Name: Ch. 2 Possible Test Questions Remember, only point form
advertisement

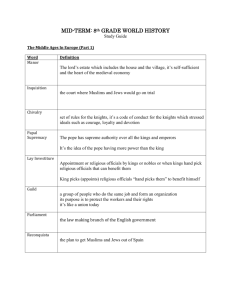
Name: _____________________________________ Ch. 2 Possible Test Questions Remember, only point form, not in complete sentences or paragraphs, 7-10 words per line. Make sure you understand the questions and your notes. Short Answer Questions: (2-3 complete sentences) 1. Who was William the Conqueror? Was he an effective leader? Why or why not? 2. Why did William the Conqueror conquer England? 3. Why was the Battle of Hastings a historical milestone? (Give 2 reasons) 4. What is feudalism? 5. How did feudalism suppress individual freedom? Who is exploited by whom? 6. Did feudalism bring an organized political system to Europe? How? 7. Which would you prefer, feudalism or democracy? Why? 8. What fundamental rights did serfs enjoy? 9. Medieval society was organized into classes into a kind of pyramid. Draw and label the pyramid. 10. Although living conditions were uncomfortable, medieval people loved life. How? 11. What is the feudal contract? Give two examples of what is included in this contract. 12. What is the Doomsday book? 13. How did a vassal gain protection as well as land from the feudal contract? What services did the vassal offer his lord? 14. How are manor communities completely self-sufficient? 15. Copy and complete the Chart Rights Responsibilities Serf Lord 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Why is religion so important to the people of the Middle Ages? What are the benefits and drawbacks to monastic life? Describe a day in the life of a monk or nun? Who had more power, the monarch or the Church? EXPLAIN. In your opinion (and using evid. we discussed in class), do you think the church is a positive or negative influence in the lives of the medieval people? Why? 21. Why was there such a long waitlist to enter the monastery or convent? 22. Why did some people choose to live in monasteries or convents? What was the monastic life like? 23. What types of offences did manor courts try? Why do you think manor courts dealt with these offences? 24. What was common law? Why was it called common law? 25. What issue did Thomas Beckett and Henry II disagree about? What did Henry want to do and why do you think Thomas refused to give in? Why did Henry and Thomas fail to compromise? 26. What are some similarities between the law in the Middle Ages and the law today? 27. Who or what can be put on trial? 28. How many types of law courts are there in the Middle Ages? What are they? 29. What are two different types of trials? 30. What is trial by ordeal? Give a couple of examples. How does this determine one’s innocence? 31. What is trial by battle? How does this determine one’s innocence? 32. Which court is responsible for which laws? 33. What is common law? Why is it called common law? 34. What types of offences did manor courts try? Why do you think manor courts dealt with these offences? Are the punishments the same across different manors? 35. Why did Church courts have the right to try and punish members of the clergy? 36. What’s the difference between being prosecuted and being sued? 37. What are 3 reasons why the Crusaders could not keep control of their conquests? 38. Why did so many people take part in the Crusades, not only knights, but also ordinary people and even children? 39. How is Richard the Lion-Hearted considered a hero in England & yet be hated by Muslims? 40. How did the Crusades help end the feudal age? 41. What are the Crusades? 42. What are the positives and negatives of the Crusades? 43. What could the barons do about a bad king? 44. What powers did the monarch have in medieval England? 45. What was the Magna Carta? What rights did the Magna Carta include? 46. Explain how the balance of power was maintained between the monarch and the barons. 47. How did King John break the feudal contract? What did the barons do to him? 48. What two things did the Church do to King John to demonstrate its great power? Paragraph Questions: (at least 8 sentences) 1. How and why did feudalism develop in Europe? 2. Describe the similarities and differences of life in the manor versus life of the ordinary people. 3. If you lived in the medieval times, would you prefer to be male or female? Why? Would you prefer life as a lord/lady of the manor or as a serf/freeholder? Why? 4. All serfs work long hours. Make a list of women’s tasks. Make a list of men’s tasks. Comment on the similarities and differences. Have things changed compared to today’s world? How? 5. Describe how the Church was significant in the lives of the medieval people. In what ways was the Church a positive influence? 6. What were trials by ordeal and trials by battle? How did medieval people justify using these methods to decide a person’s guilt or innocence? Do you think these are valid methods of determining guilt or innocence? Explain. 7. Who is Eleanor of Aquitaine? Why is she such a remarkable person? 8. Thomas Beckett, Eleanor of Aquitaine, and Richard the Lion-Hearted were heroes during the Middle Ages. What did they do that made them so popular with people all over Europe? How do these people’s character and accomplishments reflect the values of medieval society? 9. Explain the balance of power in the Middle Ages between the monarch, the barons and the Church. How did each group keep each other in check? Give examples (think: Henry II vs. Thomas Beckett, King John vs. the Church vs. the Barons) 10. Explain the Crusades. What are they, when did they happen and why did they happen? Why did so many people take part in the Crusades, not only knights, but also ordinary people and even children? What were the positive and negative influences of the Crusades for Europeans? How did the Crusades help end the feudal age?