2D - Stage 2 - Plan 8a - Glenmore Park Learning Alliance
advertisement
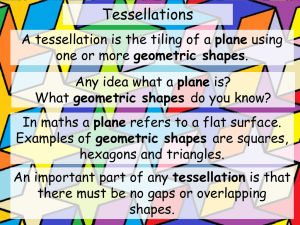
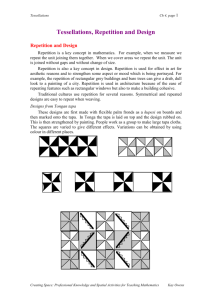
MATHEMATICS STAGE 2 TEACHING AND LEARNING OVERVIEW TERM: WEEK: 6.1 OUTCOMES: MA2-15MG STRAND: Measurement & Geometry WORKING MATHEMATICALLY: MA2-1WM & MA2-2WM Manipulates, identifies and sketches two-dimensional shapes including special quadrilaterals and describes their features CONTENT: SUB-STRAND: 2D Space 2 Create symmetrical patterns, pictures and shapes, with and without the use of digital technologies Create and record tessellating designs by reflecting, translating and rotating common shapes Use digital technologies to create tessellating designs Determine which of the special quadrilaterals can be used to create tessellating designs Explain why tessellating shapes are best for measuring area Identify shapes that do not tessellate Explain why a shape does or does not tessellate ASSESSMENT FOR LEARNING (PRE-ASSESSMENT) WARM UP / DRILL Pre-Assessment Complete the pre-assessment question attached in the resources section of this lesson plan. TENS ACTIVITY NEWMAN’S PROBLEM INVESTIGATION Joe has made a tessellating pattern using trapeziums of the same size. What did his pattern look like and which transformations were used in the process? QUALITY TEACHING ELEMENTS RESOURCES Students view short clip on different designs that tessellate including, rotational, reflective and transforming tessellations. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5-3tOa9CPb0 INTELLECTUAL QUALITY Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication QUALITY LEARNING ENVIRONMENT Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Pattern blocks, paper, pencils, crayons and computers tessellation pre-test.docx SIGNIFICANCE Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative TEACHING AND LEARNING EXPERIENCES WHOLE CLASS INSTRUCTION MODELLED ACTIVITIES Explicitly communicate lesson outcomes and expectations of work quality. Define and reinforce metalanguage used in the unit: tessellation, polygon, angle, plane, vertex and adjacent. Revise the terms translate, rotate, and reflect by watching the clip at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= 0Z1aUhGCZs0 Students recall what they know about tessellations. Discuss the three basic attributes of tessellations: First, they are repeated patterns. Ask students to find examples of repeated patterns in the room. Generate a list of the words one could use to describe these patterns. Tell students that while those are repeated patterns, only some are tessellations because tessellations are a very specific kind of pattern. Second, tessellations do not have gaps or overlaps. If students have pointed to a pattern in the room that has a gap or an overlap in it, point out that it does not fit the definition of a tessellation. Also discuss. Using pattern blocks and irregular non-tessellating shapes, demonstrate that tessellating shapes have no gaps and are best for calculating area because the whole shape is covered. GUIDED & INDEPENDENT ACTIVITIES LEARNING SEQUENCE Remediation S1 or Early S2 LEARNING SEQUENCE S2 LEARNING SEQUENCE Extension Late S2 or Early S3 Digital Tessellations: Students use the digital program to tessellate basic shapes. http://illuminations.nctm.org/Activity.aspx?id=3533 Patterns and Tessellations: Students examine and choose a more complex pattern and the computer tessellates the shape at: http://www.pbs.org/parents/education/math/games/first-second-grade/tessellation/ Tessellating Patterns: Students decorate a house using tessellating patterns. http://tlf.dlr.det.nsw.edu.au/learningobjects/Content/L7788/object/index.html Pattern Blocks: Students use sets of pattern blocks to create tessellations covering their desk. They then draw and explain to a partner what shapes they have used to create their tessellating pattern. Digital Tessellations: Students use Microsoft Word to tessellate shapes using rotations, translations and reflections to create a computer generated art work. Students fill each shape with different colours to enhance their artwork. Art Lesson: Students create artworks with tessellating patterns. https://www.pinterest.com/pin/143481938100015914/ Investigation: Part A: Students walk around classroom and identify patterns of tessellation. Make a class list of patterns observed and noted. Part B: Students identify shapes in the classroom that do not tessellate. Assessment: Students use the attached site to demonstrate their understandings of tessellation. http://illuminations.nctm.org/Activity.aspx?id=3533 Art Lesson: Hexagons Students view video and complete more complex tessellation based on a hexagon. It will require some pre-planning. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zuMVo0JWO6Y Third, tessellations can continue on a plane forever. Define plane (use a concrete example in the room) and show students how the pattern could continue on that plane if it were to go on beyond the confines of the building (e.g., it could continue as a pattern on the ceiling without any gaps or overlaps even if the ceiling were to continue forever, far beyond the walls of your school). Activity 1:.Use the site below to discuss the fact that there are no gaps. Pose the question: Can all shapes tessellate? Students list what shapes (including special quadrilaterals) can and cannot tessellate. Students justify their conclusions. http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/acti vities/Tessellate/ EVALUATION & REFLECTION Student Engagement: Achievement of Outcomes: Resources: Follow Up: