Unit study guide: Refer to previous snow days power point for help
advertisement

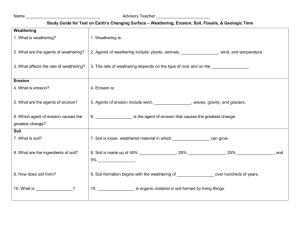
Unit study guide: Refer to previous snow days power point for help with this one This will serve as a study guide and as additional support for following up EOG prep tests. Read through the following then answer the questions at the end. This is comprehensive and will cover the material from January until today. Exploring Earth’s Surface: Earth’s topography is made up of landforms that have elevations and relief. Three common types of landforms are plains, mountains and plateaus. The atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere surround Earth’s rocky outer layer, the lithosphere. Key Words: Topography plain lithosphere elevation mountain atmosphere relief mountain range hydrosphere landform plateau biosphere landform region Model of Earth: Maps and globes are drawn to scale and use symbols to show features on Earth’s surface as seen from above. The grid of latitude and longitude lines can be used to locate points on Earth’s surface. Map projections enable map keepers to show Earth’s curved surface on flat map. Key Words: Map key degree globe equator latitude scale symbols prime meridian map projection. hemisphere longitude Maps in the computer Age Instruments carried aboard satellites in orbit around earth make pictures of the surface called satellite images. Satellite images contain information about Earth’s surface in a form that can be stored on computers as a series of 0’s and 1’s. Computers are used to store and display the information use in making maps. Key words Satellite image digitizing pixel Topographic Maps: Topographic maps portray the elevation, relief, and slope of the landforms in an area. Contour lines are the symbols used on a topographic map to show elevation and relief. The contour interval of a topographic map is the amount that elevation increases between contour lines’. In addition to showing elevation and relief, topographic maps use symbols to show a wide variety of other natural and human made features. The global positioning system is a network of satellites and ground-based units that can be used to pinpoint locations on Earth’s surface. Key Words: Topographic map contour intervalcontour line global positioning System Questions: 1. A landform that has high elevation but low relief is a a. Coastal plain c. mountain belt b. Mountain d. plateau 2. Of Earth’s four “spheres,” the one that extends into all the others is the a. Lithosphere c. biosphere b. Hydrosphere d. atmosphere 3. Latitude is a measurement of distance north or south of the a. Hemisphere c. axis b. Equator d. prime meridian 4. The show the continents without distorting their relative sizes and shapes, a map maker would choose a a. Mercator Projection c. depression b. Level area d. valley Guide Two Rocks and Weathering Rock weathers, or wears down, when it is exposed to air, water, weather, and living things at Earth’s surface Mechanical weathering break rock into smaller pieces. The agents of mechanical weathering include freezing and thawing, heating and cooling, growth of plants, actions of animals, and abrasion. Chemical weathering changes the mineral content of rock. The agents of chemical weathering are water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, living organisms, and acid rain. Climate nad rock type determine how fast weathering occurs. Key terms: Weathering abrasion Permeable ice wedging erosion chemical weathering mechanical weathering Soil Formation and composition Soil is made of small particles of rock mixed with the decaying remains of organisms Soil forms gradually in layers called horizons as bedrock weathers and organic materials build up. The three soil horizons are the A horizons, the B horizon, and the C horizon. The A horizon is made up of topsoil, which is rick in humus. The B horizon consists of clay and other particles washed down from the A horizons, but little humus. The C horizon is made up of partly weather rock without clay or humus. Plants and animals break up and mix the soil, and also add the organic materials that form humus. Soil Conservation: Soil is a valuable resource because life on land depends on it, yet it forms very slowly. Soil can be eroded away and its fertility can be decreased by improper farming practices. Plowing the Great Plains caused the Dust Bowl by removing the sod covering that kept the soil from blowing away during thoughts. Soil can be conserved and its fertility can be maintained by using various methods of soil conservation. Key words: Sod contour plowing Dust Bowl conservation plowing Contours go with the layout of the land to prevent erosion and runoff Soil was so dry that with every wind it continued to erode away. This is a picture of a large wind moving through in Oklahoma. This Dust bowl took place in the mid-west. Some of this dust ended up in North Carolina. soil conservation The dust bowl began when farmers did not protect the land, left it open to weathering and erosion, drought hit, all fertile topsoil was blown away. Contour farming Is a type of farming in which you plant ground cover around the crop to prevent runoff and soil erosion. With this erosion vital nutrients are lost, crops to not grow. Questions 1. The most important force of mechanical weathering in cool climates is a. Oxidation b. freezing and thawing c. animal activity d. abrasion 2. The most chemical weathering Is caused by a. Acid rain b. water c. oxygen d. carbon dioxide 3. The B horizon consists of a. Subsoil b. topsoil c. rock particles d. bedrock 4. One of the best types of soil for farming is a. Forrest soil b. mountain soil c. tropical soil d. prairire soil 5. Mos of the work of mixing humus into the soil is done by a. Fungi b. bacteria c. earthworm’s d. mites (remember soil is humus is composed to decomposed organic matter. Look at the one that is contact with soil especially located in topsoil all the time) Guide Three Changing Earth’s Surface Weathering, erosion, and deposition act to wear down and build up Earth’s surface Gravity pulls sediment downhill in the process of mass movement. There are four main types of mass movement: landslides, mudslides, slump, and creep Key Words: Erosion depositions sediment mass movement Water Erosion Moving water is the major force of erosion that has shaped Earth’s land surface A river may form V-shaped valleys, water falls, meandors, oxbow lakes, and flood plains. When a river slows down, it deposits some of the sediments load it carries, forming features such as alluvial fans and deltas Key Words: Runoff draining basin delta rill stalactite stream meander alluvial fan divide groundwater stalagmite river gully flood plain oxbow lake tributary The force of Moving Water: When gravitiy pulls water down a slope, water potential energy changes to kinetic energy, and it does the work. Most sediment washes or falls into streams, or is eroded from the streambed by abrasion. The greater a river’s slope or volume of flow, the more sediment it can erode Key words Energy abrasion friction potential energy load turbulence Glaciers The two kinds of glaciers are valley glaciers and continental gaciers Glaciers erode the land through two processes, plucking and abrasion Melting glaciers deposit sediment, dropping the rocks and soil that they have eroded Key words: Glacier moraine valley glacier continental glacier ice age plucking till Waves: The energy of ocean waves comes from wind blowing across the water’s surface and transferring energy to the water. Ocean waves hitting land cause erosion through impact and abrasion. Waves also move and deposit sediment along the shore. Key Words: Beach longshore drift spit Wind Erosion Wind causes erosion mainly through deflation, the blowing of surface materials The major landforms created by wind deposition are sand dunes and loess deposit Key words: Deflation sand dune loess Questions: 1. The eroded materials carried by water or wind are called a. Stalactites b. desert pavement c. sediment d. moraines 2. The downhill movement of eroded materials is known as a. Mass movement b. abrasion c. deposition d. deflation 3. A mass of rock and soil deposited directly by a glacier is called a. Load b. till c. loess d. erosion 4. When waves strike a shoreline, they concentrate their energy on a. Beaches b. cirques c. sand dunes d. headlands 5. The erosion of sediments y wind is a. Deposition b. deflation c. abrasion d. glaciation Guide Four Fossils Most fossils form when living things die and are quickly bured by sediments. Those sediments eventually harden and preserve parts of the organisms The major kinds of fossils include petrified remains, molds, casts, carbon films, trace fossils, and preserved remains The fossil record shows that many different organisms have living on Earth at different times and that groups of organisms have changed over time. Key words: Fossil paleontologist sedimentary rock petrified fossil mold carbon film trace fossil scientific theory evolution cast extinct Finding the relative ages of rocks The law of superposition can be used to determine the relative ages of rock layers Scientists also study faults, intrustions, and extrusions to find the relative ages of rock layers Index fossils are usedful in dating rock layers because they are easily recognized, occur in many different areas, and represent organism that lived during only one short period of Earth’s history. Key terms Relative age absolute age law of superposition extrusion inde fossil unconformity fault intrusion Radioactive dating During radioactive decay, the atoms of one element decay into atoms of another element. Scientists use radioactive dating to determine the absolute ages of rocks Atom radioactive decay element half-life The geologic time scale Scientist use the geologic time scale because the time sand of Earth’s history is so great The basic divisions of the geologic time scale are eras, periods and epochs Key words: Geologic time scale invertebrate epoch eras period Earth’s History A great number of different kinds of living things evolved during the “Cambrian explosion” at the beginning of the Paleozoic Era. During the Permaian Period. Earth’s continents join together and formed the supercontinent called Pangaea The extraction of the dinosaurs at the end of the Mesozoic Era created an opening for mammals, which evolved to live in most environments on land, in water, and in the air Key terms Vertebrate reptile mammal amphibian mass extinction Questions: 1. A hollow are in sediment in the shape of all or part of an organism is called a a. Mold b. cast. C. trace fossil d. carbon film 2. A gap in the geologic record formed when sedimentary rocks cover an erosion surface is called a(n) a. Intrusion b. unconformity c. fault d. extrusion 3. When a radio active element decays, it releases a. Atoms b. potassium-4o c. particles of energy d. carbon-14 4. Eras of geologic time are subdivided into a. Epochs b. centuries c. invertebrate d. amphibian 5. What is an animal that doesn’t have a backbone called a. Vertebrate b. mammal c. invertebrate d. amphibian