Definitions
advertisement
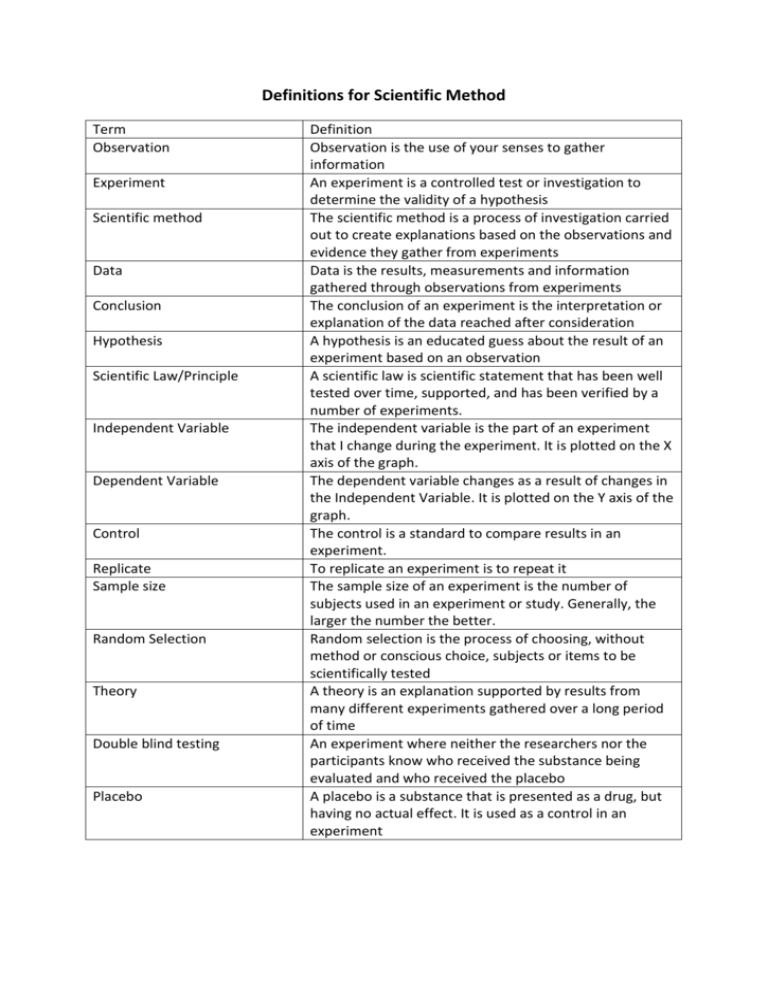
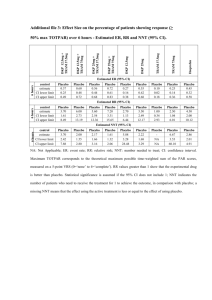
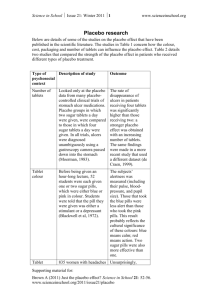
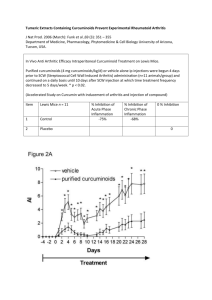
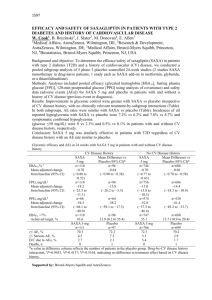
Definitions for Scientific Method Term Observation Experiment Scientific method Data Conclusion Hypothesis Scientific Law/Principle Independent Variable Dependent Variable Control Replicate Sample size Random Selection Theory Double blind testing Placebo Definition Observation is the use of your senses to gather information An experiment is a controlled test or investigation to determine the validity of a hypothesis The scientific method is a process of investigation carried out to create explanations based on the observations and evidence they gather from experiments Data is the results, measurements and information gathered through observations from experiments The conclusion of an experiment is the interpretation or explanation of the data reached after consideration A hypothesis is an educated guess about the result of an experiment based on an observation A scientific law is scientific statement that has been well tested over time, supported, and has been verified by a number of experiments. The independent variable is the part of an experiment that I change during the experiment. It is plotted on the X axis of the graph. The dependent variable changes as a result of changes in the Independent Variable. It is plotted on the Y axis of the graph. The control is a standard to compare results in an experiment. To replicate an experiment is to repeat it The sample size of an experiment is the number of subjects used in an experiment or study. Generally, the larger the number the better. Random selection is the process of choosing, without method or conscious choice, subjects or items to be scientifically tested A theory is an explanation supported by results from many different experiments gathered over a long period of time An experiment where neither the researchers nor the participants know who received the substance being evaluated and who received the placebo A placebo is a substance that is presented as a drug, but having no actual effect. It is used as a control in an experiment Term Observation Experiment Scientific method Data Conclusion Hypothesis Scientific Law/Principle Independent Variable Dependent Variable Control Replicate Sample size Random Selection Theory Double blind testing Placebo Definition Term Definition Observation is the use of your senses to gather information An experiment is a controlled test or investigation to determine the validity of a hypothesis The scientific method is a process of investigation carried out to create explanations based on the observations and evidence they gather from experiments Data is the results, measurements and information gathered through observations from experiments The conclusion of an experiment is the interpretation or explanation of the data reached after consideration A hypothesis is an educated guess about the result of an experiment based on an observation A scientific law is scientific statement that has been well tested over time, supported, and has been verified by a number of experiments. The independent variable is the part of an experiment that I change during the experiment. It is plotted on the X axis of the graph. The dependent variable changes as a result of changes in the Independent Variable. It is plotted on the Y axis of the graph. The control is a standard to compare results in an experiment. To replicate an experiment is to repeat it The sample size of an experiment is the number of subjects used in an experiment or study. Generally, the larger the number the better. Random selection is the process of choosing, without method or conscious choice, subjects or items to be scientifically tested A theory is an explanation supported by results from many different experiments gathered over a long period of time An experiment where neither the researchers nor the participants know who received the substance being evaluated and who received the placebo A placebo is a substance that is presented as a drug, but having no actual effect. It is used as a control in an experiment