summary
advertisement

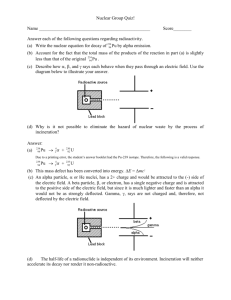
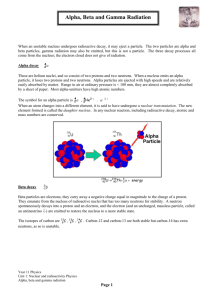
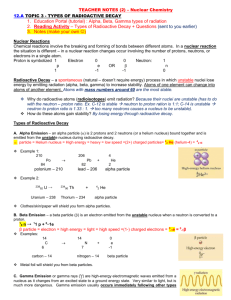
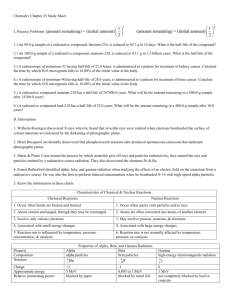
Robert Jakubek and Michael Maki Nuclear Chemistry Given Equations and Values: c=2.99792458×108 m/s, E = mc2, –dN/dt = A = kN, N = Noe–kt, A = Aoe–kt , PV=nRT, and R=0.08206 Radioactivity/ Radioactive Decay: Is a property of matter whereby an unstable nucleus spontaneously emits small particles and/or energy in order to attain a more stable nuclear state. Radioactive isotope/ Radioisotope: An isotope that contains an unstable nucleus. Sub-atomic particles: Beta particle (Electron), Alpha particle (Helium nucleus), Positron, and Neutron. Neutron: Are often emitted in nuclear reactions Positron: Are the positive equivalents of electrons or beta particles. Alpha Decay: Alpha decay is the spontaneous radioactive decay where an alpha particle is produced. Gamma Rays: Are produced when some radioactive decay events occur that leave the nucleus with excess energy. Gamma Radiation: High-energy photons that are emitted by radioactive nuclei. Gamma radiation is very high-energy ionizing radiation. Beta Decay: Beta decay refers to the spontaneous radioactive decay where a beta particle is produced. Electron Capture: Is a type of radioactive decay where the nucleus of an atom absorbs a K or L shell electron and converts a proton into a neutron. Nuclear Mass: The mass of an atomic nucleus, which is usually measured in atomic mass units. Nuclear Charge: The effective nuclear charge is the net charges an electron experiences in an atom with multiple electrons. Nucleons: Nucleons are subatomic particles, such as protons and neutrons that exist in the nuclei of atoms. Half-life: Is the time required for a quantity to fall to half its value as measured at the beginning of the time period. Nuclear Fission: A nuclear reaction in which a heavy nucleus splits spontaneously or on impact with another particle, with the release of energy. Nuclear Fusion: A nuclear reaction in which atomic nuclei of low atomic number fuse to form a heavier nucleus with the release of energy.