File
advertisement

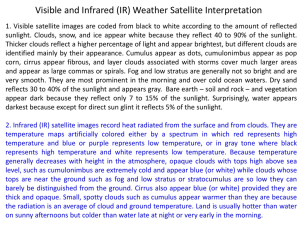
What is meteorology 7.E.1.2 Water Cycle, Clouds & Meteorology Study of the entire atmosphere, including the weather Who studies the weather Meteorologist What does a meteorologist need to know to predict weather Water Cycle Phases 1. How atmosphere heats & cools 2. How clouds form & produce rain 3. What makes the wind blow Condensation - the forming of tiny droplets of water as water vapor cools Evaporation - the process where the sun’s heat turns liquid water into water vapor Transpiration - emission of water vapor from the leaves of plants Ground Water - water beneath Earth’s surface Precipitation - any form of water that falls to Earth's surface from the clouds Run-off - water that flows across the land and enters rivers & streams; eventually flows into rivers/lakes/oceans Winds carry the water vapor from the ocean over the continents Sunlight provides the energy that evaporates water from the surface of Earth The cycling of water in and out of the atmosphere is a significant aspect of the weather patterns on Earth The water cycle never ends What are clouds How are clouds formed Cloud prefixes collection of small water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air when the air is cooled and condensation occurs cirro – high altitude alto – middle altitude nimbo – rain, precipitation cumulo – heap strato – layer 7.E.1.2 Water Cycle, Clouds & Meteorology Cloud Classifications/Types Low-level Clouds (below 6,500 feet) Stratus - uniform grey or white color Cumulus – puffy & piled up Stratocumulus - Low-level clumps or patches of cloud varying in color from bright white to dark grey Cumulonimbus – (aka thunderclouds) heavy and dense low-level clouds, extending high into the sky in towers, plumes or mountain shaped peaks Middle-level Clouds (between 6,500 and 20,000 feet above surface) Altostratus - large mid-level thin grey or blue colored clouds o sun cannot cast shadows when shining through Altocumulus – mid-level clouds that appear as cotton balls in the sky, cloud puffs or as dozens of small loose bands or ripples likes waves on the sea Nimbostratus - dark grey or bluish grey featureless layers of clouds, thick enough to block out the sun High-level Clouds (above 20,000 feet above surface) Cirrus – (aka mare’s tails) appear to be brushed across the sky and are hair-like in appearance; blue sky visible through portions of the cloud; these clouds are mostly white Cirrostratus – sheet-like, nearly transparent clouds that cover a large part of the sky Cirrocumulus – high-level cumulus clouds that have a patchy, wavelike appearance or appear as ripples in the sky