Ch 18 Practice Quiz
advertisement
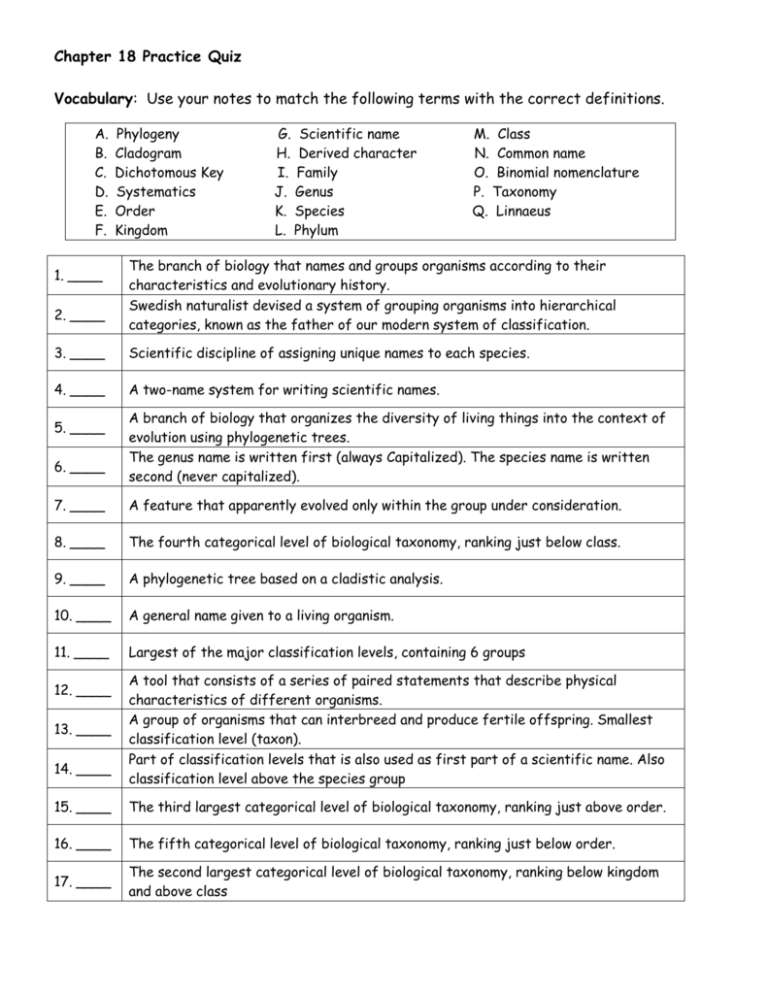
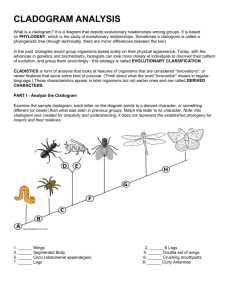
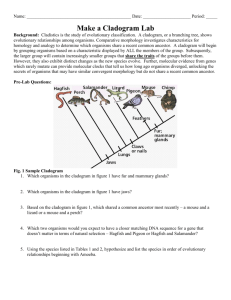
Chapter 18 Practice Quiz Vocabulary: Use your notes to match the following terms with the correct definitions. A. B. C. D. E. F. 1. ____ 2. ____ Phylogeny Cladogram Dichotomous Key Systematics Order Kingdom G. Scientific name H. Derived character I. Family J. Genus K. Species L. Phylum M. Class N. Common name O. Binomial nomenclature P. Taxonomy Q. Linnaeus The branch of biology that names and groups organisms according to their characteristics and evolutionary history. Swedish naturalist devised a system of grouping organisms into hierarchical categories, known as the father of our modern system of classification. 3. ____ Scientific discipline of assigning unique names to each species. 4. ____ A two-name system for writing scientific names. 5. ____ 6. ____ A branch of biology that organizes the diversity of living things into the context of evolution using phylogenetic trees. The genus name is written first (always Capitalized). The species name is written second (never capitalized). 7. ____ A feature that apparently evolved only within the group under consideration. 8. ____ The fourth categorical level of biological taxonomy, ranking just below class. 9. ____ A phylogenetic tree based on a cladistic analysis. 10. ____ A general name given to a living organism. 11. ____ Largest of the major classification levels, containing 6 groups 12. ____ 13. ____ 14. ____ A tool that consists of a series of paired statements that describe physical characteristics of different organisms. A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Smallest classification level (taxon). Part of classification levels that is also used as first part of a scientific name. Also classification level above the species group 15. ____ The third largest categorical level of biological taxonomy, ranking just above order. 16. ____ The fifth categorical level of biological taxonomy, ranking just below order. 17. ____ The second largest categorical level of biological taxonomy, ranking below kingdom and above class LT 2:I can describe binomial nomenclature, and how to use/construct a dichotomous key. Select 3 of the organisms on the dichotomous key worksheet to identify. List the steps taken in the dichotomous key to complete the identification. Organism # Steps (example: “1A, 2B, 3B, 4A=Cat Shark”) Select a bag of 5 leaves OR 5 pieces of hardware. Draw a branch diagram based on observable characteristics. THEN, write a dichotomous key for these items. Branch diagram: Dichotomous key: 1A. 1B. 2A. 2B. 3A. 3B. 4A. 4B. 5A. 5B. 6A. 6B. 7A. 7B. 8A. 8B. 9A. 9B. 10A. 10B. The scientific name of a certain frog was printed in a magazine like this: RANA COLATUS. As you can plainly see, it is incorrectly done. Rewrite the scientific name of that organism correctly (assume that the spelling and sequence are correct). _____________________ Name two advantages of using scientific names instead of common names. a. b. Two organisms are placed in the same species if they are able to ____________ and produce ___________________. Based on their scientific names, what can you conclude about Amoeba proteus and Amoeba hystolitica? LT 3: I can explain how Linnaeus grouped species into larger units. List the order of classification from least similar to most similar: LT 5: I can interpret a simple cladogram and construct a cladogram from data given. Below is a cladogram missing some of its parts. Use the derived characteristic chart to the right of the cladogram and filled in clues to write in the missing parts of the cladogram. Use this cladogram to answer the questions below. Organism Derived Character Backbone Legs Hair Earthworm Absent Absent Absent Trout Present Absent Absent Lizard Present Present Absent Human Present Present Present a. What trait separates the LEAST closely related organism from the other animals? b. From this cladogram, we can conclude that ______________ shares the most recent common ancestor with humans. c. Based on the cladogram above, rank each species in order of distance from the LEAST closely related organism. LT 6: I can explain how DNA sequences are used in classification. Complete the attached activity “Cladograms and Genetics”.