Air Masses and Fronts - Manhasset Public Schools
advertisement

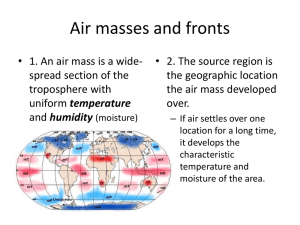
Name:________________________________________ Meteorology: Air Masses and Fronts Vocabulary Air mass: Climate: Front: High Pressure system: Humidity: Low Pressure system: Prevailing Wind: Weather: Wind: Date:___________________ Name:________________________________________ Meteorology: Air Masses and Fronts Date:___________________ Figure 1: Types and sources of air masses in the USA Figure 2. Movement of Air Masses and Fronts Name:________________________________________ Meteorology: Air Masses and Fronts Date:___________________ Review Questions: 1. The conditions of the atmosphere for the day is called ____________________. 2. The average weather that is the same every year is called ____________________. 3. A high pressure air mass brings ____________________ weather. 4. Stormy, unstable weather is found in ____________________ pressure systems. 5. The USA map indicates the locations of the high and low pressure systems. The lettered position that is probably experiencing clear skies:____________________. 6. Local weather conditions change due to the movement of ____________________. 7. An air mass that forms over northern Canada will be ____________________ and ____________________. 8. An air mass that is warm and dry will be classified as ____________________. 9. In the United States air masses move from ____________________ to ____________________. 10. A front is the ____________________ between different air masses. 11. Precipitation is likely to occur along ____________________. Name:________________________________________ Meteorology: Air Masses and Fronts Date:___________________ 12. The map shows air pressure weather systems in the USA for one day in June. Letters A, B, C, D, and E are locations in the United States. a. Locations with clear skies: ____________________ and ____________________. b. Locations probably experiencing rain: ____________________ and ____________________. c. A warm front is approaching location ____________________. d. The low pressure system will move towards ____________________. 13. Polar climates are colder than tropical climates, because at the Poles the a. Sun is lower and less direct c. Sun is higher and more direct b. Sun is lower and more direct d. Sun is higher and less direct 14. On a weather map, an air mass that is cold and dry would be labeled a. mP b. mT c. cT d. cP 15. The weather conditions in an air mass are determined by a. b. c. d. The size of the air mass The area over which the air mass formed The wind speeds in the air mass The amount of moisture in the air mass Name:________________________________________ Meteorology: Air Masses and Fronts Date:___________________ Base your answers to questions 16-18 on the diagram below which shows the location and movement of two different air masses. 16. The air mass over city B would be classified as a. maritime polar c. continental tropical b. maritime tropical d. continental polar 17. The boundary line between the two air masses is known as a. The eye c. A high pressure system b. A front d. the stratosphere 18. A weather forecast for city B would be a. Clearing skies with cooler temperatures b. Increasing clouds with cooler temperatures c. Increasing clouds with warmer temperatures d. Clearing skies with increasing temperatures 19. Tornadoes form when a very cold, dry air mass meets a very warm, moist air mass. Which two air masses could form a tornado when they meet? a. cP and cT c. cP and mT b. cT and mP d. mP and mT 20. Cool, clear weather is usually found a. In high pressure systems b. In low pressure systems 21. The climate of a region describes the a. Daily weather conditions b. Yearly weather conditions c. Latitude and altitude of the location d. Wind patterns for the area c. At fronts d. In the tropics Name:________________________________________ Meteorology: Air Masses and Fronts Date:___________________ 22. Toward which point will the Low pressure system move? a. A b. B c. C d. D Base your answers to questions 23-24 on the following diagram. Locations A and B are two source regions for air masses that affect the United States. 23. Compared to the air mass at B, the air mass at A is a. Cooler and drier c. Warmer and wetter b. Cooler and wetter d. Warmer and drier 24. On a weather map the air mass at location B would be labeled a. cP b. cT c. mT d. mP Name:________________________________________ Meteorology: Air Masses and Fronts Date:___________________ Base your answers to questions 25-28 on the following diagram. The diagram is part of a weather map for locations in the eastern United States. The map shows the location of the low pressure system, fronts, and weather stations A, B, C, and D. 25. At which station is it most likely raining? a. A b. B c. C d. D 26. As the front passes D, the air temperature will probably a. Decrease b. Increase c. Remain the same 27. In the next few hours station C can expect cloud cover to a. Decrease b. Increase c. Remain the same 28. The cold front is moving towards the a. Northeast b. Southeast c. Southwest d. Northwest Name:________________________________________ Meteorology: Air Masses and Fronts Date:___________________ 29. The map below shows a weather system affecting a part of the United States. a. Lightly shade in the area where precipitation is most likely occurring at the present time. b. Describe the weather conditions in Alabama. c. Write a weather forecast for New York which includes temperature, sky cover, and precipitation changes that may occur. d. Use a large arrow to show the direction in which the low pressure system will move. e. Describe the present weather conditions at the H. Include temperature, sky cover, and precipitation.