LQM22_Meaning, Truth & Use_2014_v2
advertisement
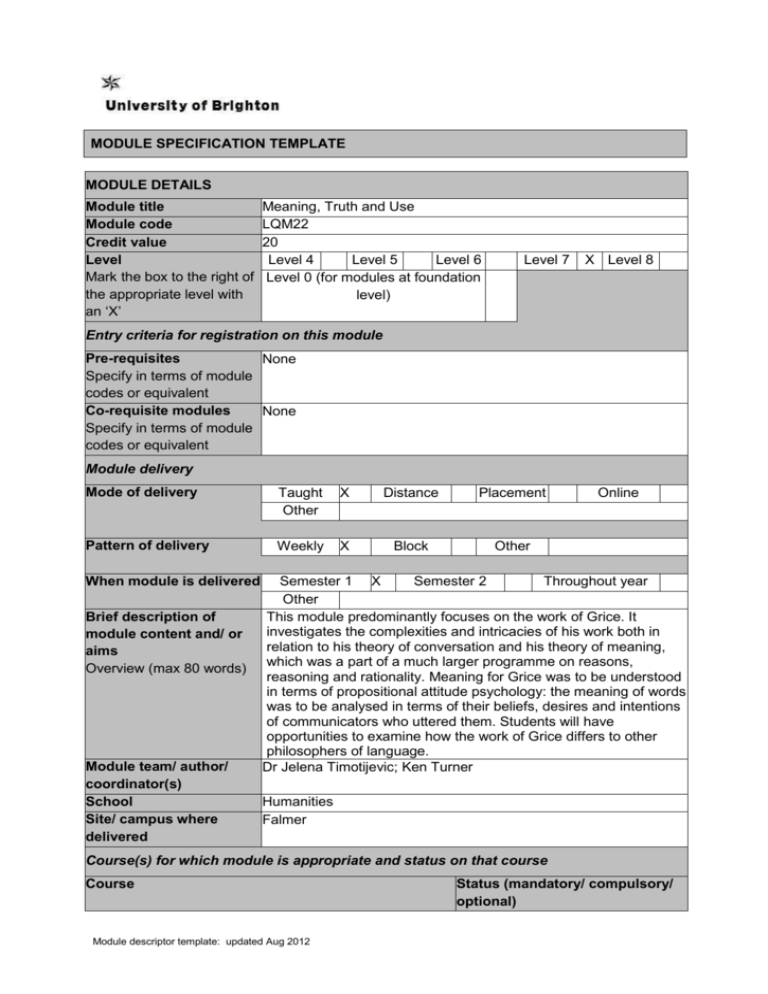
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module title Module code Credit value Level Mark the box to the right of the appropriate level with an ‘X’ Meaning, Truth and Use LQM22 20 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Level 0 (for modules at foundation level) Level 7 X Level 8 Entry criteria for registration on this module Pre-requisites None Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Co-requisite modules None Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Module delivery Mode of delivery Taught Other X Distance Placement Pattern of delivery Weekly X Block Other When module is delivered Brief description of module content and/ or aims Overview (max 80 words) Module team/ author/ coordinator(s) School Site/ campus where delivered Online Semester 1 X Semester 2 Throughout year Other This module predominantly focuses on the work of Grice. It investigates the complexities and intricacies of his work both in relation to his theory of conversation and his theory of meaning, which was a part of a much larger programme on reasons, reasoning and rationality. Meaning for Grice was to be understood in terms of propositional attitude psychology: the meaning of words was to be analysed in terms of their beliefs, desires and intentions of communicators who uttered them. Students will have opportunities to examine how the work of Grice differs to other philosophers of language. Dr Jelena Timotijevic; Ken Turner Humanities Falmer Course(s) for which module is appropriate and status on that course Course Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 Status (mandatory/ compulsory/ optional) MA Linguistics MA English Language MA Philosophy of Language MRes Linguistics Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Optional MODULE AIMS, ASSESSMENT AND SUPPORT Aims Learning outcomes Give students an opportunity to develop an in-depth and analytical understanding of linguistic, philosophical and logical theories that investigate meaning and truth in natural language Provide students with an intellectual context to develop critical approaches to, and undertake analysis in, elaborate theoretical perspectives to studying use in natural language. Examine and critically evaluate how linguistic, philosophical and logical tools contribute to the analysis of meaning and use for a selection of natural language constituents and constructions In relation to the QAA Framework for Higher Education Qualifications and the SEEC level descriptors for M level study, by the end of the module students should be able to: 1. Demonstrate and ability to critically evaluate complex and often counter intuitive theoretical concepts that can be employed to analyse meaning, truth and use of language 2. Demonstrate a critical understanding of current research literature related to the study of linguistic meaning, logical truth and natural language use 3. Demonstrate an ability to identify and examine a range of controversies related to truth and use in the context of meaning in language 4. Demonstrate an ability to apply the above concepts to analysing natural language with uniqueness and creativity Content Learning support Conventionality Cooperative principle Meaning, implicature Natural and non-natural meaning Pragmatics Propositional attitudes Truth and natural language; logical truth Theory of mind Campbell, J. K. O’Rourke, M. and Shier, D. eds. (2002) Meaning and Truth: Investigations in Philosophical Semantics. New York/London: Seven Bridges Press. Grice, P. (1989) Studies in the Way of Words. Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press. Grice, P. (1991) The Conception of Value. Oxford: Oxford Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 University Press. Grice, P. (2001) Aspects of Reason. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Murasugi, K. and Stainton, R. eds. (1999) Philosophy and Linguistics. Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press. O’Rourke, M. and Washington, C. eds. (2007) Situating Semantics: Essays on the Philosophy of John Perry. London: MIT Press. Predelli, S. (2005) Contexts: Meaning, Truth and use of Language. Oxford: Clarendon Press. Richard, M. (2008) When Truth Gives Out. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Saka, P. (2007) How to Think about Meaning. Dordrecht: Springer. Journals: Mind and Language Linguistics and Philosophy Journal of Semantics Stanford Encyclopaedia of Philosophy http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/pragmatics/ Pragmatics and speech acts http://www.universalteacher.org.uk/lang/pragmatics.htm Other: Current Research in the Semantics/Pragmatics Interface. Teaching and learning activities Details of teaching and learning activities Contact Time: Lectures and tutorials Non-contact Time: Directed reading Allocation of study hours (indicative) Where 10 credits = 100 learning hours Study hours SCHEDULED 20 This is an indication of the number of hours students can expect to spend in scheduled teaching activities including lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshops/ studios, fieldwork, external visits, and work-based learning. Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY All students are expected to undertake guided independent study which includes wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, the completion of assessment tasks, and revisions. PLACEMENT The placement is a specific type of learning away from the University that is not work-based learning or a year abroad. 180 TOTAL STUDY HOURS 200 Assessment tasks Details of assessment for this module General criteria for assessment are framed by the SEEC descriptors for M level. Against specific criteria, credit will be awarded for: 1. Ability to to critically evaluate complex and often counter intuitive theoretical concepts that can be employed to analyse meaning, truth and use of language (LO1) 2. Critical understanding of current research literature related to the study of linguistic meaning, logical truth and natural language use (LO2) 3. Ability to to identify and examine a range of controversies related to truth and use in the context of meaning in language (LO3) 4. Ability to apply the above concepts to analysing natural language with uniqueness and creativity (LO4) All learning outcomes must be achieved in order to pass the module at the threshold level. Assessment will be in the context of the University of Brighton Assessment Policy and the Faculty Code of Practice in Assessment, and students will be required to complete the following tasks: Task 1 100% Students submit one essay of 4,000 words which is a critically reflective and independent analysis that addresses interaction of meaning, truth and use of natural language The task will be marked on a percentage basis. The module pass mark is 50%. Referral task: Reworking of original task Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 Types of assessment task1 Indicative list of summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression. WRITTEN Written exam COURSEWORK Written assignment/ essay, report, dissertation, portfolio, project output, set exercise PRACTICAL Oral assessment and presentation, practical skills assessment, set exercise % weighting (or indicate if component is pass/fail) 100% EXAMINATION INFORMATION Area examination board PG Programme Linguistics and English language Refer to Faculty Office for guidance in completing the following sections External examiners Name Position and institution Date appointed Date tenure ends Prof. Daniel Kadar Professor of Linguistics and English language, Uni. of Huddersfield 1st Jan. 2015 31st Dec. 2019. QUALITY ASSURANCE Date of first approval Only complete where this is not the first version 2009 Date of last revision Only complete where this is not the first version 2009 Date of approval for this version Version number 2 Modules replaced n/a 1 Set exercises, which assess the application of knowledge or analytical, problem-solving or evaluative skills, are included under the type of assessment most appropriate to the particular task. Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 Specify codes of modules for which this is a replacement Available as free-standing module? Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 Yes X No