unit 3 – pelagic zone
advertisement

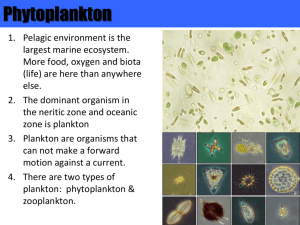
UNIT 3 – PELAGIC ZONE Phytoplankton Pelagic environment is the largest marine ecosystem. More food, oxygen and biota (life) are here than anywhere else. The dominant organism in the neritic zone and oceanic zone is ___________ _______________ are organisms that cannot make a forward motion against a current. There are two types of plankton: ________________________________ Phytoplankton are _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Produce __________ of all atmospheric oxygen, and are critical biomass. They are adapted to a floating lifestyle because of their: 1. Small size - diffusion is quick, frictional drag from large surface area to low volume ratio helps slow sinking. 2. Structure - disks shaped or chains aid in floating. 3. Low density - light ions and lipid by-products of photosynthesis reduce density and aid floating. They are grouped by ______________. Different pigments allow them to take advantage of different light penetration at various depths. Phytoplankton are found in 3 kingdoms and 5 phyla. Commercially, algae are used as ____________________ to give a smooth texture to puddings, toothpaste, ice cream, and shoe polish. A “bloom” is an increase in population density of phytoplankton associated with _____________________. It can be the result of upwelling or excessive nutrients. Upwelling is caused ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Blooms are good for the food chain, fishing, and _______________________ Blooms of some plankton, especially in warm water, may be harmful. When storms follow hot, dry weather, dominant cysts of toxic phytoplankton may be released. As these toxic blooms enter the food chain, they give off chemical neurotoxins that paralyze the predator’s nerves controlling breathing and heart rate. Human consumption of these organisms result in ______________________ ____________________________________ due to biomagnification. The dominant phytoplankton in warm water are ______________________. They cause a condition called red tide. Red tides is a result of a wind pattern, Peruvian fishermen named “El Nino”. The name refers to the Christ Child, because the condition was first observed during the warm, Christmas months of the Southern Hemisphere. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Zooplankton Zooplankton are _________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ They are the smallest and most numerous marine animals. Their population density depends on ________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ There are two groups of zooplankton: 1. Meroplankton - planktonic larvae who will become _____________________________ __________________________________________________________ - The advantage of meroplankton lifestyle is reduced competition from adults for the same basic needs. - Predation is extremely high because of their size and lack of adaptability. 2. Holoplankton - __________________________________________________________ - Remain visible, but tiny Copepods (phylum: Arthropoda) are 95% of all zooplankton. Others are krill, foraminifera and members of the Kingdom Protista, Phylum Protozoa Zooplankton are grouped by the way they move. 1. By ___________________________________________ 2. By ___________________________________________ 3. By ___________________________________________ Vertical Migration Vertical migration is a daily pattern of phytoplankton and zooplankton changing positions like a day and night shift. During the day – - phytoplankton produce _______________________________________ - Because oils are less dense than water, the products of photosynthesis increase their _____________________. As the sun goes down – - The phytoplankton __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ - In response to the “rain” of phytoplankton descending, the zooplankton move up in the water column to graze on them. As the sun comes up – - Photosynthesis again causes more production than the organisms need at that time, the phytoplankton become lighter and begin to float upward. - The zooplankton begin their downward response to graze again and to take advantage of reduced visibility and less heat than at the surface. These two periods of grazing: - __________________________________________________________ - __________________________________________________________ - __________________________________________________________ Taxonomy Taxonomy is a system of grouping organisms based on Phylogeny (evolutionary relationships) Biochemistry Morphology (structure) There are 7 taxa: 1. Kingdom: the 5 kingdoms are: - ______________________ - ______________________ - ______________________ - ______________________ - ______________________ 2. Phylum: major marine phyla from kingdom Animalia: - Porifera - Cnidaria - Annelida - Mollusca - Arthtropoda - Echinodermata - Chordata 3. Class: major marine classes from Phylum Mollusca: - ___________________ - ___________________ - ___________________ From Phylum Arthropoda: - ___________________ From Phylum Chordata: - Chondrichtyes - Osteichthyes - Amphibia - Reptilia - Aves - Mammalia 4. Order: - Subgroups of a class - for birds and fish the suffix is “formes” 5. Family: - subgroups of an order; - suffix is “ae” Ex: ________________________ 6. Genus: - subgroups of families - first part of scientific name - always capitalized Ex: Homo 7. Species: - __________________________________________________________ - second part of the scientific name - always in lower case Ex: sapiens Carrolus Linneaus developed a system of naming organisms based on visible characteristics. The use of terms (genus & species) is called binomial nomenclature or the scientific name. A ___________________________ is used to identify the names of unfamiliar organisms. The key is based on two choices for each pair or related characteristics. Scientists use a revised system based on biochemistry to name all the discovered organisms. Only about 1 million of nearly 10 million organisms have been identified and named so far. Order Cetacea - Whales, Dolphins, Porpoises Phylum Chordata; Class Mammalia Cetaceans are grouped on the basis of their mouths: a. Mysticeti - __________________________________________________________ - Both nostrils have a blow hole b. Ordontoceti - __________________________________________________________ - Carnivores - 2 nostrils but only 1 blow hole - Smaller in size Marine Mammal Characteristics: 1. __________________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________ 4. __________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________ 6. __________________________________________________ Blue whale - ________________________________________ - 100 ft. long - 150 tons. Narwhal - ________________________________________ - left tooth found only in males. Beluga whales - pure white as adults - “sea canaries” Dolphins - are the most social 7 intelligent whale. - Body temperature of 97.7o F - 7 minutes between breaths - 25 mph swimming speed - River dolphins of S. America cannot swim in a straight line Marine Mammals Protection Act of 1972 Whales and all marine mammals are protected Passed in response to ____________________ killing of dolphins in huge 4,000 ft long nets. Many are still being hunted to extinction under the guise of scientific research or are by-catch of the tuna fishery. 1 million deaths/year Tuna caught on lines is “certified” as dolphin safe by company employees International Whaling Commission (I.W.C.) is a whaler’s organization that sets quotes based on catch size. They are not a regulatory agency and compliance is voluntary. Cetacean Adaptations: Swimming: - powerful tail flukes - __________________________________________________________ - Sei whales are fastest (40mph) Digestion - Multi-compartmentalized stomachs “chew” food - Teeth are conical and unspecialized - Baleen whales o feed by swimming through pockets of plankton o ______________________________________________________ o Stomachs hold 2 tons of krill - Toothed whales hunt in packs and seek out individual fish, penguins, seals, sharks or other whales. Circulation - high blood volume holds maximum oxygen and glucose levels - Large whales have large veins - Blood can be shunted to brain, heart, lungs, and muscles and away from stomach and kidneys to protect vital organs. - A 4-chambered heart can transfer arteriole heat to the _____________ __________________________________________________________ - ___________________ insulates against the cold. - Overheating is solved by _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________. - Whales in captivity exercise less and often lose the ability to cool off by straightening the fins. Senses - Vision is poor - Vocalizations & echo-location compensate - Whales have no vocal cords but make songs, clicks and shines by vibrations in the _________________________. - Communicate to: o __________________________________ o __________________________________ o __________________________________ - Families of whales have their own dialect - Sounds are emitted and amplified in the head through an oil filled cavity called a ______________. - __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ - The sounds are extremely accurate and VERY LOUD - Can be used to stun prey - Blue whale can make a sound of 188 decibels. (can rupture a human eardrum) - When whales enter the thermocline, sounds can be heard 1/4 of the distance around the earth. Diving: - lungs are completely filled and emptied quickly through the blow hole on the top of the head. - A trachea under the blow hole connects directly to _____________. - Cannot breathe through their mouth. - The nasal passage closes when relaxed to prevent water from entering the lungs & allows them to sleep for short periods without drowning. - __________________________________________________________ - Some whales go to depths of 13,000 ft and breathe every 90 minutes - __________________________________________________________ - __________________________________________________________ Excretory: - Specialized kidneys allow whales to drink salt water. - The urine is very saline Reproduction - mating usually occurs in _____________________________ - Implantation of the egg may be delayed several months, so that gestation finishes up in the warm summer months. - Many whales only have one calf every ___________________. - Babies weigh _____________________