Study Guide – Astronomy Define Each: 1. Precession 2. Nutation 3
advertisement

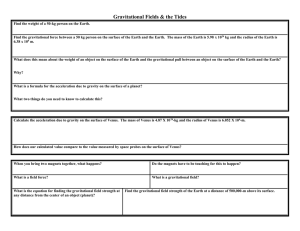
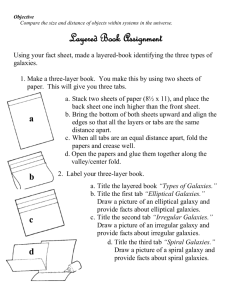
Study Guide – Astronomy Define Each: 1. Precession 2. Nutation 3. Plane of the ecliptic 4. Spring tides 5. Neap tides 6. Revolution 7. Rotation 8. Tidal Range 9. Big Bang Theory 10. Parallax 11. Light-year 12. Apparent Magnitude/brightness 13. Absolute Magnitude/brightness 14. Binary stars 15. Chromosphere 16. Corona 17. Photosphere 18. Nuclear Fusion 19. Sunspots 20. Prominences 21. Solar Winds 22. Solar Flares 23. Auroras 24. Spiral Galaxy 25. Elliptical Galaxy 26. Irregular Galaxy 27. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Things to know: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What does e=mc^2 mean and how does it explain the amount of energy that is released during nuclear fusion? Understand how binary stars orbit each other. Know what the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude is. Be able to explain the difference between spring tides and neap tides and how the position of the moon affects them. How does the tilt of Earth’s axis affects its seasons? Need to be able to explain the big bang and evidence that supports the theory. Understand how galaxies, stars, solar systems, and planets form. Important diagrams to memorize: 1. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram (pg. 704) 2. Galaxies (spiral, elliptical, and irregular) (pg. 717) 3. 4. Structure of the sun (pg. 685) Precession (pg. 625) Practice Makes Perfect (write the page number you found your answer): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. pg. 629 (1-2) pg. 639 (4) pg. 690 (1-8) pg. 695 (7-10; 22) pg. 697 (2-6) pg. 706 (1-5) pg. 721 (1-7) pg. 725 (1-5; 9-14; 22-23)