ACTION POTENTIAL PRACTICE QUIZ The ______ is the main part
advertisement

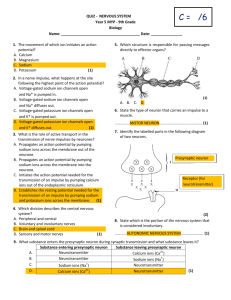
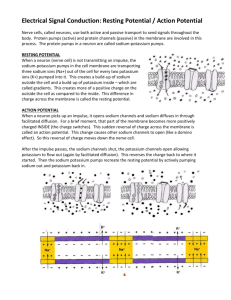
ACTION POTENTIAL PRACTICE QUIZ 1. The ______ is the main part of the neuron that contains neurotransmitter receptors (i.e. receives incoming messages), and the ______ is the main conductor of the action potential along the neuron's length. A. Axon, dendrites B. Dendrite, axon C. Soma, axon D. Nodes of Ranvier, dendrite 2. In response to an action potential, a presynaptic neuron releases a chemical called a ______ which diffuses across the ______ to activate ______ on the postsynaptic cell. A. Neurotransmitter, synaptic gap, synaptic vesicles B. Neurotransmitter, synaptic gap, receptors C. Neuromodulator, synaptic gap, motor end plate D. Catecholamine, myelin, receptors 3. During its resting state, the electrical charge inside the neuron is ______ compared to the outside. a. Negative (-70mv) b. Positive (+70mv) c. Neutral (0mv) d. It differs greatly depending upon what part of the neuron is examined 4. During the neuron's resting state, large amounts of positive ______ ions are found in the extracellular fluid, whereas relatively more positive ______ ions are found inside the cell. a. Sodium, potassium b. Potassium, chloride c. Chloride, anions d. Sodium, lithium 5. The site where the threshold potential (-55mv) has to occur first in order to produce an action potential is the: a. Axon b. Axon hillock c. Dendritic spines d. Soma (= cell body) 6. The reason why there is a sudden shift in the electrical potential of the neuron (from about 70mv to about +50mv) during an action potential is largely due to the sudden influx of ______ ions. a. b. c. d. Potassium Sodium Calcium Chloride 7. The sodium-potassium pump functions to pump A) sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell. B) sodium ions into the cell and potassium ions out of the cell. C) sodium and potassium ions into the cell. D) sodium and potassium ions out of the cell. E) sodium and potassium ions in both directions across the cell membrane. 8. Depolarization occurs because... A) potassium ions continue to diffuse out of the cell after the inactivation gates of the voltagegated sodium ion channels begin to close. B) the extra efflux of potassium ions causes the membrane potential to become slightly more positive than the resting value. C) the increased potassium ion permeability lasts slightly longer than the time required to bring the membrane potential back to its resting level. D) more sodium ions diffuse into the cell than potassium ions diffuse out of it. E) the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels begin to open and the diffusion of sodium ions decreases. 9. Repolarization occurs because... A) potassium ions continue to diffuse out of the cell after the inactivation gates of the voltagegated sodium ion channels begin to close. B) the extra efflux of potassium ions causes the membrane potential to become slightly more positive than the resting value. C) the increased potassium ion permeability lasts slightly longer than the time required to bring the membrane potential back to its resting level. D) more sodium ions diffuse into the cell than potassium ions diffuse out of it. E) the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels begin to open and the diffusion of sodium ions decreases. 10. Hyperpolarization, or afterpotential occurs because... A) potassium ions continue to diffuse out of the cell after the inactivation gates of the voltagegated sodium ion channels begin to close. B) the extra efflux of potassium ions causes the membrane potential to become slightly more positive than the resting value. C) the increased potassium ion permeability lasts slightly longer than the time required to bring the membrane potential back to its resting level. D) more sodium ions diffuse into the cell than potassium ions diffuse out of it. E) the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels begin to open and the diffusion of sodium ions decreases. 11. What ion is responsible for the depolarization phase of the Action Potential? A Iron ions B Potassium ions C Calcium ions D Sodium ions 12. What ion is responsible for the repolarization phase of the Action Potential? A Calcium ions B Sodium ions C Potassium ions D Iron ions 13. When a stimulus causes the membrane potential to reach the __________, an action potential starts. A axon hillock B threshold C receptors D axon 14. The _________ is the protein in the membrane that is involved in restoring the membrane potential in the last phase of the action potential. A V-gated K Channel B V-gated Na Channel C Na/K Pump D Isolectric Pump 15. An action potential... A) causes the neuron cell membrane to become unable to alter its charge. B) causes the outside of the neuron cell membrane to become positively charged in reference to the inside. C) causes the inside of the neuron cell membrane to become positively charged in reference to the outside. D) causes the inside of the neuron cell membrane to become negatively charged in reference to the outside. E) causes the inside of the neuron cell membrane to become neutrally charged in reference to the outside. MAKE SURE YOU CAN TELL THE STAGE IF SHOWN A DIAGRAM. ALSO LOOK AT THE GRAPH YOU DREW IN CLASS AND BE ABLE TO NAME AND DESCRIBE ALL PARTS.