Antiemetic drugs
advertisement

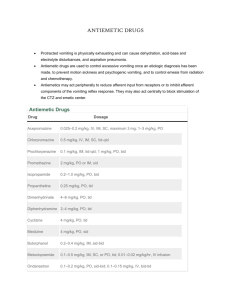
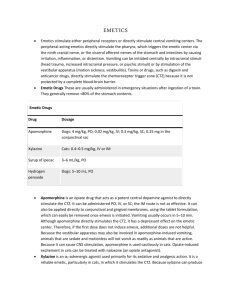
Anti-emetic drugs Vomiting Vomiting is the expulsion of gastric contents through the mouth It is often preceded by nausea Vomiting can be a valuable, life-saving physiological response (toxins, alcohol) Severe vomiting may cause dehydration, acid-base imbalance, electrolyte depletion and aspiration pneumonia Causes of nausea and vomiting Drugs - Cancer chemotherapy- Opiates- Radiation, general anesthesia Vestibular disorders: motion sickness Endocrine causes: pregnancy • food intolerance • viral & bacterial infection • disturbances of the middle ear (equilibrium) • severe pain • shock Control of Vomiting Reflex 2 centers play imp. role in the vomiting reflex The chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) is outside BBB respond directly to chemical stimuli in blood and cerebrospinal fluid. The vomiting center (VC) in the medulla – receives inputs from several sources (?)and coordinates the motor mechanisms of vomiting Chemical transmitters & receptors involved in vomiting Histamine (H1 ) Ach (muscarinic) Dopamine (D2 ) 1 5-hydroxytryptamine ( 5-HT3) Antiemetic drugs 1- Anti-muscarinic drugs 2- Anti-histaminics (H1) 3- Dopamine (D2) antagonists 4-Serotonin (5 HT3) antagonists 5- Cannabinoids 6- Corticosteroids Anti-muscarinic Drugs Receptors found in VC and vestibular N Anticholinergic drugs that can cross the BBB, will act directly on the vomiting center and have anti-emetic properties This is the oldest group of drugs used to treat N & V, although this was not their original intention Example: Scopalamine Routes of administration of Scopolamine Advantage of transdermal drug delivery Provides a controlled release of the drug into the patient Lower incidence of adverse effects Produces relief for 72 hours Adverse Effects Anti-histaminic H1Drugs Dimenhydrinate , Meclizine , Cyclizine , 2 Side effects occur with 1st generation antihistaminic Antimuscarinic : sedation, dizziness, confusion, dry mouth, blurring of vision , urinary retention 5-HT3Receptor Blockers Mechanism of action: They block 5-HT3 receptors: 1- Peripherally in upper GIT 2- Centrally in the vomiting center and CTZ Ondansetron (Zofran) Granisetron They caue Headache & dizziness ,Diarrhea A physician prescribed Ondansetron Tab. for prophylaxis of motion sickness. Even though ondansetron is a potent antiemetic it didn’t produce any effect in this patient. Can you explain why ? Vestibular nuclei has only muscarinic and H1 histaminic receptors • Dopamine D2 Receptor Blockers ( D2 antagonists ) Benzamides Phenothiazines :prochlorperazine Butyrophenones : Droperidol Benzamides Antagonize D2 receptors in CTZ, periphery Metoclopramide (Primperan) Domperidone (Motilium) Treatment of vomiting induced by chemotherapy, radiation, opiates 3 Which is a better antiemetic– Metoclopramide or Domperidone ?????????????? Metoclopramide: Adverse effects Extrapyramidal effects, Tardive dyskinesia , Parkinsonian-like symptoms Tardive dyskinesia Repetitive, involuntary, purposeless movements (usually involve the face) like tongue protrusion, lip smacking, and rapid eye blinking. It occurs with chronic treatment (months to years) and may be irreversible Cannabinoids Active ingredient in marijuana. Used in severe N & V due to cancer chemotherapy Nabilone & Dronabinol May act by inhibiting the vomiting center but the mechanism is unclear Adverse effects include: Euphoria , dysphoria, hallucinations Corticosteroids Dexamethasone (Decadron) Uses: to augment the antiemetic effect of 5HT3 receptor antagonists like “ondansetron” in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced vomiting (brain tumors) to counteract the development of edema, which may compress other brain structures. Benzodiazepines Lorazepam, alprazolam Sedative , anxiolytic, amnestic properties Rx of N & V of Pregnancy The use of antiemetics during the 1st trimester of pregnancy possible teratogenic effect 4 Non-pharmacologic interventions eat smaller meals more frequently, eat blander foods avoid spicy, fatty, or strongly odorous foods Taking prenatal vitamins at bedtime and suspending iron therapy Rx of N & V of Pregnancy Pyridoxine (vitamin B6 ) is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin and is a necessary coenzyme in the metabolism of lipids, carbohydrates, and amino acids. Dimenhydrinate • 5