Chapter 2
advertisement

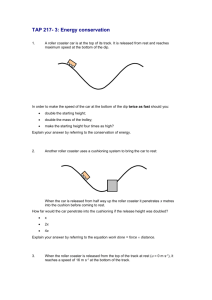
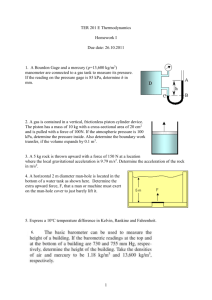
Assignment No. 1 Chapter 1: 1.5 Pressures up to 3,000 bar are measured with a dead-weight gauge. The piston diameter is 4mm. What is the approximate mass in Kg of the weights required? 1.10 The first accurate measurements of the properties of high-pressure gases were made by E. H. Amagat in France between 1869 and 1893. Before developing the dead-weight gauge, he worked in a mine shaft, and used a mercury manometer for measurements of pressure to more than 400 bar. Estimate the height of manometer required. 1.14 A 70-watt outdoor security light burns, on average, 10 hours a day. A new bulb costs $ 5.00, and the lifetime is about 1,000 hours. If electricity costs $ 0.10 per kW-hour, what is the yearly price of “security,” per light? 1.18 An automobile having a mass of 1,250 kg is traveling at 40 m.s-1. What is its kinetic energy in kJ? How much work must be done to bring it to a stop? Chapter 2: 2.4 An electric motor under steady load draws 9.7 amperes at 110 volts, delivering 1.25 (hp) of mechanical energy. What is the rate of heat transfer from the motor, in kW? 2.7 A renowned laboratory reports quadruple-point coordinates of 10.2 Mbar and 24.1°C for four-phase equilibrium of allotropic solid forms of the exotic chemical β-miasmone. Evaluate the claim. 2.12 Heat in the amount of 7.5 kJ is added to a closed system while its internal energy decreases by 12 kJ. How much energy is transferred as work? For a process casing the same change of state but for which the work is zero, how much heat is transferred? 2.17 A hydroturbine operates with a head of 50 m of water. Inlet and outlet conduits are 2 m in diameter. Estimate the mechanical power developed by the turbine for an outlet velocity of 5 m s-1. 2.23 A stream of warm water is produced in a steady-flow mixing process by combining 1.0 kg s-1 of cool water at 25 °C with 0.8 kg s-1 of hot water at 75 °C. During mixing heat is lost to the surroundings at the at the rate of 30 kJ s-1. What is the temperature of the warm-water stream? Assume the specific heat of water constant at 4.18 kJ kg-1 K-1. 1 2.28 Water flows through a horizontal coil heated from the outside by high-temperature flue gases. As it passes through the coil the water changes state from liquid at 200 kPa and 80 °C to vapor at 100 kPa and 125 °C. Its entering velocity is 3 m s-1 and its exit velocity is 20 m s-1. Determine the heat transferred through the coil per unit mass of water. Enthalphies of the inlet and outlet streams are: Inlet: 334.9 kJ kg-1; Outlet: 2,726.5 kJ kg-1 2.36 One kilogram of air is heated reversibly at constant pressure from an initial state of 300 K and 1 bar until its volume triples. Calculate W, Q, ΔU and ΔH for the process. Assume for air that PV/T = 83.14 bar cm3 mol-1 K-1 and Cp = 29 J mol-1 K-1. 2. 37 The conditions of a gas change in a steady-flow process form 20 °C and 1,000 kPa to 60°C and 100 kPa. Devise a reversible nonlfow process (any number of steps) for accomplishing this change of state, and calculate ΔU and ΔH for the process on the basis of 1 mol of gas. Assume for the gas that PV/T is constant. Cv = (5/2)R and Cp = (7/2)R. 2