Instructor Guide - UNDP GEF Global Healthcare Waste Project
advertisement

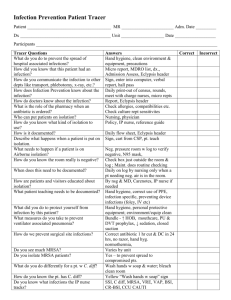
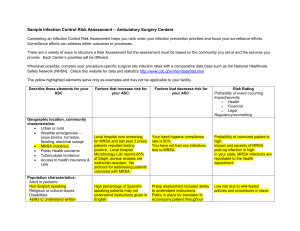
UNDP GEF Project on Global Healthcare Waste INSTRUCTOR GUIDE MODULE 25: HOSPITAL HYGIENE , INFECTION CONTROL AND HEALTHCARE WASTE MANAGEMENT 1 UNDP GEF Project on Global Healthcare Waste MODULE 25: HOSPITAL HYGIENE, INFECTION CONTROL AND HEALTHCARE WASTE MANAGEMENT Estimated Time Module Overview Learning Objectives Target Audience Lecture: 1 hour Explain the importance of hospital hygiene Describe nosocomial infections, their sources, and routes of transmission Present standard and transmission-based precautions for infection control Describe cleaning, disinfection, sterilization, and hand hygiene Present measures to improve infection control Describe components of an infection control program Understand the problem of nosocomial infections and how to prevent them Understand basic concepts of cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization Describe hand hygiene procedures Understand the link between infection control and healthcare waste management Administrative personnel HCWM coordinators Facility managers Infection control and prevention officers and members of the Infection Control or Nosocomial Infection Control Committee Healthcare professionals Healthcare waste workers and housekeeping/cleaning staff (Note: Presentation slides should be adjusted to fit the needs of waste workers and cleaners.) Facility support staff including central sterile supply staff and engineering staff involved in maintenance of sterilization equipment Other positions within facility 2 UNDP GEF Project on Global Healthcare Waste Instructor Preparation Materials Needed Student Preparation Review Questions Make notes pages of PowerPoint slides to hand out to class Look over any other materials included in the References Make copies of any additional documents/readings that may be handed out to class, such as those included in the References Prepare any additional notes to be discussed during the presentation Prepare any additional discussion points or review questions You may add any further information on patient safety. Projector Student handouts: slides, exercise, homework Flip chart and marker pens and/or board and chalk Read Chapter 12 in the Blue Book What are the potential routes of disease transmission and how can they be eliminated? What are the main components of the infection control program of your facility? Discuss any available surveillance data related to nosocomial infections in your facility? What are your specific responsibilities regarding hospital hygiene and infection control? What areas of patient safety would you like to focus on in your facility? What are the barriers to patient safety? How can proper health care waste management minimize disease transmission? 3 UNDP GEF Project on Global Healthcare Waste PRESENTATION Slide Number/Title Slide 1: Title Slide Slide 2: Module Overview Slide 3: Learning Objectives Slide 4: Guiding Principles Slide 5: Why Hospital Hygiene? Slide 6: Nosocomial Infections Slide 7: Common Sites of Nosocomial Infections Slide 8: Examples of Sources of Nosocomial Infections Slide 9: Examples of Nosocomial Agents From Environmental Sources Slide 10: Examples of Nosocomial Agents By Type of Infection Teacher’s Notes Introduce the outline and major points of the presentation Describe what participants will learn at the end of this module. Healthcare waste management is an integral part of hospital hygiene and infection control Pathogens can be found on many surfaces. Nosocomial infections are also known as hospital-acquired infections, hospital-associated infections and hospital infections. They are infections that are not present in the patient at the time of admission to a healthcare facility, but develop during the course of the patient’s stay. You may ask for examples from the students. There may be other infections that occur in your region or at specific facilities that are not listed here and in the following slides, and which you may wish to include in the presentation. You may ask students for examples of cases in their facility. 4 UNDP GEF Project on Global Healthcare Waste Slide 11: Antibiotic Resistant Microorganisms Slide 12: Routes of Transmission of Nosocomial Infections Slide 13: Routes of Transmission of Nosocomial Infections Slide 14: Spread of Nosocomial Infections Antibiotic resistant microorganisms are becoming an increasing problem in healthcare Routes of transmission include: -contact -blood borne -vector -droplet -airborne Many of the listed diseases can spread by more than one route. The figure shows only a few of the many diseases that may be transmitted within a health-care facility. Source: Diagram from Blue Book Slide 15: Guiding Principles Slide 16: Chain of infection Knowing the chain of infection helps identify effective points to prevent disease transmission. http://www.hjulmandweb.dk/HCRWCD/Gauteng%20HCW%20Project/13%20External%20Docs%20%28WHO,%20etc.%29/himpacts.pdf http://faculty.ccc.edu/tr-infectioncontrol/chain.htm Use the above links to : Describe the transmission of infections via the chain of infection. Describe the significance of the chain of infection to implement control measures and protect workers (that is, to break the chain of infection). Can participants think of any examples of interventions? 5 UNDP GEF Project on Global Healthcare Waste Slide 17: Standard Precautions Slide 18: Transmission-Based Precautions Slide 19: Some Standards of Hospital Hygiene Slide 20: Cleaning Slide 21: Sterilization and Disinfection Slide 22: Methods for Sterilization and Disinfection Slide 23: Main Chemical Disinfectants Slide 24: Main Chemical Disinfectants Slide 25: Main Chemical Disinfectants Slide 26: Hand Hygiene Cleaning is the most basic measure for maintaining hygiene in a healthcare facility. Major chemical disinfecting agents, their spectrum, uses, advantages, and disadvantages are displayed in the chart covering the following three slides. Review proper hand hygiene techniques 6 UNDP GEF Project on Global Healthcare Waste Slide 27: Hand Hygiene Diagram As the hands of healthcare workers are the most frequent vehicle of hospital infections, hand hygiene, including both hand washing and hand disinfection, is the primary preventive measure. Thorough hand washing with adequate quantities of water and soap removes more than 90% of the transient bacteria/flora, including all or most contaminants. Killing all transient flora with all contaminants within a short time (a few seconds) necessitates hygienic hand disinfection: only alcohol or alcoholic preparations act sufficiently fast. Hands should be disinfected with alcohol when an infected tissue or body fluid is touched without gloves. Slide 28: Hand Hygiene Slide 29: Hand Hygiene Technique with Soap and Water Recommended Duration: 40-60 seconds Slide 30: Hand Hygiene Technique with Alcohol-Based Formulation Recommended Duration: 20-30 seconds Slide 31-32: Measures for Improving Infection Control Slide 33: Measures for Improving Infection Control Go over wasteful practices that should be eliminated in order to improve infection control. No-cost measures: using good infection control practices 7 UNDP GEF Project on Global Healthcare Waste Slide 34-35: Measures for Improving Infection Control Slide 36: Infection Control Program Slide 37: Infection Control Program Slide 38: Review questions and discussion References (in order as they appear in slides) Low-cost measures: cost-effective practices Generate a discussion based off these questions. Blue Book, Chapter 12 Nursing Times.net: “Standard Principles: Hospital Environmental Hygiene and Hand Hygiene.” http://www.nursingtimes.net/nursing-practice/clinical-zones/infection-control/standardprincipleshospital-environmental-hygiene-and-hand-hygiene/291499.article Institut de veille sanitaire Enquête nationale de prévalence des infections nosocomiales, France, juin 2006, Vol. 1, Tableau 31, p. 24. WHO: Review of Health Impacts from Microbiological Hazards in Health-Care Wastes. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/medicalwaste/en/microbhazards0306.pdf Infection Control for Nursing Students: Chain of Infection. http://faculty.ccc.edu/tr-infectioncontrol/chain.htm WHO: Standard Precautions in Healthcare. Infection Control, October 2007. http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/EPR_AM2_E7.pdf WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care, 2009. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2009/9789241597906_eng.pdf 8