of image formation? c) What part of the eye creates the shape? d) What part of the eye adjusts the amount of light entering? e) What condition does this person suffer from? f) How can it be corrected using lenses? g) Sketch a ray diagram to show how corrective lenses will work for this condition.