Informative/Descriptive Essays
advertisement
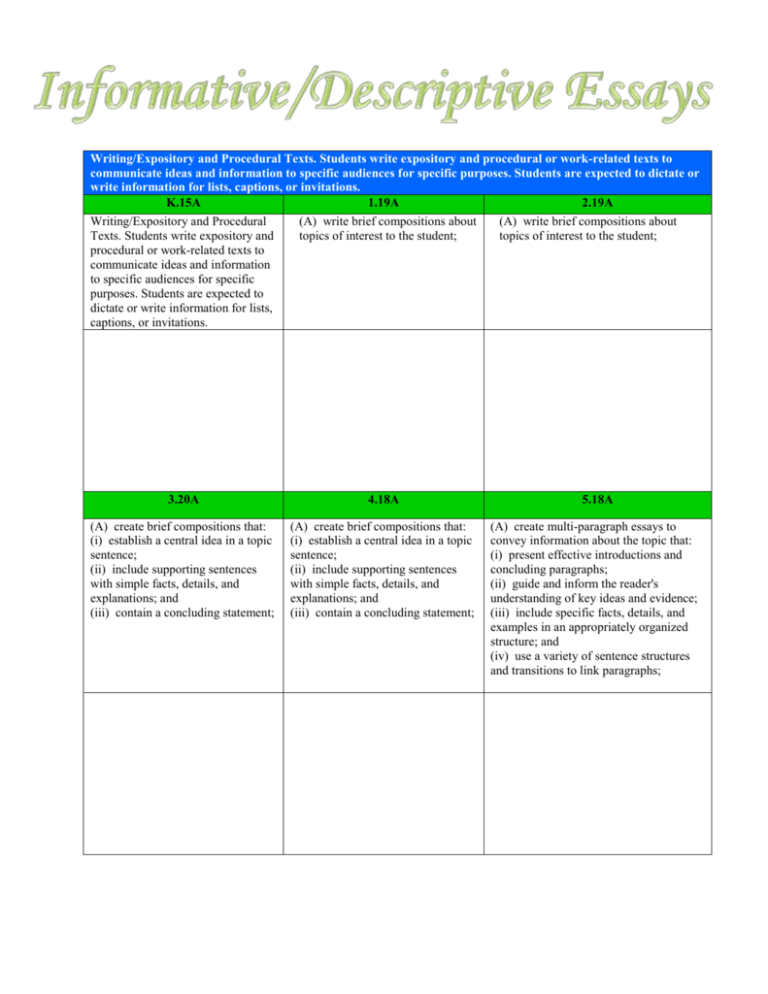
Writing/Expository and Procedural Texts. Students write expository and procedural or work-related texts to communicate ideas and information to specific audiences for specific purposes. Students are expected to dictate or write information for lists, captions, or invitations. K.15A 1.19A 2.19A Writing/Expository and Procedural Texts. Students write expository and procedural or work-related texts to communicate ideas and information to specific audiences for specific purposes. Students are expected to dictate or write information for lists, captions, or invitations. (A) write brief compositions about topics of interest to the student; (A) write brief compositions about topics of interest to the student; 3.20A 4.18A 5.18A (A) create brief compositions that: (i) establish a central idea in a topic sentence; (ii) include supporting sentences with simple facts, details, and explanations; and (iii) contain a concluding statement; (A) create brief compositions that: (i) establish a central idea in a topic sentence; (ii) include supporting sentences with simple facts, details, and explanations; and (iii) contain a concluding statement; (A) create multi-paragraph essays to convey information about the topic that: (i) present effective introductions and concluding paragraphs; (ii) guide and inform the reader's understanding of key ideas and evidence; (iii) include specific facts, details, and examples in an appropriately organized structure; and (iv) use a variety of sentence structures and transitions to link paragraphs; 2.20A 3.21A and 4.19A Writing/Persuasive Texts. Students write persuasive texts to influence the attitudes or actions of a specific audience on specific issues. Students are expected to write persuasive statements about issues that are important to the student for the appropriate audience in the school, home, or local community. Writing/Persuasive Texts. Students write persuasive texts to influence the attitudes or actions of a specific audience on specific issues. Students are expected to write persuasive essays for appropriate audiences that establish a position and use supporting details. 5.19A Writing/Persuasive Texts. Students write persuasive texts to influence the attitudes or actions of a specific audience on specific issues. Students are expected to write persuasive essays for appropriate audiences that establish a position and include sound reasoning, detailed and relevant evidence, and consideration of alternatives. Writing/Persuasive Texts. Students write persuasive texts to influence the attitudes or actions of a specific audience on specific issues. Students are expected to write persuasive essays for appropriate audiences that establish a position and include sound reasoning, detailed and relevant evidence, and consideration of alternatives. 6.18A 7.18A 8.18A Writing/Persuasive Texts. Students write persuasive texts to influence the attitudes or actions of a specific audience on specific issues. Students are expected to write persuasive essays for appropriate audiences that establish a position and include sound reasoning, detailed and relevant evidence, and consideration of alternatives.. (A) establishes a clear thesis or position; (B) considers and responds to the views of others and anticipates and answers reader concerns and counter-arguments; and (C) includes evidence that is logically organized to support the author's viewpoint and that differentiates between fact and opinion. . (A) establishes a clear thesis or position; (B) considers and responds to the views of others and anticipates and answers reader concerns and counter-arguments; and (C) includes evidence that is logically organized to support the author's viewpoint and that differentiates between fact and opinion. Writing/Persuasive Texts. Students write persuasive texts to influence the attitudes or actions of a specific audience on specific issues. Students are expected to write an argumentative essay (E3/E4-e.g., evaluative essays, proposals) to the appropriate audience that includes: E1.16 E2.16 E3.16 E4.16 (A) a clear thesis or position A) a clear thesis or position (A) a clear thesis or position (A) a clear thesis or position based on logical reasons based on logical reasons based on logical reasons based on logical reasons with supported by precise and supported by precise and supported by precise and various forms of support (e.g., relevant evidence; relevant evidence; relevant evidence, including hard evidence, reason, (B) consideration of the (B) consideration of the facts, expert opinions, common sense, cultural whole range of information whole range of information quotations, and/or expressions assumptions); and views on the topic and and views on the topic and of commonly accepted (B) accurate and honest accurate and honest accurate and honest beliefs; representation of divergent representation of these views; representation of these views (B) accurate and honest views (i.e., in the author's (C) counter-arguments based (i.e., in the author's own representation of divergent own words and not out of on evidence to anticipate and words and not out of context); views (i.e., in the author's context); address objections; (C) counter-arguments based own words and not out of (C) an organizing structure (D) an organizing structure on evidence to anticipate and context); appropriate to the purpose, appropriate to the purpose, address objections; (C) an organizing structure audience, and context; audience, and context; and (D) an organizing structure appropriate to the purpose, (D) information on the (E) an analysis of the relative appropriate to the purpose, audience, and context; complete range of relevant value of specific data, facts, audience, and context; (D) information on the perspectives; and ideas. (E) an analysis of the relative complete range of relevant (E) demonstrated value of specific data, facts, perspectives; consideration of the validity and ideas; and (E) demonstrated and reliability of all primary (F) a range of appropriate consideration of the validity and secondary sources used; appeals (e.g., descriptions, and reliability of all primary (F) language attentively anecdotes, case studies, and secondary sources used; crafted to move a analogies, illustrations). and disinterested or opposed (F) language attentively audience, using specific crafted to move a rhetorical devices to back up disinterested or opposed assertions (e.g., appeals to audience, using specific logic, emotions, ethical rhetorical devices to back up beliefs); and assertions (e.g., appeals to (G) an awareness and logic, emotions, ethical anticipation of audience beliefs). response that is reflected in different levels of formality, style, and tone. Writing/Expository and Procedural Texts. Students write expository and procedural or work-related texts to communicate ideas and information to specific audiences for specific purposes. Students are expected to: E1.15A E2.15A E3.15A E4.15A (A) write an analytical essay of sufficient length that includes: (i) effective introductory and concluding paragraphs and a variety of sentence structures; (ii) rhetorical devices, and transitions between paragraphs; (iii) a controlling idea or thesis; (iv) an organizing structure appropriate to purpose, audience, and context; and (v) relevant information and valid inferences; (A) write an analytical essay of sufficient length that includes: (i) effective introductory and concluding paragraphs and a variety of sentence structures; (ii) rhetorical devices, and transitions between paragraphs; (iii) a thesis or controlling idea; (iv) an organizing structure appropriate to purpose, audience, and context; (v) relevant evidence and well-chosen details; and (vi) distinctions about the relative value of specific data, facts, and ideas that support the thesis statement; (A) write an analytical essay of sufficient length that includes: (A) write an analytical essay of sufficient length that includes: (i) effective introductory (i) effective introductory and concluding paragraphs and concluding paragraphs and a variety and a variety of sentence structures; of sentence structures; (ii) rhetorical devices, and (ii) rhetorical devices, transitions between and transitions between paragraphs; paragraphs; (iii) a clear thesis (iii) a clear thesis statement or controlling statement or controlling idea; idea; (iv) a clear organizational (iv) a clear schema for conveying ideas; organizational schema (v) relevant and for conveying ideas; substantial evidence and (v) relevant and substantial evidence and well-chosen details; well-chosen details; and (vi) information on all relevant perspectives and (vi) information on consideration of the multiple relevant validity, reliability, and perspectives and a relevance of primary and consideration of the secondary sources; and validity, reliability, and relevance of primary and secondary sources; (vii) an analysis of views and information that contradict the thesis statement and the evidence presented for it;






