RNA polymerase
advertisement

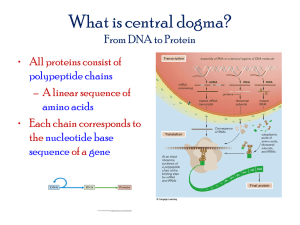
Name: ______________________________ Period: _____ Date: ________________________ Ch 13 Pretest: RNA and Protein Synthesis Matching: Place the letter of the word that best answers the question on the blank. Letters may be used once, more than once or not at all 1. _______ matches amino acids to the growing polypeptide 2. _______ process of rewriting DNA into RNA, takes place inside the nucleus 3. _______ nitrogen base that binds with adenine in RNA 4. _______ any error in the DNA sequence, or gene expression 5. _______ 3-nucleotide sequence on the tRNA that matches mRNA 6. _______ coded message copied from DNA that leaves the nucleus 7. _______ building blocks of proteins 8. _______ five carbon sugar found in RNA 9. _______ cause of a mutation A. amino acid B. anticodon C. codon D. chromosome mutation E. deletion F. frameshift mutation G. inversion H. mRNA I. mutagen J. mutation K. nondisjunction L. peptide bond M. point mutation N. polypeptide O. promoter P. protein synthesis Q. ribose R. rRNA S. RNA T. RNA polymerase U. substitution V. tRNA W. termination signal X. transcription Y. translation Z. translocation AA. uracil 10. _______ frameshift mutation where a nucleotide has been removed 11. _______ process of making proteins out of RNA (in general) 12. _______ forms between two amino acids to make a protein 13. _______ chromosome mutation where segment breaks off, flips around and reattaches 14. _______ three nitrogen bases on mRNA, acts as a code 15. _______ process of mRNA being decoded into a protein, done by ribosomes 16. _______ chain of amino acids 17. _______ material that makes up ribosomes 18. _______ general term for any change in a DNA or RNA sequence 19. _______ enzyme responsible for copying DNA onto mRNA 20. _______ single strand of ribose + phosphate + nitrogen base 1 There are three types of RNA listed below. Name each one and tell its function in transcription/translation (protein synthesis) 21. mRNA 22. rRNA 23. tRNA There are two steps in transcription, the first step of protein synthesis. Draw/describe each below the number. 24. 25. 26. Where in the cell does transcription take place? There are three steps in translation, the second step of protein synthesis. Draw/describe each below the number. 27. 28. 29. 30. Where in the cell does translation take place? Here is a DNA strand: T A C G T C A T A C G C A T A 31. The matching DNA strand is: 32. The matching RNA strand is: 33. The amino acids would be: (use ½ sheet provided) 2 Here is a list of point mutations. Describe each: 34. Substitution 35. Insertion 36. Deletion Here is a list of chromosomal mutations. Describe each: 37. Deletion 38. Duplication 39. Inversion 40. Translocation 41. Nondisjunction 3 Answer Key__ Name: _ Period: _____ Date: ________________________ Ch 13 Pretest: RNA and Protein Synthesis Matching: Place the letter of the word that best answers the question on the blank. Letters may be used once, more than once or not at all V___ matches amino acids to the 1. ___ growing polypeptide A. amino acid B. anticodon takes place inside the nucleus C. codon D. chromosome mutation in RNA E. deletion F. frameshift mutation gene expression G. inversion H. mRNA that matches mRNA I. mutagen J. mutation leaves the nucleus K. nondisjunction L. peptide bond X___ process of rewriting DNA into RNA, 2. ___ AA___ nitrogen base that binds with adenine 3. __ J___ any error in the DNA sequence, or 4. ___ B___ 3-nucleotide sequence on the tRNA 5. ___ H___ coded message copied from DNA that 6. ___ A___ building blocks of proteins 7. ___ Q___ five carbon sugar found in RNA 8. ___ I 9. ___ ___ cause of a mutation E___ frameshift mutation where a nucleotide 10. ___ has been removed P___ process of making proteins out of RNA 11. ___ M. point mutation N. polypeptide O. promoter P. protein synthesis Q. ribose R. rRNA S. RNA T. RNA polymerase (in general) U. substitution V. tRNA a protein W. termination signal X. transcription breaks off, flips around and reattaches Y. translation Z. translocation L___ forms between two amino acids to make 12. ___ G___ chromosome mutation where segment 13. ___ C___ three nitrogen bases on mRNA, acts as 14. ___ AA. uracil a code Y___ process of mRNA being decoded into a protein, done by ribosomes 15. ___ 4 N___ chain of amino acids 16. ___ R___ material that makes up ribosomes 17. ___ M___ general term for any change in a DNA or RNA sequence 18. ___ T___ enzyme responsible for copying DNA onto mRNA 19. ___ S___ single strand of ribose + phosphate + nitrogen base 20. ___ There are three types of RNA listed below. Name each one and tell its function in transcription/translation (protein synthesis) (transcription & translation) takes info from DNA out of nucleus to be decoded 21. mRNA (translation) makes up ribosome that decode mRNA using tRNA to make proteins 22. rRNA (translation) brings amino acids to the ribosome, anticodon matches with codon on mRNA, peptide bond forms 23. tRNA There are two steps in transcription, the first step of protein synthesis. Draw/describe each below the number. 24. 25. DNA opens up (RNA polymerase) mRNA matches one side of DNA 26. Where in the cell does transcription take place? 5 nucleus There are three steps in translation, the second step of protein synthesis. Draw/describe each below the number. 27. 28. 29. Ribosome codon matches attaches anticodon to mRNA peptide bond forms 30. Where in the cell does translation take place? Cytoplasm using ribosomes (could also say ER) Here is a DNA strand: T A C G T C A T A C G C A T A 31. The matching DNA strand is: A T G C A G T A T G C G T A T 32. The matching RNA strand is: A U G C A G U A U G C G U A U 33. The amino acids would be: (use ½ sheet provided) met - glu - tyr - ala - tyr Here is a list of point mutations. Describe each: 6 one letter put in in place of another 34. Substitution: new letter put in, (new letter added) 35. Insertion: 36. Deletion: one letter left out Here is a list of chromosomal mutations. Describe each: 37. Deletion: one or more genes left out extra copies of one or more genes 38. Duplication: put in backwards, or order switched 39. Inversion: gene one or more genes moved for one chromosome to another 40. Translocation: homologs don’t separate correctly during anaphase I 41. Nondisjunction: 7 8