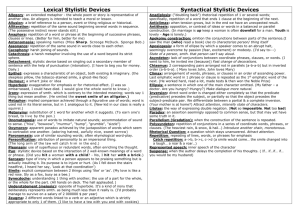
Quick list of terms we used for rhetorical analysis of speeches. Note
advertisement
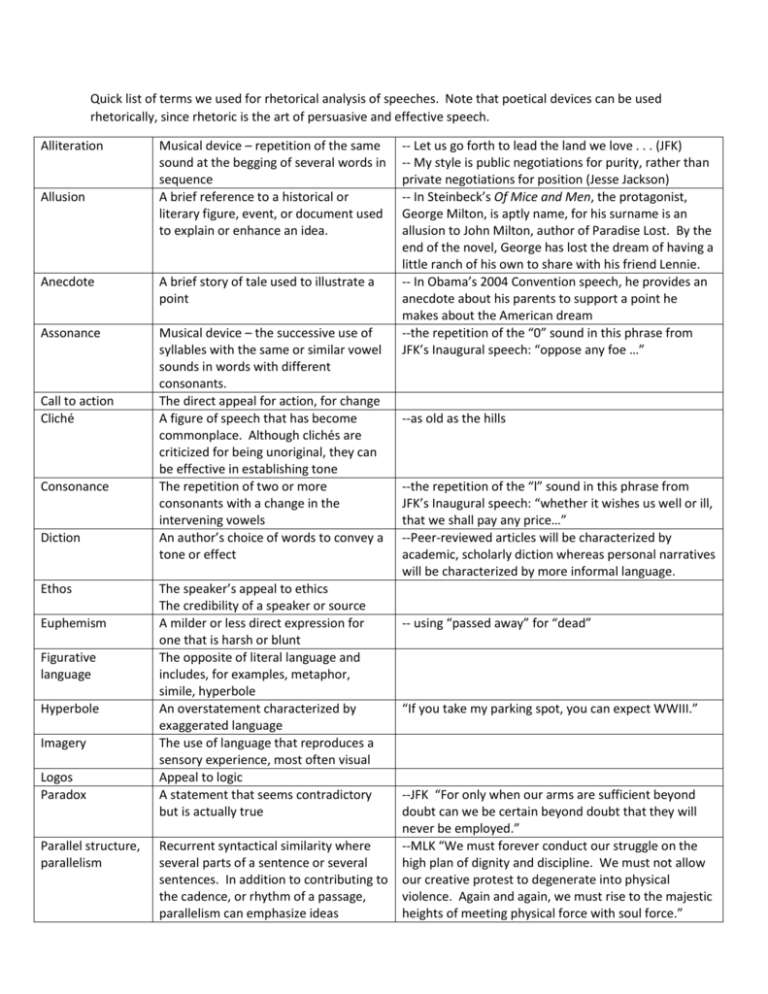
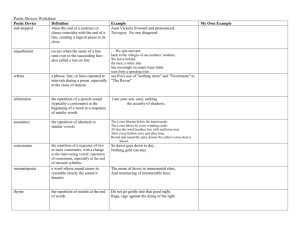
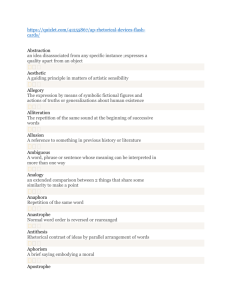
Quick list of terms we used for rhetorical analysis of speeches. Note that poetical devices can be used rhetorically, since rhetoric is the art of persuasive and effective speech. Alliteration Allusion Musical device – repetition of the same sound at the begging of several words in sequence A brief reference to a historical or literary figure, event, or document used to explain or enhance an idea. Anecdote A brief story of tale used to illustrate a point Assonance Musical device – the successive use of syllables with the same or similar vowel sounds in words with different consonants. The direct appeal for action, for change A figure of speech that has become commonplace. Although clichés are criticized for being unoriginal, they can be effective in establishing tone The repetition of two or more consonants with a change in the intervening vowels An author’s choice of words to convey a tone or effect Call to action Cliché Consonance Diction Ethos Euphemism Figurative language Hyperbole Imagery Logos Paradox Parallel structure, parallelism The speaker’s appeal to ethics The credibility of a speaker or source A milder or less direct expression for one that is harsh or blunt The opposite of literal language and includes, for examples, metaphor, simile, hyperbole An overstatement characterized by exaggerated language The use of language that reproduces a sensory experience, most often visual Appeal to logic A statement that seems contradictory but is actually true Recurrent syntactical similarity where several parts of a sentence or several sentences. In addition to contributing to the cadence, or rhythm of a passage, parallelism can emphasize ideas -- Let us go forth to lead the land we love . . . (JFK) -- My style is public negotiations for purity, rather than private negotiations for position (Jesse Jackson) -- In Steinbeck’s Of Mice and Men, the protagonist, George Milton, is aptly name, for his surname is an allusion to John Milton, author of Paradise Lost. By the end of the novel, George has lost the dream of having a little ranch of his own to share with his friend Lennie. -- In Obama’s 2004 Convention speech, he provides an anecdote about his parents to support a point he makes about the American dream --the repetition of the “0” sound in this phrase from JFK’s Inaugural speech: “oppose any foe …” --as old as the hills --the repetition of the “l” sound in this phrase from JFK’s Inaugural speech: “whether it wishes us well or ill, that we shall pay any price…” --Peer-reviewed articles will be characterized by academic, scholarly diction whereas personal narratives will be characterized by more informal language. -- using “passed away” for “dead” “If you take my parking spot, you can expect WWIII.” --JFK “For only when our arms are sufficient beyond doubt can we be certain beyond doubt that they will never be employed.” --MLK “We must forever conduct our struggle on the high plan of dignity and discipline. We must not allow our creative protest to degenerate into physical violence. Again and again, we must rise to the majestic heights of meeting physical force with soul force.” Pathos Rebuttal Refutation Repetition Rhetorical question Syntax Thesis Tricolon Appeal to emotion Part of an argument in which the author discredits an argument by offering an opposite point of view Part of an argument in which the author produces evidence that a claim is untrue When a word, phrase or sentence is repeated The use of questioning to be persuasive. Rhetorical questions are effective only if the writer knows how his or her audience would respond Word order in a sentence The focus statement of an essay; the premise statement upon which the point of view or discussion is based A broad term for the use of repetition in threes --And what sort of soldiers are those you are to lead? Are they reliable, are they brace, are they capable of victory? (MacArthur, The Corps) We were frightened; the noise had been so loud, so sharp. The loud, sharp noise frightened us. -- Government of the people, by the people, for the people... (Lincoln)