09 APD Excellent examples of H&Ps part 2
advertisement

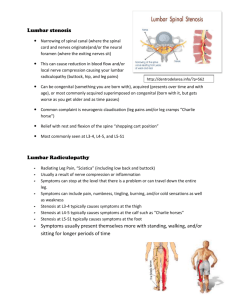
M2 Admission Note 11/2/2010 2:00pm CC: Ms. S.S. is a 71 year-old female complaining of bilateral lower back, buttock, and posterior and lateral leg pain. Source: The history was provided by Ms. S.S., who appears to be a reliable informant. HPI: Ms. S.S. has experienced 4 years of progressively worsening pain in her lower back, “pinching” in her buttocks, bilateral radiating pain in her posterior and lateral legs (left > right), and numbness and tingling in both feet. Over the last 2 months, she has rated her pain as 10/10 and was forced to quit her parttime job in September, stating that she could no longer stand for more than a few minutes at a time. Ms. S.S. has found minor relief with Aleve. She states that the pain is worsened by lifting medium to heavy objects (e.g., a gallon of milk). Ms. S.S. has undergone physical therapy and epidural steroid injections with minimal to no relief of symptoms. Ms. S.S. has had an MRI showing spinal stenosis. Dr. Surgeon performed a lumbar laminectomy of L4-L5 on 11/1/10. PMH: 1) Osteoarthritis 2) Hypertension 3) Hypercholesterolemia 4) Right eye retinal detachment (2000) Past Surgical History: 1) tonsillectomy at age 10 2) Total hysterectomy (2007) Meds: 1) “Norvas” (Norvasc?)5mg1 tablet q day 2) Simvastatin 20mg 1 tablet q PM Allergies: NKDA Family History: Father, deceased age unknown, cause unknown Mother, deceased age 70, cause “lung related” Sister, deceased age early 50s, car accident, healthy at the time Patient has no children Social History: Ms. S.S. worked as technologist in the pathology department of local hospital for past 30 years, stopped working in September 2010 (see HPI). M2 Physicianship Applied Physical Diagnosis Excellent Examples of H&Ps – Part 2 Divorced, lives alone Patient has no history of smoking Patient has no history of illict drug use Alcohol: one drink every 1 to 2 months Review of Systems: General: no weight changes, fatigue, weakness, fevers or chills Skin: no rashes, masses, jaundice, bruising, or changes in hair or nails HEENT: + right eye blindness, + left eye cataract, no headaches, diplopia, or visual blurring in left eye; no hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo, earache, or discharge; no epistaxis or stuffiness; + goiter, no sore throat, hoarseness, or dysphagia Musculoskeletal: + arthritis, + bilateral shoulder pain (left > right), bilateral knee pain, and low back pain; no gout, cramps, or muscle weakness Endocrine: no diabetes, heat/cold intolerance, polydipsia, polyphagia, diaphoresis, skin color change, or excess hair growth Pulmonary: no cough, dyspnea, wheezing, asthma, bronchitis, emphysema, pneumonia, or TB Cardiovascular: + high blood pressure, “slight” anemia, and bilateral varicose veins on calves; denies murmurs, orthopnea, chest pains, palpitations, edema, or recent transfusions GI: + lactose intolerance; no nausea, vomiting, heartburn, changes in appetite, bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, gas, jaundice, hemorrhoids,melena, or hematochezia GU: no polyuria, hematuria, dysuria, urgency, hesitancy, incontinence, or urinary tract infection Neuro: + numbness/tingling in feet bilaterally (left > right), no headaches, fainting, seizures, paralysis, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, tremors, or depression Gynecological: menopause age early 50s Physical Exam: General: older, groggy, well-nourished woman, lying in bed, pleasant and cooperative during exam Vitals: Temp (not measured), BP = 124/78, HR = 80, RR = 20 Skin: No rashes, lesions, erythema, or bruising M2 Physicianship Applied Physical Diagnosis Excellent Examples of H&Ps – Part 2 HEENT: Cranium normal; no occipital, post-auricular, submandibular, or cervical lymphadenopathy; tympanic membranes unremarkable; blind in right eye, visual acuity 20/40 in left eye, extraocular movements intact, right pupil round, unreactive to light and lacks consensual light reflex, right eye accomodation present; left pupil round, and reactive to light and accommodation; no sinus tenderness; oral cavity unremarkable; neck is supple with a small yet palpable goiter, no tracheal deviation. Lungs: anterior and posterior fields clear to auscultation bilaterally Cardiac: regular rate and rhythm. Normal S1 and S2. No murmurs, gallops, or rubs Abdomen: Soft, nondistended, nontender, active bowel sounds. No masses or organomegaly, no costovertebral angle tenderness. Hysterectomy scar present. Extremities: No edema, clubbing, cyanosis Breast, Genital, and Rectal: not conducted Neuro: Mental status: alert, fully oriented, answers questions appropriately Cranial nerves: II-XII intact bilaterally Motor: normal tone. Strength 5/5 throughout bilaterally Sensory: normal vibratory, pinprick, and proprioceptive sense throughout bilaterally Problem List: 1) low back, buttock, and leg pain 2) hypertension 3) Hypercholesterolemia 4) Goiter Assessment and Plan: Ms. S.S. is a 71 female with a history of osteoarthritis, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia who presents with four years of progressively worsening and radiating low back, buttock, and posterior and lateral leg pain. Status post lumbar laminectomy of L4-L5. 1) Bilateral low back, buttock, and leg pain Assessment: Differential diagnosis for pain in this region includes lumbar spinal stenosis, sciatic nerve entrapment, peripheral vascular disease, vascular claudication, and urinary tract infection. The presence of an infection could be detected with urinalysis. Although a UTI could cause referred pain to the patient’s lower back, it is unlikely that it would cause pain in her legs. This diagnosis also seems unlikely considering the patient’s denial of polyuria, hematuria, or urgency. Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) or claudication in M2 Physicianship Applied Physical Diagnosis Excellent Examples of H&Ps – Part 2 Ms. S.S.’s lower extremities could explain the pain in her legs and tingling in her feet. She is at risk for PVD considering her age, hypertension, high cholesterol, and the presence of varicose veins on her posterior legs. Claudication could be evaluated with an angiography or Doppler ultrasound of her lower extremities. Pertinent negatives for PVD include no history of diabetes or smoking, a normal dorsalis pedis pulse, and no subjective feelings of cold feet. Likely diagnoses include lumbar spinal stenosis and sciatic nerve entrapment. MRI would be one of the best ways to differentiate between a central (stenosis or disc protrusion) or peripheral (sciatic nerve) issue. If the symptoms were caused by sciatic nerve impingement, such as in the case of piriformis syndrome, improvement would have been expected with the patient’s more conservative measures like physical therapy. A recent MRI showed lumbar spinal stenosis in the L4-L5 region of the patient, making this the most likely cause of her symptoms. This diagnosis is supported by the patient’s osteoarthritis and subjective complaints of increased pain with standing and loading. With this diagnosis, the physical exam prior to surgery would have been likely to find decreased lumbar extension, and in the area of L4-L5 decreased sensation, strength, decreased reflex, and a characteristic pain pattern in the posterior legs with worse signs unilaterally. Ms. S.S. underwent a L4-L5 lumbar laminectomy yesterday. Plan (post-op): a) Social work consult: determine possible in-home care since patient lives alone b) Physical and occupational therapy consult c) Patient education regarding deep vein thrombosis (DVT): look out for hard, red, swollen, painful calves or difficulty breathing. If symptoms develop, patient should go to the ER immediately d) Pain management and education about side effects of narcotics including driving impairment and constipation e) Follow up with surgeon in one week 2) Hypertension Assessment: Ms. S.S. has a history of high blood pressure and is currently taking Norvasc (5mg) 1 tablet q day. Blood pressure today was 124/78 which indicates that the patient is likely receiving an sufficient dose of medication. Plan: Continue to monitor blood pressure in her PCP’s office and at home to ensure continued progress Educate patient on the importance of low sodium diet and exercise once she is recovered from surgery 3) Hypercholesterolemia M2 Physicianship Applied Physical Diagnosis Excellent Examples of H&Ps – Part 2 Assessment: Ms. S.S. has a history of high cholesterol that she currently is treating with Simvastatin (20mg) 1 tablet q PM. Plan: a) Continue to monitor cholesterol in her PCP’s office b) Check liver function tests every 6 months c) Educate patient about avoiding grapefruit juice while on medication d) Educate patient on the importance of low cholesterol diet and exercise 4) Goiter Assessment: Ms. S.S. was told she had a goiter about 3 years ago by her PCP. It is small, yet palpable during physical exam of the neck. The goiter is asymptomatic and her PCP feels that at this time it does not warrant treatment. Ms. S.S. agrees with this assessment. Plan: a) Educate patient about possible symptoms including: tight feeling in the throat, coughing, hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing or breathing. b) Follow up with PCP/endocrinologist if any changes noted in order to assess cause and begin treatment (Synthroid, surgery, etc). c) Check TSH, Free T4. Student Name, M2 M2 Physicianship Applied Physical Diagnosis Excellent Examples of H&Ps – Part 2