Handout - WordPress.com
advertisement
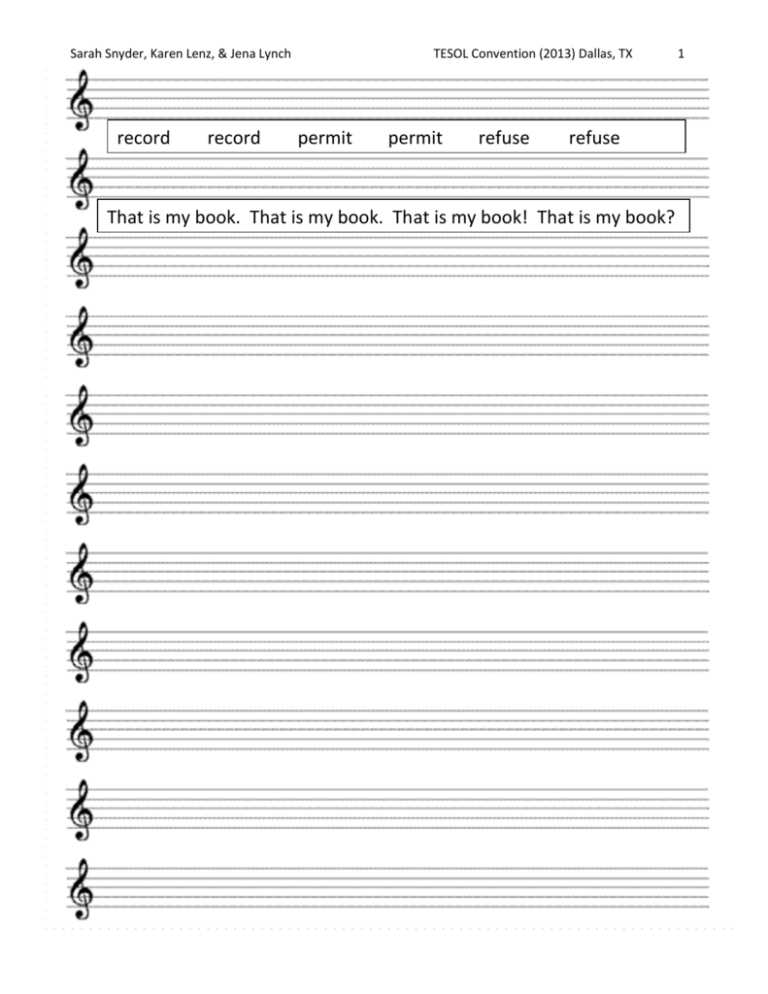
Sarah Snyder, Karen Lenz, & Jena Lynch record record TESOL Convention (2013) Dallas, TX permit permit refuse refuse That is my book. That is my book. That is my book! That is my book? permit refuse refuse 1 Sarah Snyder, Karen Lenz, & Jena Lynch TESOL Convention (2013) Dallas, TX 2 A Programmatic Enhancement: Teaching Suprasegmental Features through Musical Heuristics Steps for including suprasegmental instruction in your program (Nation & Macalister, 2010): 1. Project description 5. Aims, goals, and objectives 8. Evaluation plan 2. Environment analysis 6. Content and Sequencing 9. Teacher resources 3. Needs analysis 7. Syllabus and activities 10. Advertisement 4. Guiding Principles Selected References *Belcher, D. (2009). What ESP is and can be: An introduction. In D. Belcher (Ed.), English for specific purpose in theory and practice (pp. 1–20). Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press. Celce-Murcia, M., Brinton, D. M., Goodwin, J. M., & Griner, B. (2010). Teaching pronunciation: A course book and reference guide (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Christison, M.A., & Stoller, F. L. (Eds.). (2012). A handbook for language program administrators (2nd ed.). Miami Beach, FL: Alta Book Center. Derwing, T., Munro, M., & Wiebe, G., (1998). Evidence in favor of a broad framework for pronunciation instruction. Language Learning, 48, 393–410. Derwing, T., & Munro, M. (2005). Second language accent and pronunciation teaching: A research-based approach. TESOL Quarterly, 39, 379–397. Field, J. (2005). Intelligibility and the listener: The role of lexical stress. TESOL Quarterly, 39(3), 399-423. Finegan, E. (2008). Language: Its structure and use (5th ed.). New York, NY: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. Folse, K. S. (2006). The art of teaching speaking: Research and pedagogy for the ESL/EFL classroom. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press. Flowerdew, J., & Peacock, M. (2001). The EAP curriculum: Issues, methods, and challenges. In J. Flowerdew & M. Peacock (Eds.), Research perspectives on English for academic purposes (pp. 177–194). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. Levis, J. M., & Grant, L. (2003). Integrating pronunciation into ESL/EFL classrooms. TESOL Journal, 12(2), 13-19. Nation, I. S. P., & Macalister, J. (2010). Language curriculum design. New York, NY: Routledge. Nunan, D. (1989). Hidden agendas: The role of the learner in programme implementation. In R. K. Johnson (Ed.), The second language curriculum (pp. 176–186). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. Shaila, M. Y., & Trudell, B. (2010). From passive learners to critical thinkers: Preparing EFL students for university success. English Teaching Forum, 48(3), 2–9. Wang, J., & Snyder, S. (unpublished manuscript). Using music to teach suprasegmental features of English. *(Bold=Curriculum, Fine=Suprasegmental) Presenter Bios: All presenters will graduate with MA-TESL degrees in May 2013 from NAU. Presenters share interests in English language teaching, curriculum design, assessment, basic literacy, and college composition. Please don’t hesitate to contact us for more information! Sarah Snyder: ses223@nau.edu Karen Lenz: krs366@nau.edu Jena Lynch: jkl92@nau.edu