Exercise Chapter 3 - MATHCFS-STUDENTS-PAGE
advertisement
Exercise Chapter 3
1. For the function 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) below, find all relative maximum points and minimum points
by applying the first derivative test. Then, determine the intervals where 𝑓(𝑥) is
increasing and decreasing.
i)
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 − 24
ii)
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 − 3𝑥
2. Find (a) the intervals of increase or decrease, (b) the local maximum and minimum
values, (c) the intervals of concavity, and (d) the inflection points. (e) sketch the graph.
i)
𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 3 − 3𝑥 2 − 12𝑥
ii)
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 − 6𝑥 2
iii)
𝑓(𝑥) = 3𝑥 5 − 5𝑥 3 + 3
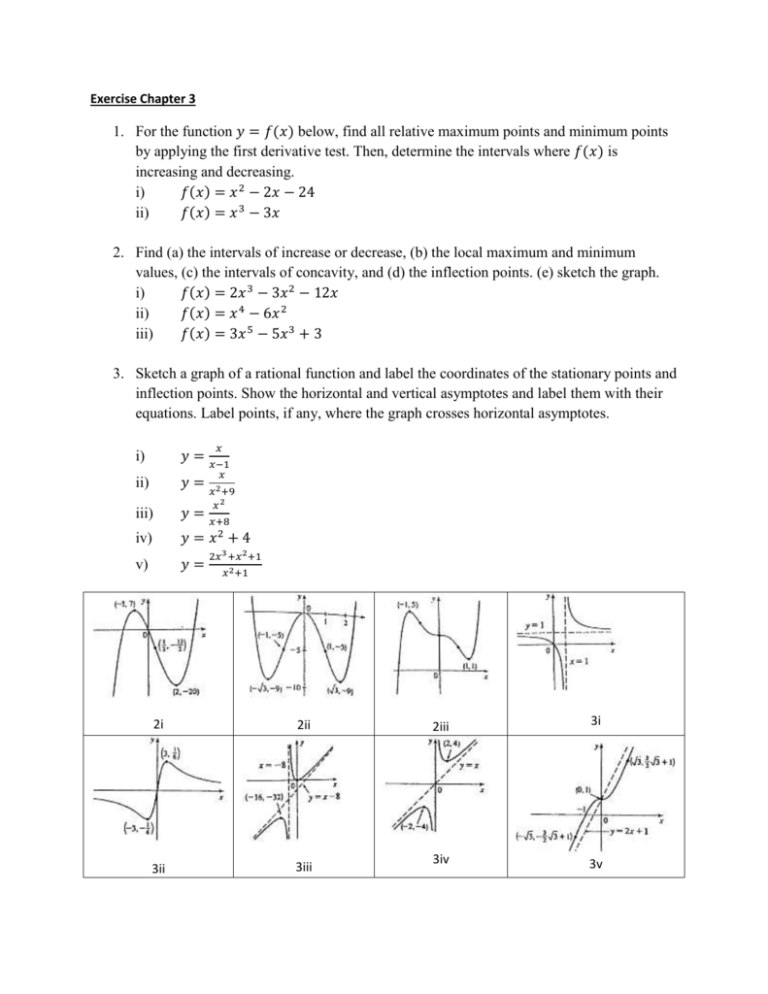
3. Sketch a graph of a rational function and label the coordinates of the stationary points and
inflection points. Show the horizontal and vertical asymptotes and label them with their
equations. Label points, if any, where the graph crosses horizontal asymptotes.
𝑥
i)
𝑦 = 𝑥−1
ii)
𝑦 = 𝑥 2 +9
iii)
𝑦=
iv)
𝑦 =𝑥 +4
v)
𝑦=
𝑥
𝑥2
𝑥+8
2
2𝑥 3 +𝑥 2 +1
𝑥 2 +1
2i
2ii
3ii
3iii
2iii
3i
3iv
3v
1.
Find the critical numbers and the relative extrema for the functions, if any:
(a) y x 3 3x 3
{ans: x=-1, 1, rel max (-1,5), rel min (1,1) }
2
(b) y 2 x 3x 3
{ans: none}
(c) y x 8 x 2
(ans: x=-2,2, rel max at (2,4), rel min at (-2,-4)}
(d) y
x2 3
x2
{ans: x=1, 2, 3, rel max (1,2), rel min (3,6) }
(e) y x 2 1
{ans: x=0, rel max (0,1)
1
3
(f) y x x 3 3
2.
2
{ans: x=0, -3, no rel extrema}
For each of the given function;
i) find the x and y intercepts (if any).
ii) all the asymptotes (if any)
iii) the interval of increase and decrease
iv) local maximum / local minimum
v) interval of concavity
vi) inflection point (if any)
vii) sketch the function completely.
(b) f x 2 x 3 6 x 2 3
f ( x) 9 x 3 4 x 4
(a)
y
f(x)=-2x^3+6x^2-3
9
y
8
f(x)=9x^3-4x^4
9
7
8
6
7
5
6
4
5
3
4
2
3
1
2
x
-9
1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
-1
9
-2
-1
-3
-2
-3
-4
-4
-5
-5
-6
-6
-7
-7
-8
-8
-9
-9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(c) f x
1 2x
1 x
x3 1
x2 9
(d) f x
2
y
f(x)=(1+2x)/(1-x)^2
9
y
f(x)=((x^3)-1)/((x^2)-9)
9
8
8
7
7
6
6
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
x
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-9
9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
2
3
4
5
-1
-1
-2
-2
-3
-3
-4
-4
-5
-5
-6
-6
-7
-7
-8
-9
-8
-9
A curve has the equation y x 3 ax 2 bx c . The curve cuts the y-axis at
3.
7
y 13 and has stationary points at x 1 and x .
3
(a)
Find the values of a, b and c.
{ans: a=5, b=7, c=-13}
(b)
Find the inflection points
{ans: x=-5/3}
(c)
Sketch the graph of y.
y
f(x)=x^3 + 5 x^2 +7x -13
25
20
15
10
5
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
-5
-10
-15
-20
-25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
6
7
8
9
Question
1. Find the critical points for the curve
a. 𝑦 = 𝑥 3 + 7𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 + 2
b. 𝑓(𝑥) = √𝑥 2 − 9
c. 𝑥 2 + 2𝑦 2 − 2𝑥 + 8𝑦 − 9 = 0
2
3 5
d. 𝑦 = 𝑥 3 − 6𝑥 3
5
2
e. 𝑦 = (𝑥 2 − 16)3
2. Given 𝑦 = 3𝑥 4 − 4𝑥 3 . Find if exist, the maximum and minimum points using the first
derivative test.
3
3. A curve is given by the function 𝑓(𝑥) = √𝑥 − 3.
a. Find the first and second derivative of 𝑓.
b. Find the coordinates ot the critical point(s).
c. Determine the nature of the points whether they are maximum, minimum or point
of inflection.
4. For the function 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 − 8𝑥 2 , find
a. the stationary points.
b. the intervals where 𝑓 is increasing or decreasing.
c. the relative maximum and minimum points.
d. the intervals where 𝑓 is concave upwards and 𝑓 is concave downwards.
e. The points of inflection.
Hence sketch the graph of 𝑓(𝑥).
5. Sketch the graph of
1
a. 𝑦 = 4𝑥 2 +
b. 𝑦 =
c. 𝑦 =
d. 𝑦 =
𝑥 2 +1
𝑥 2 −9
2𝑥
9 − 𝑥2
2𝑥 2
𝑥 2 +4
𝑥
ANSWERS
1
a
b
c
d
e
2
3
a
b
1 31
( , ) , (−5,77)
3 27
(3,0), (−3,0)
(1,5), (1,1), (1 − 3√2, −2) , (1 + 3√2, −2)
(0,0); maximum, (4, −9.071)minimum
(−4,0); minimum, (4,0); minimum , (0, 6.352); maximum
No relative extremum at 𝑥 = 0. (1,-1) is a minimum point.
1
2
′
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) =
2 , 𝑓′ (𝑥) =
5
3(𝑥 − 3)3
9(𝑥 − 3)3
(3,0)
4
c
a
b
c
d
e
5
a
b
c
d
No extremum point. Inflection point: (1,0)
(0,0), (2, −16), (−2, −16)
Increasing: (−2,0) ∪ (2, +∞) ; Decreasing: (−∞, −2) ∪ (0,2)
Relative maximum:(0,0) , Relative minimum:(2,-16) and (−2, −16)
2
2
2
2
Concave up: (−∞, − ) ∪ ( , +∞) , Concave down: (− , )
√3
√3
√3 √3
2
896
(±
,−
)
81
√3
1) Find the intervals where the function is increasing and decreasing.
1
i)
[Ans: increasing on ,3 3, ]
f x x 3 3x 2 9 x 20
3
1
ii)
[Ans: increasing , 1 1, , decreasing 1,0 0,1 ]
f x 1 2
x
iii)
f x x4 4 x3 10
[Ans: increasing 3, , decreasing ,0 0,3 ]
2) Find the critical points for the following functions.
t
t 1
i)
h t
ii)
f x 6 x5 33x4 30x3 100
iii)
g t 3 t 2 2t 1
[Ans: t 0 and t 1]
3
and t 1]
5
1
[Ans: t 0, t ]
5
[Ans: x 5, x 0, x
3) Determine where the function is concave upward and concave downward.
2
5
i)
[Ans: concave up 1, , concave down ,1 ]
f x x 1 3
3
1
ii)
[Ans: concave up ,0 0, ]
g x x 2
x
4) Sketch the graph of
i)
g x 4 3x 2 x 3
Ans:
y
f(x)=4-3x-2(x^3)
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
-8
-9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
g x
ii)
1
x x
2
Ans:
y
f(x)=((1/2)*x)-(x^(1/2))
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
-8
-9
h x
iii)
3 4
x 2 x3 6 x 2 8
2
Ans:
y
f(x)=(3/2)(x^4)-2(x^3)-6(x^2)+8
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
-8
-9
f x
iv)
3x
x x6
2
Ans:
y
f(x)=(3x)/((x^2)-x-6)
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
-8
-9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
9
v)
g t 2
5
t 2
2
Ans:
y
f(x)=2+(5/(x-2)^2)
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
-8
-9
vi)
x3 x
g x
x x 1
Ans:
y
f(x)=((x^3)-x)/(x*(x+1))
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
-8
-9
5) Determine the relative extrema of the function f x x3 3x2 24x 32 .
[Ans: relative maximum: f 2 60 , relative minimum: f 4 48 ]
9
6) Sketch the graph of a function having the following properties:
f 1 4
f 0 2
f 1 0
f 1 0
f x 0 on , 1 1,
f x 0 on 1,1
f x 0 on , 0
f x 0 on 0,
Ans:
f(x)
(-1,4)
(0,2)
x
(1,0)
Question
1.
Identify critical points and find the maximum and minimum value on the given interval I.
f(x) = 𝑥 2 + 2x; I =[ , ]
2 2
b)
r(θ) = 2 cos 𝜃; I = [
c)
2.
3 1
a)
2
3
4
, ]
3
g(t) =[𝑡 ] ; I = [-1, 8]
Sketch the graph
a)
f x x 2 x 1 x 1
b)
f x 2 x 3 3x 2 12 x 50
2
3.
−𝜋 𝜋
2
For each of the given function;
i) find the x and y intercepts (if any).
ii) all the asymptotes (if any)
iii) the interval of increase and decrease
iv) local maximum / local minimum
v) interval of concavity
vi) inflection point (if any)
vii) sketch the function completely.
1 x
1 x
(a)
f ( x)
(b)
f x 4 x 3x 3
(c)
f x
4
1 2x
1 x 2
3
1
5
Critical points: - 2, - 1, 2 ; maximum value 4 ; minimum value - 1
answers: 1a)
𝜋
4
𝜋
3
1b)
Critical points: - , 0, ; maximum value 2; minimum value 1
1c)
Critical points: -1, 0, 8; maximum value 4; minimum value 0
Answer 2a
y
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
-0.1
-0.2
-0.3
-0.4
-0.5
-0.6
-0.7
-0.8
-0.9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Answer 2b
y
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
x
-70
-65
-60
-55
-50
-45
-40
-35
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
-10
-20
-30
y
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
-8
-9
Answer 3a
y
12
10
8
6
4
2
x
-13
-12
-11
-10
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
-2
-4
-6
-8
-10
-12
Answer 3b
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Answer 3c
y
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
x
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
-8
-9
Question
1) Find the critical numbers and the relative extrema for the functions, if any:
a) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 3 + 2𝑥 2
b) 𝑦 = 𝑥 3 − 3𝑥 + 3
2
c) 𝑦 = (𝑥 − 3) ⁄5
d) 𝑦 = |𝑥 2 − 1|
e) 𝑦 = 𝑥√8 − 𝑥 2
f) 𝑦 =
𝑥 2 −3
𝑥−2
2) The graph of f ' on (1, 6) is shown below. Find the intervals on which f is increasing or decreasing.
3) The graph of f ', the derivative of a function f, is shown below. Find the relative extrema of f.
4) The graph of f is shown below and f is twice differentiable. Which of the following statements is true:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
f(5) < f '(5) < f ''(5)
f ''(5) < f '(5) < f (5)
f '(5) < f (5) < f ''(5)
f '(5) < f ''(5) < f (5)
f ''(5) < f (5) < f '(5)
5)
INTERVAL
𝒙<𝟏
𝟏<𝒙<𝟐
𝟐<𝒙<𝟑
𝟑<𝒙<𝟒
𝟒<𝒙
SIGN OF 𝒇′ (𝒙)
−
+
+
−
−
SIGN OF 𝒇′′ (𝒙)
+
+
−
−
+
A sign chart is presented for the first and second derivative of a function 𝑓. Assuming
that 𝑓 is continuous everywhere . Find
a) the interval on which 𝑓 is increasing and decreasing
b) the interval on which 𝑓 is concave up and down.
c) The 𝑥-coordinates of all inflection points
6) Find the absolute maximum and minimum values of 𝑓 on the closed interval, and state
where the values occur.
a) 𝑓(𝑥) = 4𝑥 2 − 12𝑥 + 10 ; [1,2]
b) 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 − 2)3 ; [1,4]
𝑐) 𝑓(𝑥) =
3𝑥
√4𝑥 2 + 1
; [−1,1]
d) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 − 2𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥 ; [−𝜋⁄4 , 𝜋⁄2]
e) 𝑓(𝑥) = 1 − |9 − 𝑥 2 | ; [1,2]
7) For each of the given function;
i) find the x and y intercepts (if any).
ii) all the asymptotes (if any)
iii) the interval of increase and decrease
iv) local maximum / local minimum
v) interval of concavity
vi) inflection point (if any)
vii) sketch the function completely.
𝑎) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 − 3𝑥 3 + 3𝑥 2 + 1
3𝑥 2 − 8
𝑏) 𝑓(𝑥) = 2
𝑥 −4
𝑐) 𝑓(𝑥) =
2𝑥 − 𝑥 2
𝑥2 + 𝑥 − 2
𝑑) 𝑓(𝑥) =
(𝑥 − 2)3
𝑥2
𝑒)𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥
2⁄ 5
3( −
2
𝑥)
𝑓) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 √4 − 𝑥 2
𝑔) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 −
1
𝑥
8)
A curve has the equation 𝑦 = 𝑥 3 + 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐. The curve cuts the y-axis at 𝑦 =
7
−13 and has stationary points at 𝑥 = −1 and 𝑥 = − 3.
9)
(a)
Find the values of a, b and c.
(b)
Find the inflection points
(c)
Sketch the graph of 𝑓
Let 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 + 𝑝𝑥 + 𝑞. Find the values of 𝑝 and 𝑞 such that 𝑓(1) = 3 is an extreme
value of 𝑓 on [0,2]. Is this value a maximum or minimum?
10)
Find the values of of 𝑎, 𝑏, 𝑐 and 𝑑 so that the function
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑎𝑥 3 + 𝑏𝑥 2 + 𝑐𝑥 + 𝑑
has relative minimum at (0,0) and relative maximum at (1,1).
Answer
1
a) 0, − 3
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
rel max (-1,5) and min (1,1)
3
rel. max (0,1)
rel max (2,4) and min (-2,-4)
rel. max (1,2) and min (3,6)
2. decreasing [1,2] ∪ [5,6], increasing [2,5]
3. rel. max x=-2, rel.min x=3
4.C
5. increasing [1.3], decreasing (−∞, 2] ∪ [3, +∞)
Concave up (−∞, 2) ∪ (4, +∞), concave down (2,4)
6.
a) max =2 at x=1,2, min =1 at x=3/2
b) max =8 at x=4, min=-1 at x =1
c) max = 3⁄√5 at x=1, min −3⁄√5 at x=-1
d) max =√2 − 𝜋⁄4 at 𝑥 = −𝜋⁄4, min −√3 + 𝜋⁄3 𝑎𝑡 𝑥 = 𝜋⁄3
7.a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
g)
8.
a) a=5 , b = 7, c = -13
b) x=-5/3
9.
p = -2, q= 4 , x = 1 is minimum value.
10. a = -2 , b = 3 , c= 0, d = 0
Question
1.
f ( x)
x2
x2 4
2.
f x
1
1
2( x 2) 2( x 2)
4.
5.
f ( x) 4 x 3 9 x 4
f ( x) x 4 6 x 2 5
3 x 1
f ( x)
x 12
2
3.
Task; For each of the given function;
i) find the x and y intercepts (if any).
ii) all the asymptotes (if any)
iii) the interval of inc. and dec.
iv) local maximum / local minimum
v) interval of concavity
vi) inflection point (if any)
vii) sketch the function completely.
Answer
x2
1. f ( x) 2
x 4
f ( x)
2.
3 x 1
f ( x)
x 12
2
3.
1
1
2( x 2) 2( x 2)
4.
4
2
5. f ( x) x 6 x 5
f ( x) 4 x 3 9 x 4
1. Find the critical points for the following functions.
(a) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 − 8𝑥 2 + 3
3
(b) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 + 4
(c) 𝑓(𝑥) = √𝑥 2 − 64
Ans: (a) (0, 3), (2, -13) and (-2, -13)
(b) (0, 4)
(c) (-8, 0), (8, 0)
2. Find the interval where f ( x)
2 3 13x 2
x
6x 1
3
2
is increasing or decreasing.
1
2
𝟏
Ans: (−∞, ) , (6, ∞) increasing, ( , 6) decreasing
𝟐
1
3. It is given that y 6(5 x) 3 .
(a) Find
(i)
dy
dx
(ii)
d2y
dx 2
(b) Find t he coordinates of the critical point, and determine the nature of the
Ans: (𝒂)(i) −
2
(ii) −
2
(5−𝑥)3
4
5
3(5−𝑥)3
(b) (5,0) is a point of inflection.
4. Sketch the graph for
3
2
(a) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 + 3𝑥 − 4
3
2
(b) 𝑓(𝑥) = −𝑥 − 𝑥
(c) 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 4 − 8𝑥
5. Sketch the curve 𝑦 =
(d) 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 4 − 8𝑥 2 + 6
9𝑥−6
.
𝑥+7
2
6. Sketch the curve 𝑦 = 1 − 𝑥
point.
4𝑥
7. Sketch the curve 𝑦 = 1+𝑥+𝑥2
8. Given 𝑓(𝑥) = 3𝑥 4 − 16𝑥 3 + 18𝑥 2 , with domain (−∞, +∞)
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 12𝑥 3 − 48𝑥 2 + 36𝑥 and 𝑓 ′′ (𝑥) = 36𝑥 2 − 96𝑥 + 36.
i.
ii.
Using Second Derivative Test, find the relative maximum and/or relative minimum, if any.
Determine the intervals where the function are increasing and decreasing, if any.
9. Given 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 − 4𝑥 3 + 10, with domain (−∞, 0) ∪ (0, +∞).
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 4𝑥 3 − 12𝑥 2 and 𝑓 ′′ (𝑥) = 12𝑥 2 − 24𝑥.
i.
ii.
Find the intervals where the function is concaving upwards and downwards.
Find the inflection point(s).
10. Given the following information on the function 𝑓(𝑥), hence sketch the graph of the function.
i)
Domain is (−∞, 2) ∪ (2, +∞).
ii)
Interval where functions is increasing are (2,5)
iii)
Interval where functions is decreasing are (−∞, 2) ∪ (5, +∞)
iv)
Interval where functions is concave upwards are (−5,2) ∪ (4, +∞)
v)
Interval where functions is concave downwards are (−∞, −5) ∪ (2,4)
vi)
𝑓(−5) = 2 , 𝑓(4) = 4 and 𝑓(5) = 6
lim+ 𝑓(𝑥) = 1,
lim 𝑓(𝑥) = 8 , 𝑎𝑛𝑑
lim 𝑓(𝑥) = 0
vii) lim− 𝑓(𝑥) = −3 ,
𝑥→2
Answer
4a
𝑥→2
𝑥→−∞
𝑥→+∞
4b
4c
4d
5
Horizontal asymptote at y = 9, Vertical asymptote at x = -7
6
7
8
9
Minumum point =(-1, -4), Maximum point = (1, 4/3)
Max pt: (1,5). Min pt : (0, 0), (3, -27)
Increase: (−∞, 𝟎] ∪ [𝟏, 𝟑]
Decrease: [𝟎, 𝟏] ∪ [𝟑, ∞)
Concave up: (−∞, 𝟎) ∪ (𝟐, ∞)
Concave down: (0,2)
Inflection point at (0,10) and (2,-6)